Cotton homologous structure field transcription factor gene GbHDTF1 and and application thereof
A technology of homeodomain and transcription factor is applied to the cloning of cotton homeodomain transcription factor gene GbHDTF1 to control the application field of cotton verticillium wilt, and can solve the problem that the detailed regulatory network is not very clear and so on.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: GbHDTF1 gene isolation and clone
[0035] The preliminary work of the applicant of the present invention is to study the transcriptome sequencing data of the roots of sea island cotton 'Hai 7124' (China Cotton Germplasm Bank, Beijing, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Institute of Crop Variety Resources) after inoculation with Verticillium wilt. Down-regulated genes after Verticillium wilt.
[0036] Use the obtained EST sequence to perform sequence alignment in the cotton D genome database (http: / / www.phytozome.net / cotton.php) to obtain a candidate DNA sequence matching the gene, and use the DNA sequence as a template to design primers GbHDTF1-OE-F (5'GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTCCATGGCTTCTGCTTTGTCAGT3') and GbHDTF1-OE-R (5'GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCACATTGTCATCCCTAAACAGTAAAC3'), the DNA, cDNA and ORF sequences of GbHDTF1 were amplified from the total DNA and cDNA of sea island cotton 'Hai 7124', respectively. A cotton homology domain transcripti...
Embodiment 2
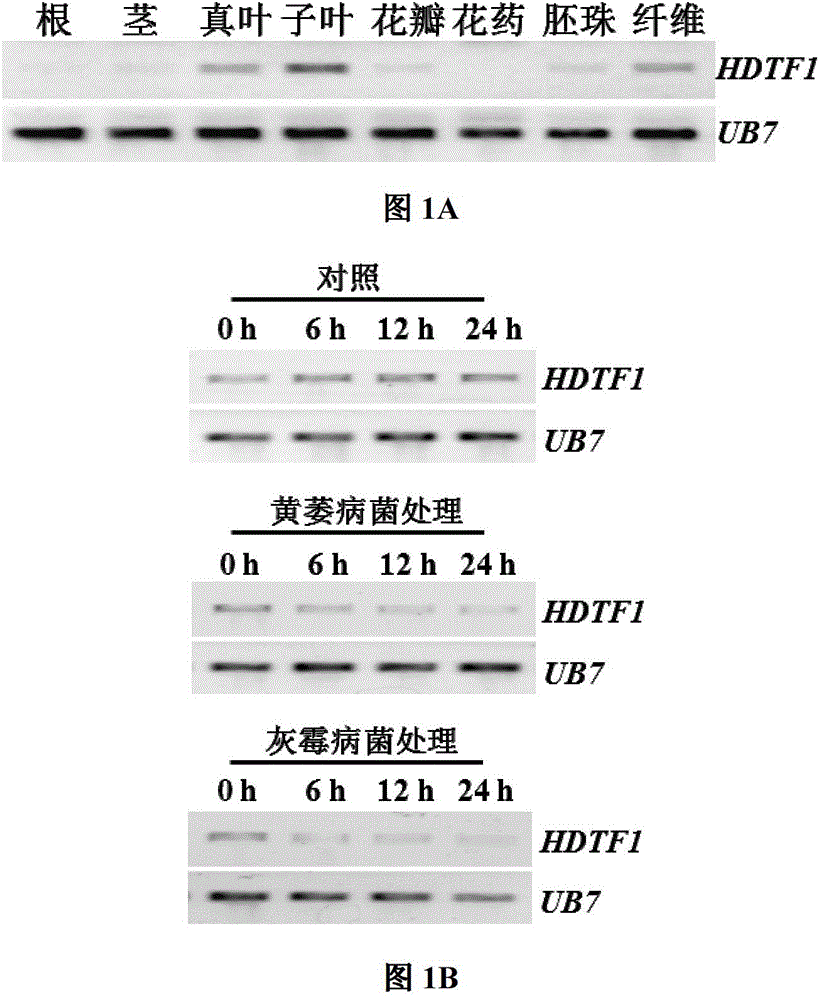
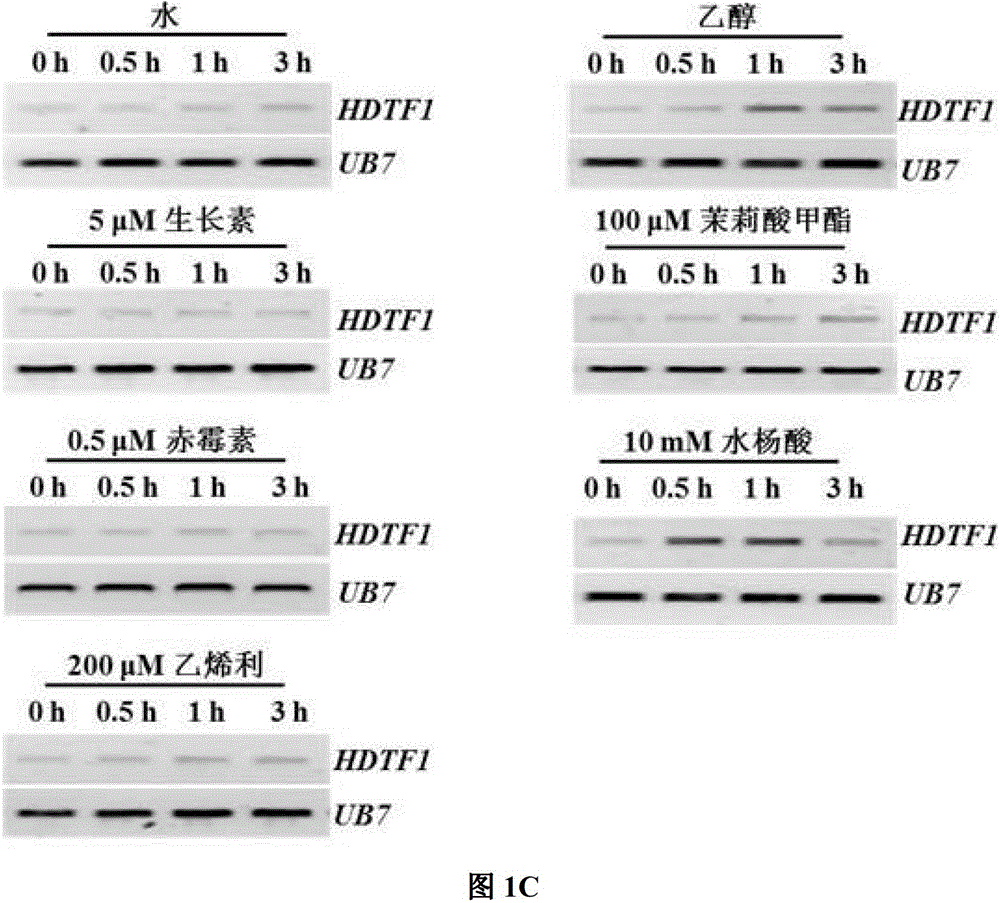
[0038] Example 2: Expression analysis of GbHDTF1 in different cotton tissues and its response to plant disease resistance signaling molecules
[0039] Using sea island cotton 'Hai 7124' as the material, RNA was extracted from eight different tissues of roots, stems, cotyledons, true leaves, fibers, ovules, petals and anthers. protocol for isolation of high quality RNA from Gossypium spp.suitable for cDNA library construction.Acta Agronomica Sinica.2005,31:1657-1659). After RNA extraction was completed, it was treated with DNaseI (purchased from Promega), and the RNA integrity was detected by 1.2% (w / v) agarose gel (EtBr) electrophoresis (5V / cm). The determination of nucleic acid concentration was carried out on a Beckman DU800 spectrophotometer (purchased from Beckman, USA). RNAs with a 260 / 280 ratio between 1.9 and 2.1, and RNAs with a 260 / 230 ratio greater than 2.0 were used for further analysis. The expression level of GbHDTF1 gene was detected by RT-PCR. cDNA synthesis ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Construction of viral interference vector, RNAi inhibitory expression vector and overexpression vector and VIGS-mediated transformation
[0043] The following primers were designed according to the gene sequence of GbHDTF1: forward primer GbHDTF1-trv-s (5'CGACGACAAGACCCTGGCGAGGAAGACGGCAACGAC3'), reverse primer GbHDTF1-trv-a (5'GAGGAGAAGAGCCCTATGTTTGGTTTCAGGCATTGGT3'), and then PCR amplification was performed using GbHDTF1 gene cDNA as template The resulting product and pTRV:RNA2 vector (a gift from Dr. Thomma, Wageningen University, The Netherlands) were double-enzyme digested with restriction enzymes BamH1 and Kpn1 (purchased from NEB, China). The PCR product after digestion was connected with the pTRV:RNA2 plasmid fragment recovered by digestion with T4 ligase (purchased from Invitrogen, USA), and the ligation product was the viral silencing vector pTRV2-GbHDTF1 (see image 3 A) ( Figure 4 A), the vector was subjected to heat shock transformation (operate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com