Method for removing alkali metals in sintering process
An alkali metal removal technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of low overall utilization level and soaring iron ore prices, and achieve the effect of being beneficial to blast furnace smelting, reducing alkali metal harm, and reducing alkali metal load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
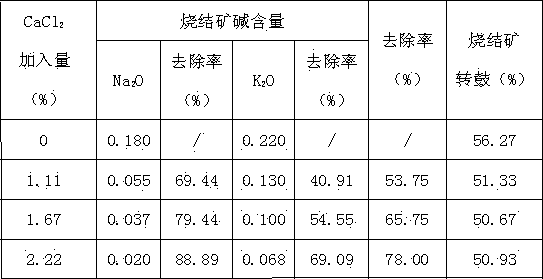
[0023] A. Raw materials are prepared according to the following mass percentages: iron powder ore: 30-60%, concentrate: 40-70%, CaCl 2 Flour: 1.11%, dolomite: 8-12%, limestone: 1.5-6.5%, quicklime: 3-5%, fuel: 5-6.5%;
[0024] B. Send the raw materials prepared in step A into the mixing mixer, add water to stir and granulate, and control the moisture content of the mixture particles to 6-8%;
[0025] C. Send the mixed material particles prepared in step B to the sintering machine trolley, control the material layer height of the mixed material particles to 600-700mm, and ignite and sinter at the ignition temperature of 1100-1300°C to obtain sintered ore ;
[0026] D. The sintered ore obtained in step C is conventionally crushed, sieved, cooled, and then sprayed with 0.5-0.7 kg of sintered ore per ton, and the concentration of 0.015% CaCl 2 The solution is sprayed on the sinter.
Embodiment 2
[0028] A. Raw materials are prepared according to the following mass percentages: iron powder ore: 30-60%, concentrate: 40-70%, CaCl 2 Powder: 1.67%, dolomite: 8-12%, limestone: 1.5-6.5%, quicklime: 3-5%, fuel: 5-6.5%;
[0029] B. Send the raw materials prepared in step A into the mixing mixer, add water to stir and granulate, and control the moisture content of the mixture particles to 6-8%;
[0030] C. Send the mixed material particles prepared in step B to the sintering machine trolley, control the material layer height of the mixed material particles to 600-700mm, and ignite and sinter at the ignition temperature of 1100-1300°C to obtain sintered ore ;
[0031] D. The sintered ore obtained in step C is conventionally crushed, sieved, cooled, and then sprayed with 0.5-0.7 kg of sintered ore per ton, and the concentration of 0.015% CaCl 2 The solution is sprayed on the sinter.
Embodiment 3
[0033] A. Raw materials are prepared according to the following mass percentages: iron powder ore: 30-60%, concentrate: 40-70%, CaCl 2 Powder: 2.22%, dolomite: 8-12%, limestone: 1.5-6.5%, quicklime: 3-5%, fuel: 5-6.5%;
[0034] B. Send the raw materials prepared in step A into the mixing mixer, add water to stir and granulate, and control the moisture content of the mixture particles to 6-8%;
[0035] C. Send the mixed material particles prepared in step B to the sintering machine trolley, control the material layer height of the mixed material particles to 600-700mm, and ignite and sinter at the ignition temperature of 1100-1300°C to obtain sintered ore ;
[0036] D. The sintered ore obtained in step C is conventionally crushed, sieved, cooled, and then sprayed with 0.5-0.7 kg of sintered ore per ton, and the concentration of 0.015% CaCl 2 The solution is sprayed on the sinter.
[0037] In all the above-mentioned embodiments, the conventional sintering process is used in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com