Method for fermentation production of micro molecular weight dextran
A dextran and micro-molecular-weight technology, applied in the field of fermentation, can solve problems such as low sucrose conversion efficiency, insufficient material exchange, and large molecular weight of the product, and achieve the effects of favorable fermentation process control, short fermentation cycle, and high fermentation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] The composition of the fermentation medium is Na 2 HPO 4 1.4 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.3 g / L, peptone 2 g / L, sucrose 130 g / L, pH 6.4, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0056] Fermentation culture conditions:
[0057] Inoculate the Leuconostoc enterococcus bacteria liquid with 10% inoculation amount in a 5L fermenter with 2.7 L fermentation medium for fermentation, the temperature is 26°C, and the rotation speed is 50rpm in the early stage of fermentation. Gradually increase the rotation speed to 100rpm, adjust the pH to 6.5 through 1mol / L NaOH solution, and continuously inject a small amount of sterile air;
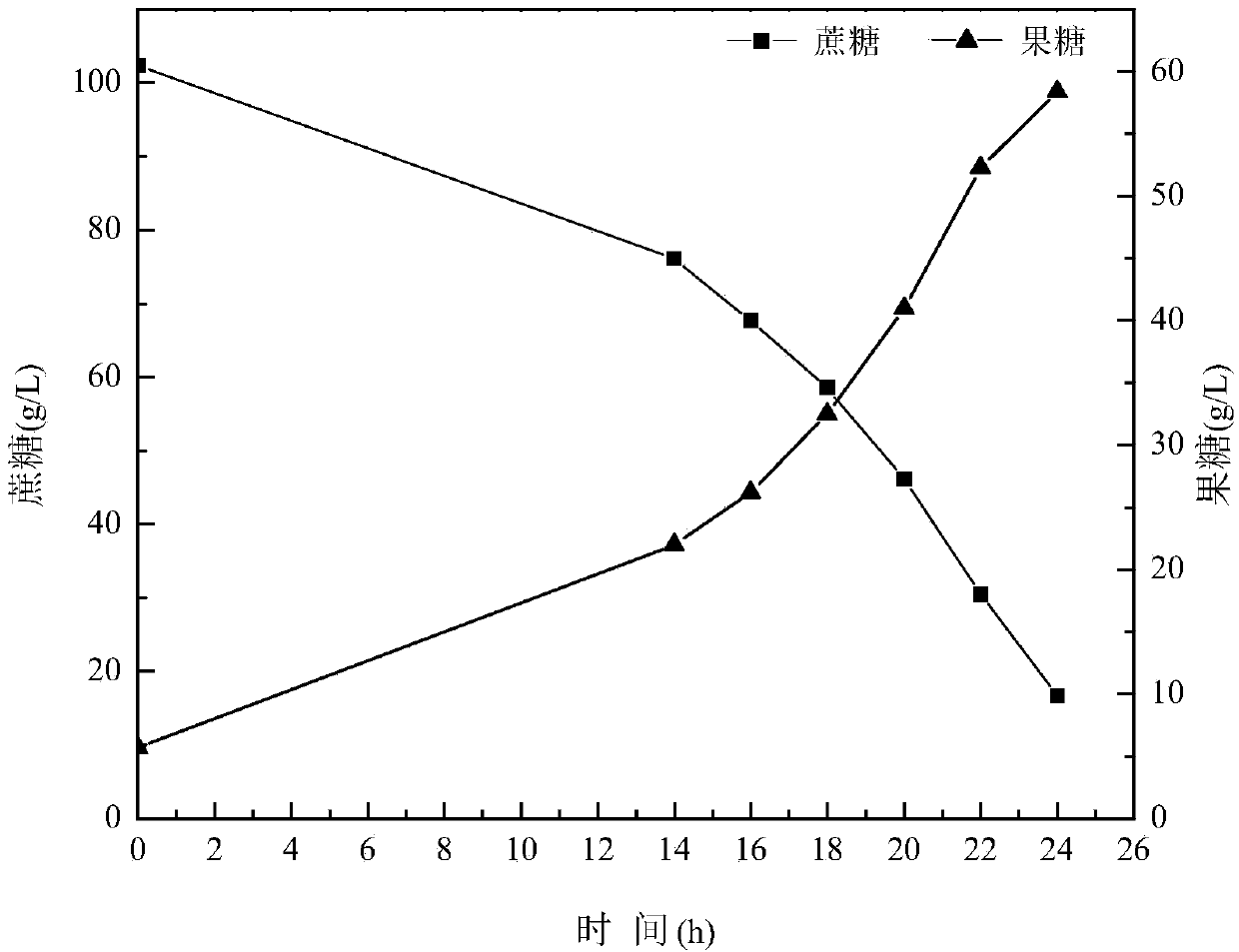
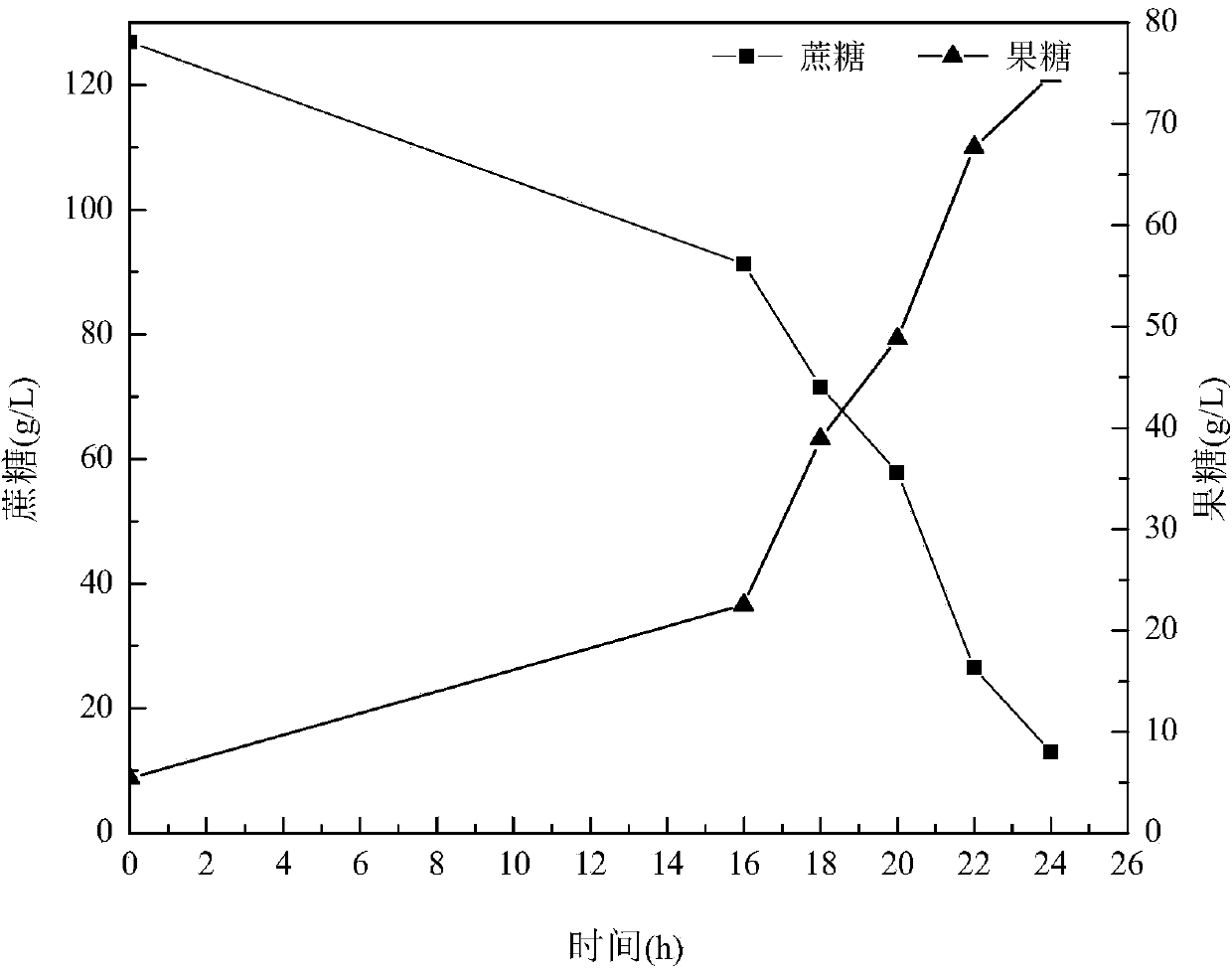
[0058] After 16 hours of fermentation, the bacteria enter the logarithmic growth phase, add dextran hydrolase to the fermentation system to make the final concentration 0.2U / mL, and at the same time add 240g of sucrose with a concentration of 600g / L at a flow rate of 45g / h;
[0059] After feeding, add dextran hydrolase to the fermenter again to make the final conce...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The composition of the fermentation medium is Na 2 HPO 4 1.4 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.3 g / L, peptone 2 g / L, sucrose 130 g / L, pH 6.4, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0063] Fermentation culture conditions:
[0064] Inoculate the Leuconostoc enterococcus bacteria liquid with 10% inoculation amount in a 5L fermenter with 2.7 L fermentation medium for fermentation, the temperature is 26°C, and the rotation speed is 50rpm in the early stage of fermentation. Gradually increase the rotation speed to 100rpm, adjust the pH to 6.5 through 1mol / L NaOH solution, and continuously inject a small amount of sterile air;
[0065] After 16 hours of fermentation, the bacteria enter the logarithmic growth phase, add dextran hydrolase with a final concentration of 0.2U / mL to the fermentation system, and simultaneously add 360g of sucrose with a concentration of 600g / L at a flow rate of 45g / h;
[0066] After feeding, dextran hydrolase was added to the fermenter again to make the final con...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The composition of the fermentation medium is Na 2 HPO 4 1.4 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.3 g / L, peptone 2 g / L, sucrose 130 g / L, pH 6.4, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0070] Fermentation culture conditions:
[0071] Inoculate the Leuconostoc enterococcus bacteria liquid with 10% inoculation amount in a 5L fermenter with 2.7 L fermentation medium for fermentation, the temperature is 26°C, and the rotation speed is 50rpm in the early stage of fermentation. Gradually increase the rotation speed to 100rpm, adjust the pH to 6.5 through 1mol / L NaOH solution, and continuously inject a small amount of sterile air;
[0072] After 16 hours of fermentation, the bacteria enter the logarithmic growth phase, add dextran hydrolase with a final concentration of 0.2U / mL to the fermentation system, and simultaneously add 360g of sucrose with a concentration of 600g / L at a flow rate of 45g / h;
[0073] After feeding, add dextran hydrolase to the fermenter again to make the final concentra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distribution coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distribution coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distribution coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com