Microstress-induced reaction method and preparation method of pointer nuclear-shell microparticles using same
A micro-stress and reaction technology, applied in the field of micro-machining, can solve the problems of reducing the dimensional accuracy of the product structure, high production cost and difficulty, increasing operation time and difficulty, etc., achieving huge application potential, strong directivity, and traceability strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0050] Preparation method of pointer core-shell microparticles
[0051] In a second aspect of the present invention, a method for preparing pointer core-shell microparticles is provided, the method comprising the following steps:
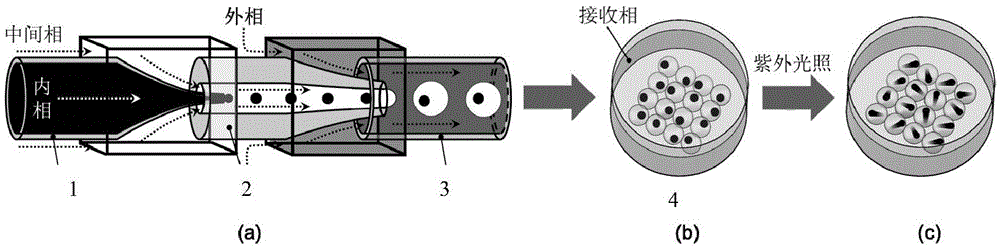
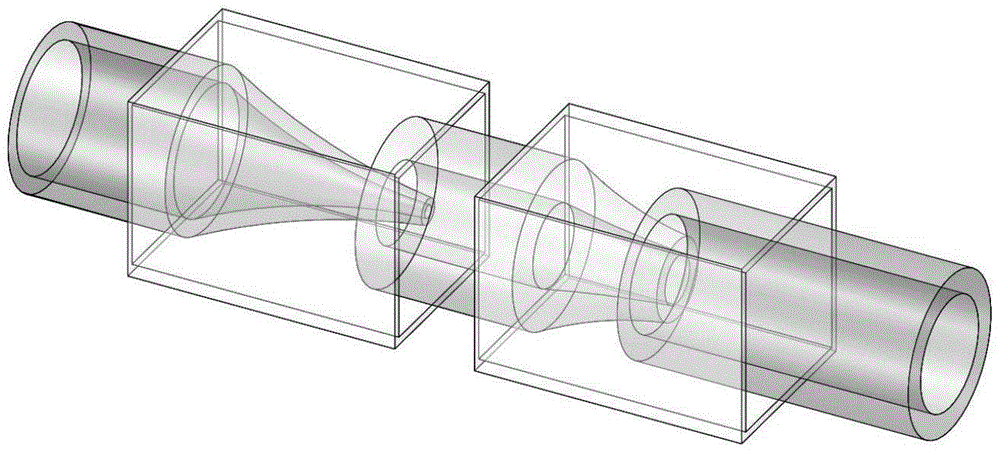
[0052] (1) Droplet preparation: Utilizing the mechanism of droplet manipulation, through the shrinkage of the geometric size of the microchannel in the microfluidic device and the mutual shearing and sticking effects of the internal phase, the intermediate phase, and the external phase fluid, a microfluidic device is formed. Water-in-oil-in-water (W / O / W) composite emulsion droplets containing an inner droplet;
[0053] (2) Emulsion collection: the emulsion droplets obtained in step (1) are collected in a container containing the receiving phase; and
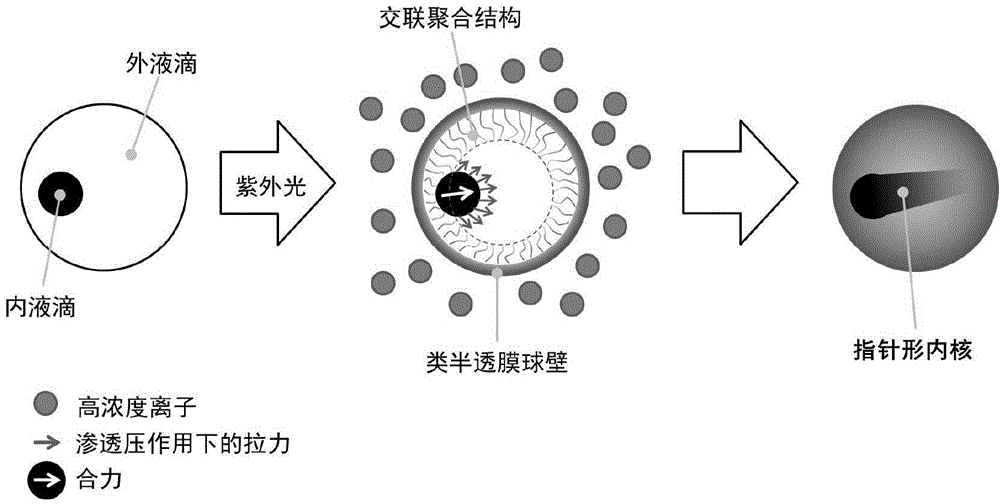
[0054] (3) Droplet polymerization reaction and formation of pointer microparticles: the emulsion obtained in step (2) is placed under ultraviolet light, and the outer droplet part undergoes polymeri...
Embodiment 1
[0087] Preparation and parameter regulation of pointer microparticles:
[0088] The particle preparation process is as follows figure 2 As shown, the microfluidic device used is as image 3 shown. The inner phase solution is an aqueous solution of surfactant 1% Pluronic F-127 (Sigma-Aldrich, U.S.), 5% glycerol and 1% carbon ink, and the middle phase is 5% PGPR90 (polyglyceryl ricinoleate). , Denmark Danisco company), 1% HMPP (2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propanone, EGDMA (ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) company) solution, the internal phase solution is an aqueous solution that is dissolved with surfactant 1% Pluronic F-127 and 5% glycerin, and the receiving phase is dissolved with surfactant 1% Pluronic F-127, 5% glycerin and 1mol / L chloride An aqueous solution of calcium. The internal phase, intermediate phase, and external phase were passed into the microfluidic device at flow rates of 50 μL / h, 800 μL / h, and 4000 μL / h, respectively, and the receivin...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Preparation and Characterization of Magnetically Responsive Functionalized Pointer Microparticles:
[0091] The particle preparation process is as follows figure 2 As shown, the microfluidic device used is as image 3 shown. The internal phase solution is dissolved in surfactant 1% Pluronic F-127, 5% glycerin, 1% carbon ink and 50% Fe 3 o 4 The aqueous solution of magnetic nanoparticles, the middle phase is EGDMA solution dissolved with PGPR90 and HMPP, the inner phase solution is an aqueous solution dissolved with surfactant Pluronic F-127 and glycerin, and the receiving phase is dissolved with surfactant 1% Pluronic F-127 , 5% glycerin and 1mol / L calcium chloride aqueous solution. The internal phase, intermediate phase, and external phase were passed into the microfluidic device at flow rates of 100 μL / h, 1000 μL / h, and 6000 μL / h, respectively, and the receiving phase was poured into a petri dish. The droplet formation process in the microfluidic device is as fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com