Biodegradable polylactic acid material for 3D printing and preparation method thereof
A technology of polylactic acid and polycarbonic acid, which is applied in the field of three-dimensional printing materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of low thermal deformation temperature of polylactic acid, low impact strength of polylactic acid, low thermal deformation temperature, etc., and achieve melt strength and heat resistance Improvement, high transparency, good flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
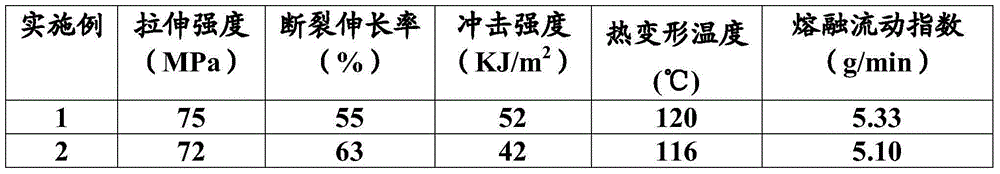
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Based on the parts by weight of polylactic acid after drying. 800 grams of dried polylactic acid (Natureworks2002D), 160 grams of polybutylene carbonate (PBC), 20 grams of polypropylene adipate, 3 grams of composite antioxidant, 3 grams of stearic acid and 20 grams of talcum powder were pre-mixed in a high-speed mixer for 30 minutes; after fully mixing, add 0.1 gram of dicumyl peroxide (DCP) and 1 gram of triallyl isocyanurate and continue mixing for 5 minutes. The mixed material is obtained; the mixed material is added to a twin-screw extruder with a length-to-diameter ratio of 40:1, melted and blended at a temperature of 150-190 ° C, and stretched into strips and cut by air cooling Particles; the obtained granular mixed resin slices are vacuum-dried to remove water to obtain a modified biodegradable polylactic acid composite material (moisture content <0.6% by weight).
[0056] The modified biodegradable polylactic acid composite material obtained above was fed into ...
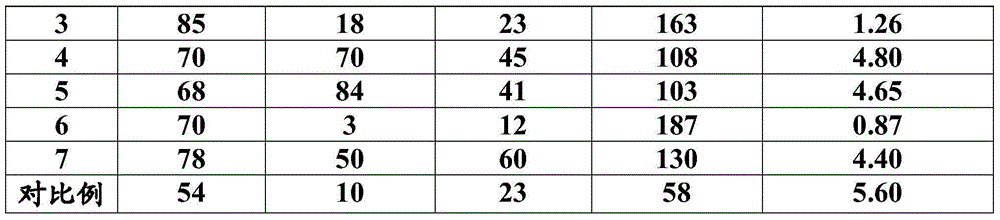
Embodiment 2
[0058] Based on the parts by weight of polylactic acid after drying. Dry polylactic acid (Natureworks4032D) 670 grams, polybutylene carbonate (PBC) 150 grams, polyhexamethylene carbonate (PHC) 100 grams, polysuccinic acid 1,2-propylene glycol 30 grams, triphenyl phosphite 3 grams of ester, 3 grams of calcium stearate and 50 grams of silicon dioxide were premixed in a high-speed mixer for 30 minutes; after mixing well, 1 gram of dicumyl peroxide (DCP) and triallyl After 0.5 g of isocyanurate, continue mixing for 5 minutes to obtain a mixed material; add the mixed material to a twin-screw extruder with a length-to-diameter ratio of 40:1, and carry out the process at a temperature of 150-190 ° C. Melt blending, stretching into strips and pelletizing by air cooling; vacuum drying and dewatering treatment of the obtained granular mixed resin slices to obtain biodegradable materials containing aliphatic polycarbonate (moisture content<0.6% by weight %).
[0059] The modified biode...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Based on the parts by weight of polylactic acid after drying. 640 grams of dried polylactic acid (Natureworks4032D), 140 grams of poly(1,2-propylene carbonate) (PPC), 20 grams of poly(1,2-propylene adipate), 3 grams of composite antioxidant, phosphorous acid 3 grams of trimethyl ester and 200 grams of talcum powder were premixed in a high-speed mixer for 30 minutes; DHBP) 1 gram, triallyl isocyanurate 1 gram and continue mixing for 5 minutes to obtain a mixed material; the mixed material is added to a twin-screw extruder with a length-to-diameter ratio of 40:1, Melt blending at a temperature of 150-190°C, air-cooled, stretched into strips, and pelletized; the obtained granular mixed resin slices are vacuum-dried to remove water to obtain a modified biodegradable polylactic acid compound Material (moisture content <0.6% by weight).
[0062] The modified biodegradable polylactic acid composite material obtained above was fed into a single-screw extruder with an aspect r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com