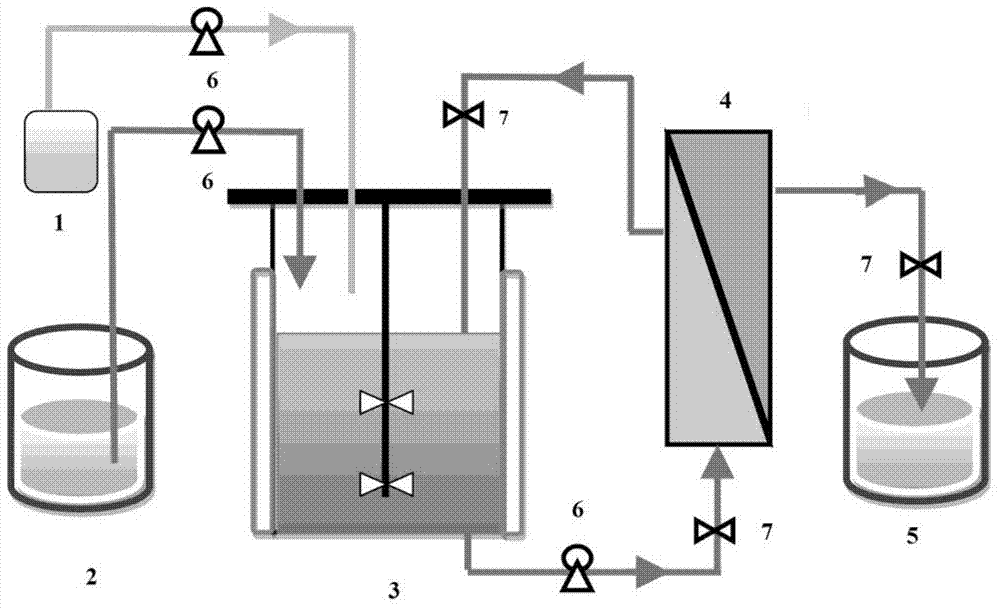
Method for producing lactic acid through continuously fermenting batches of lignocellulose hydrolysate by coupling fermenting and membrane separation
A technology of lignocellulose and hydrolyzate, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of long cycle and low yield, and achieve the effects of improving fermentation intensity, reducing production cost and shortening fermentation cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
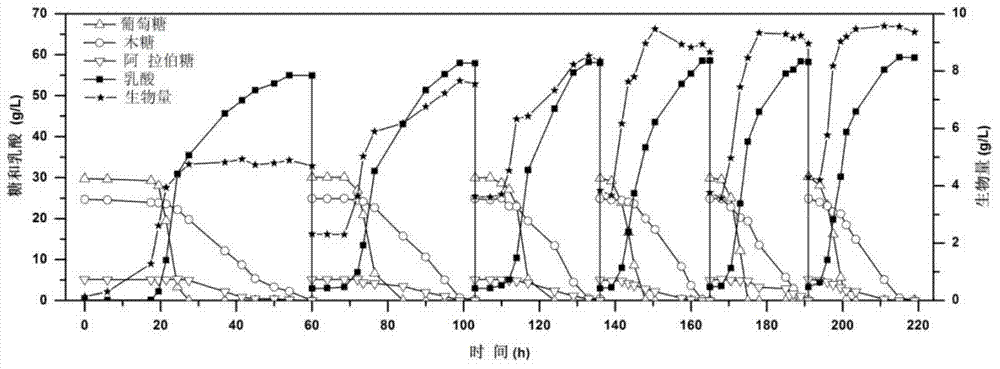
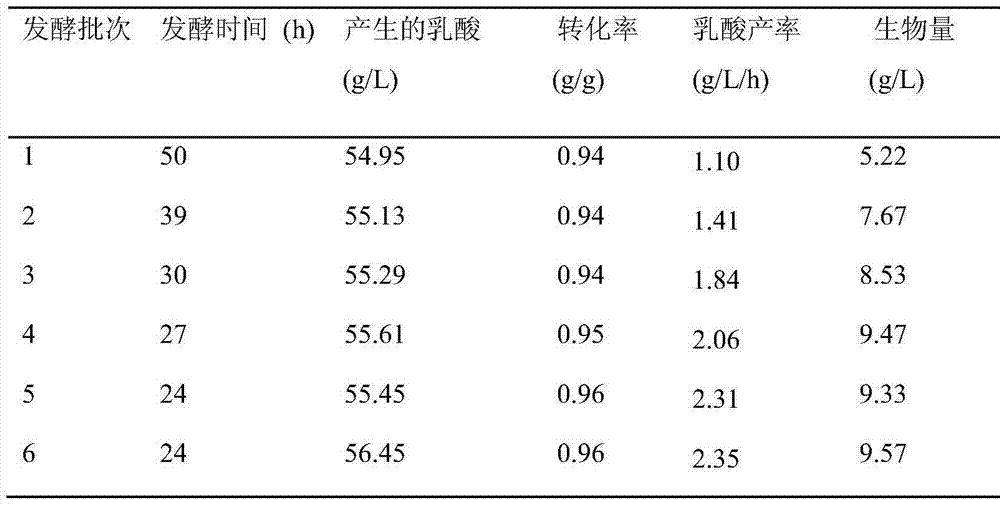
[0025] The method for producing lactic acid by fermentation of the mixed sugar in the hydrolysate of wheat straw in open cell recycling.
[0026] The composition of each medium used in this embodiment is as follows:
[0027] MRS medium (peptone 10g / L, beef powder 10g / L, yeast powder 0.5g / L, anhydrous sodium acetate 0.5g / L, hydrogen citrate diamine 0.2g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g / L) . The MRS medium added 10g / L glucose is the seed medium.
[0028] The specific method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] 1. Preparation of wheat straw hydrolysate: use 2% (w / v) sulfuric acid to treat wheat straw powder at 121°C for 90 minutes, with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, and the liquid obtained after filtering the pretreatment mixture is the wheat straw dilute acid Hydrolyzate. Use cellulase to enzymatically decompose the solid material obtained after dilute acid pretreatment (the main component is cellulose), and add 20FPU cellulase per gram of cellulose. En...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The method of open cell cycle recycling and utilization of mixed sugar in the bagasse hydrolysate to produce lactic acid by fermentation.
[0039] The seed culture medium formula used in this example is the same as in example 1.
[0040] The specific method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] 1. Preparation of bagasse hydrolysate: bagasse is dried and crushed into powder with an average size of 40 mesh. The bagasse powder is treated by ammonia steam explosion. The treatment conditions are: pressure 1.5MPa, maintenance for 10 min, solid-liquid ratio 1:6 (mass volume ratio), and ammonia water dosage is 5%. After pretreatment, solid-liquid separation obtains the pretreatment liquid and the bagasse solids (the main component is cellulose). Use cellulase to enzymatically hydrolyze bagasse solids, add 20FPU cellulase per gram of cellulose, enzymatic hydrolysis conditions: 50℃, pH5.0, 200rpm, enzymatic hydrolysis time 48h. After the enzymolysis, the pretreatm...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The method of open cell cycle recycling and utilization of mixed sugar in switchgrass hydrolysate to produce lactic acid by fermentation.
[0048] The seed culture medium formula used in this example is the same as in example 1.
[0049] 1. Preparation of switchgrass hydrolysate: switchgrass is dried and crushed into powder with an average size of 40 mesh. Switchgrass powder is pretreated with dilute acid under the conditions: pressure 135℃, 10min, 2% (w / v) sulfuric acid, solid-liquid ratio 1:8 (mass volume ratio). After pretreatment, after pretreatment, solid-liquid separation obtains the pretreatment liquid and switchgrass solids (the main component is cellulose). Use cellulase to enzymatically hydrolyze switchgrass solids, add 20FPU cellulase per gram of cellulose, enzymatic hydrolysis conditions: 50℃, pH5.0, 200rpm, enzymatic hydrolysis time 48h. After the enzymolysis, the pretreatment solution and enzymolysis solution were combined, and concentrated using a rolled pol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com