Method for preparing sugar and ethanol by using cassava wastes
A waste, cassava technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of cassava waste treatment, inability to fully utilize raw materials, and low utilization rate of cassava, so as to improve the biological efficiency of cassava. The effect of utilization rate, improving biotransformation rate, huge economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
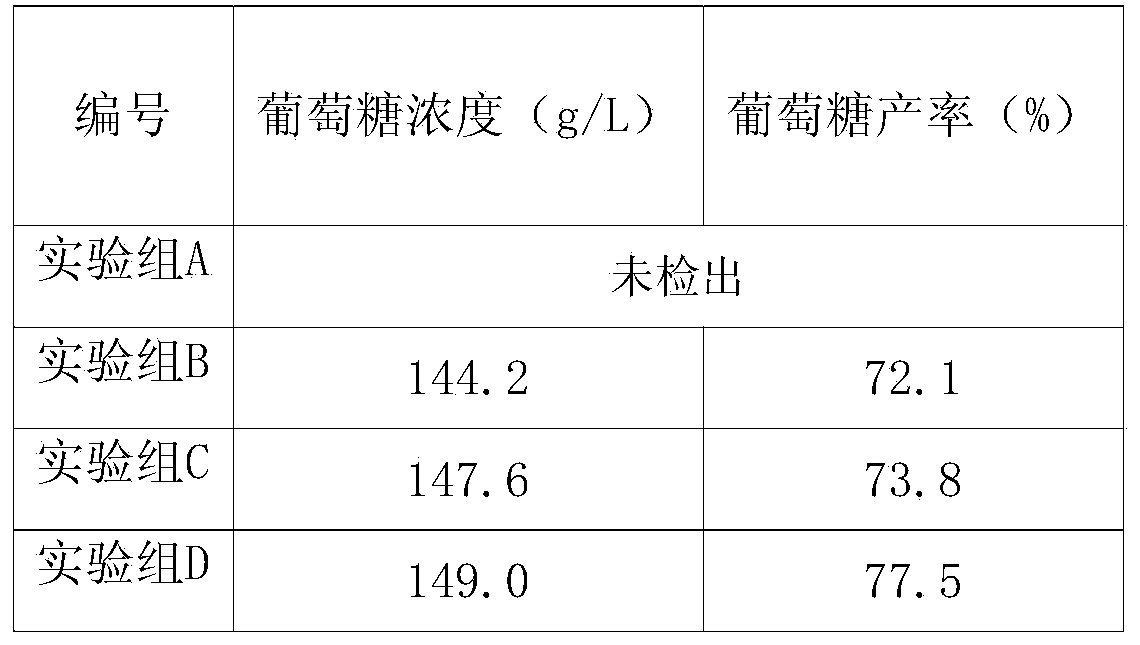
[0040] A method for producing sugar and ethanol from cassava waste, comprising the steps of:
[0041] (1) Take 50g of cassava waste residue (by dry weight), add water to make a solution with a mass percentage of 20%;
[0042] (2) Add 0.4 liters per kilogram of cassava waste residue (by dry weight) to add microbial culture solution to the cassava waste residue prepared in step (1), and enzymatically hydrolyze it for 5 hours at a temperature of 45°C, and then Add 100U of α-amylase per gram of cassava residue (by dry weight), hydrolyze for 1.5 hours at a temperature of 90°C, and then add 150U of glucoamylase per gram of cassava residue (by dry weight), Under the condition of 60°C, hydrolyze for 2.5 hours to obtain glucose mash;
[0043] (3) Add 0.002g of yeast per gram of dry material to add high-temperature-resistant yeast to the glucose mash prepared in step (2), culture it statically at 30°C, and carry out ethanol fermentation for 48 hours, then purify and separate , to prod...
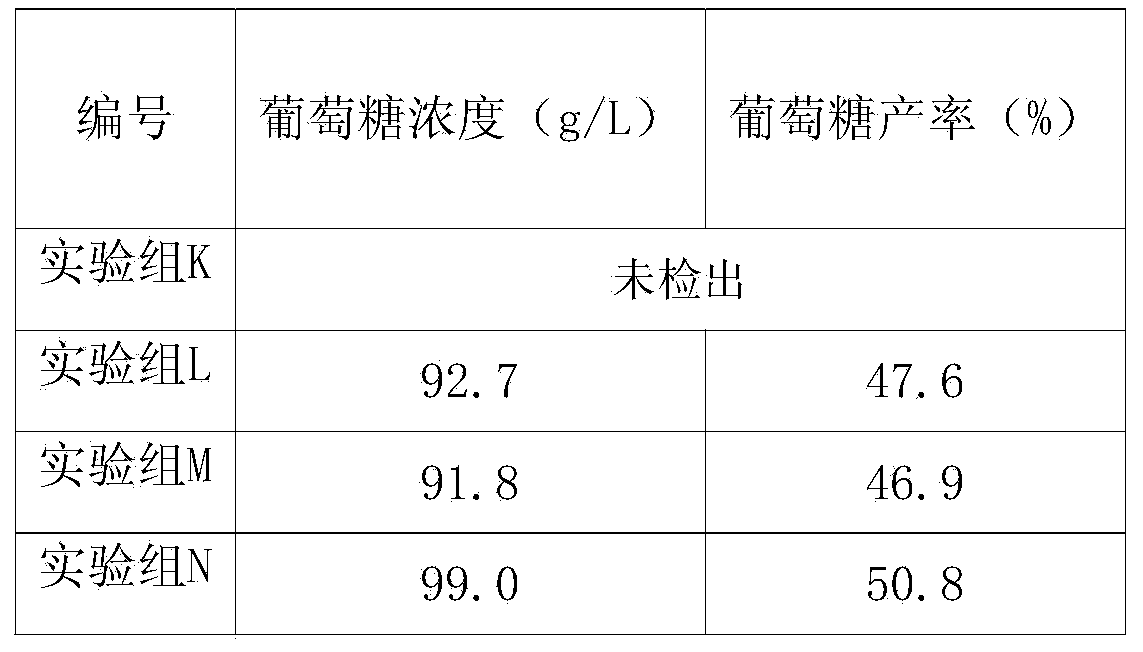
Embodiment 2
[0074] Raw material description
[0075] The cassava residue comes from Guangxi, with a water content of 6.2%, solid content: starch 62%, crude protein 4.8%, crude fat 1.5%, ash 11.2%, cellulose and hemicellulose and others 14.3%.
[0076] A method for producing sugar and ethanol from cassava waste, comprising the steps of:
[0077] (1) Take 50g of cassava waste residue (by dry weight), add water to make a solution with a mass percentage of 20%;
[0078] (2) Add 0.4 liters per kilogram of cassava waste residue (by dry weight) to add microbial culture solution to the pretreated cassava waste residue prepared in step (1), and enzymatically hydrolyze it for 5 hours at a temperature of 45°C , then add 100U of α-amylase per gram of cassava residue (by dry weight), hydrolyze for 1 hour at a temperature of 90°C, and then add 150U of glucoamylase per gram of cassava residue (by dry weight) , under the condition of a temperature of 60°C, hydrolyze for 2 hours to obtain glucose mash; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com