Electrochemical method for treating industrial wastewater
An industrial wastewater and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of easy passivation of the plate, high power consumption, and reduced performance reliability, and achieve the effects of uniform oxide film, stable voltage, and reliable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The original arsenic concentration of arsenic-containing wastewater from a concentrator is 18.3mg / L. After adjusting the pH value to 5 with quicklime, it enters an electrochemical device with a magnesium plate as the anode. The current density is 6mA / cm 2 , the distance between the plates is 10mm. After 240s of electrochemical treatment, the treated water is discharged to the clarification tank. After standing still for 60 minutes, the arsenic concentration in the water is detected to be 0.2mg / L, which is lower than the limit of 0.5mg / L. Repeat the test more than 10 times, and the concentration of arsenic in the effluent can reach the standard.
Embodiment 2
[0040] The original concentrations of copper and zinc in the electroplating wastewater of a certain factory were 19.5ppm and 23ppm respectively. After adjusting the pH value to 6 with sodium hydroxide, it entered the electroplating system with a magnesium alloy plate (in this example, the grade of magnesium alloy: AZ31) as the anode. Chemical device, current density using 8mA / cm 2 , the distance between the plates is 8mm. After 300s of electrochemical treatment, it is discharged into the clarification tank. After standing still for 60 minutes, the concentration values of copper and zinc in the water are detected to be 0.6mg / L and 0.2mg / L respectively, lower than the national The limit value of copper 1mg / L and zinc 5mg / L in the "Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard" meets the discharge standard.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The zinc and cadmium in the wastewater of a smelter exceeded the standard, the original zinc concentration was 41mg / L, the cadmium concentration was 15.7mg / L, and the pH value was 3.8. Raw water directly enters the electrochemical device with magnesium alloy plate (in this embodiment, magnesium alloy grade: AZ40) as the anode without adjusting the pH value, the distance between the plates is 12mm, and the current density is 10mA / cm 2 , the electrolysis time was 360s, and the effluent was discharged into the clarification tank and left to stand for 60 minutes. The concentration values of zinc and cadmium in the water were detected by sampling as 0.4mg / L and 0.07mg / L respectively, which met the discharge standard.
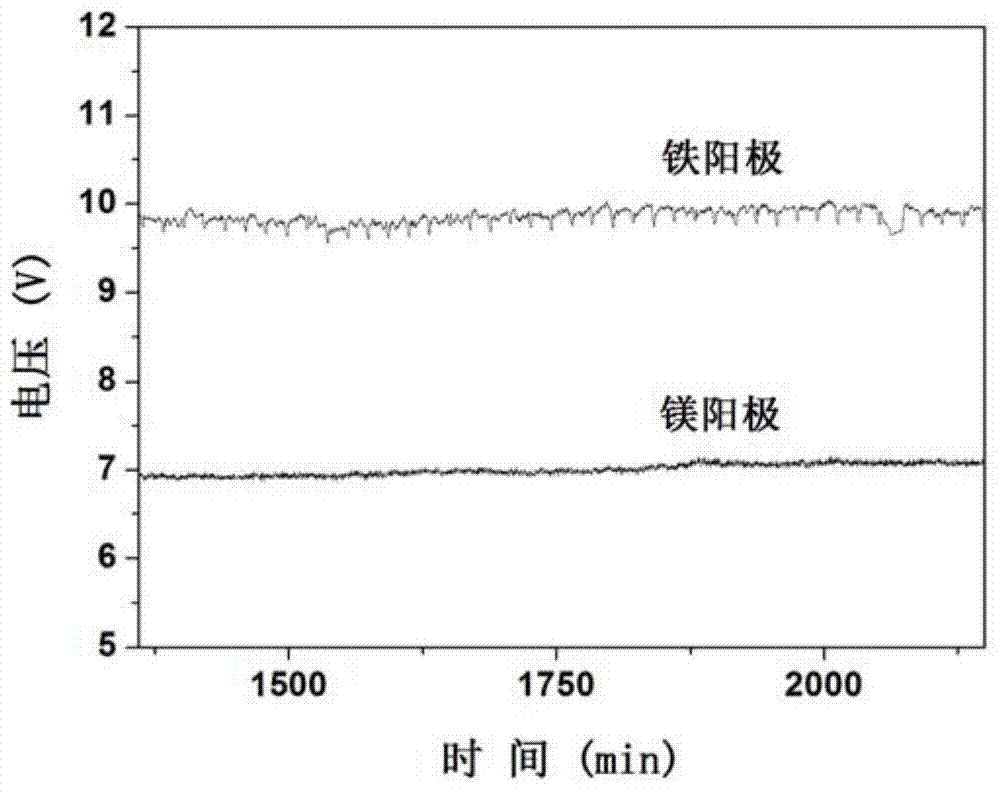
[0043] Under the same parameters, when iron is used as the anode, the zinc content in the effluent water is 0.53mg / L, and the cadmium content is 4.8mg / L. The performance of cadmium removal is seriously interfered by zinc, and cadmium cannot be effectively rem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com