Method for associating plants and microorganisms to accumulate heavy metal cadmium in soil and application thereof
A microorganism and soil technology, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of limited application of phytoremediation technology, limited absorption capacity, low biomass, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting growth and root extraction of heavy metals, low cost, and good restoration effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Screening, identification and biological characteristic analysis of cadmium-resistant bacteria
[0023] A plant leaf was collected from the Dabaoshan tailings area (contaminated area) in Shenzhen, rinsed with deionized water, soaked in 70% alcohol for 20 seconds, then soaked in 2.5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 minutes, and rinsed repeatedly with sterile water. The rinsed sterile water was spread on the plate of solid LB medium (10g protein powder, 5g yeast extract, 10g NaCl, 1000mL distilled water). If there is no microbial growth after cultivation, it indicates that the disinfection is complete. On the aseptic operating table, take an appropriate amount of the above-mentioned thoroughly sterilized plant tissue into a sterile mortar, add 1mL of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, grind it thoroughly, and then dilute it in a 10-fold gradient series for 10-10 6 Times, spread on solid LB medium, culture for 48h, pick different forms of bacterial isolates for purificat...
Embodiment 2
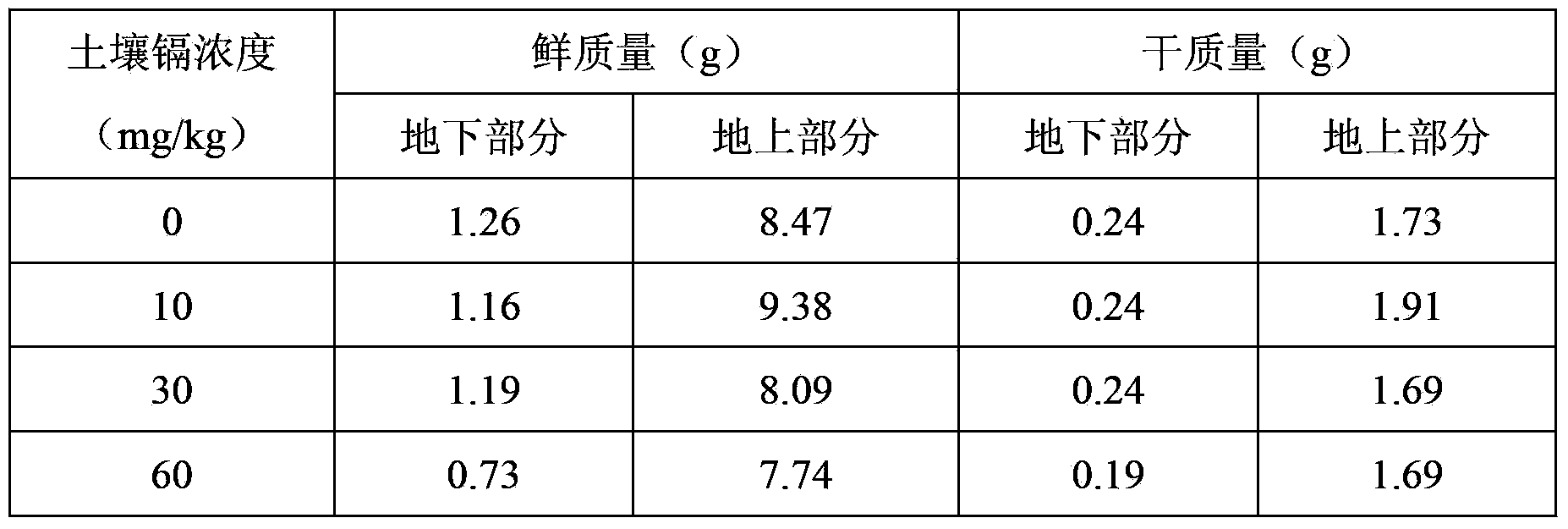
[0026] The enrichment ability of cadmium in the soil of embodiment 2 green beetle seeds
[0027] The soil used in the pot experiment was collected from a local mushroom plantation in Nanshan District, Shenzhen. After removing foreign matter, it was air-dried indoors, ground, mixed, and passed through a 4mm sieve. The seeds of Pleurotus chinensis are first germinated on wet filter paper, then transferred to the seedling medium and cultivated to the 4-6 leaf stage, and set aside.
[0028]The test uses plastic pots with a diameter of about 15cm, and each pot is filled with about 2kg of soil. The heavy metal cadmium is added into the pot in the form of a solution and mixed evenly. The contaminated soil with cadmium content of 10mg / kg, 30mg / kg and 60mg / kg is prepared, and the same amount of soil is planted respectively. At the 4-6 leaf stage of the plant, weeds were planted. At the same time, the soil without cadmium was used as the control, and the soil water content was kept at 7...
Embodiment 3
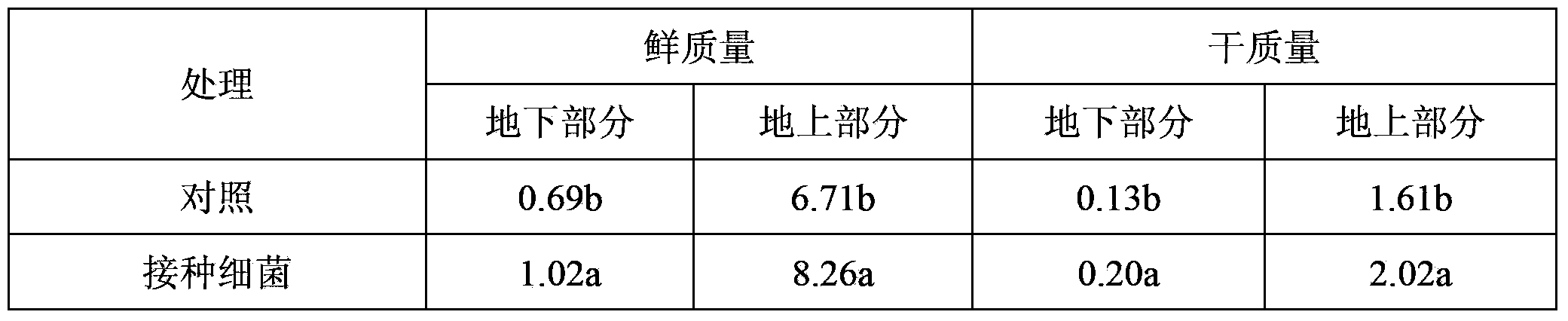
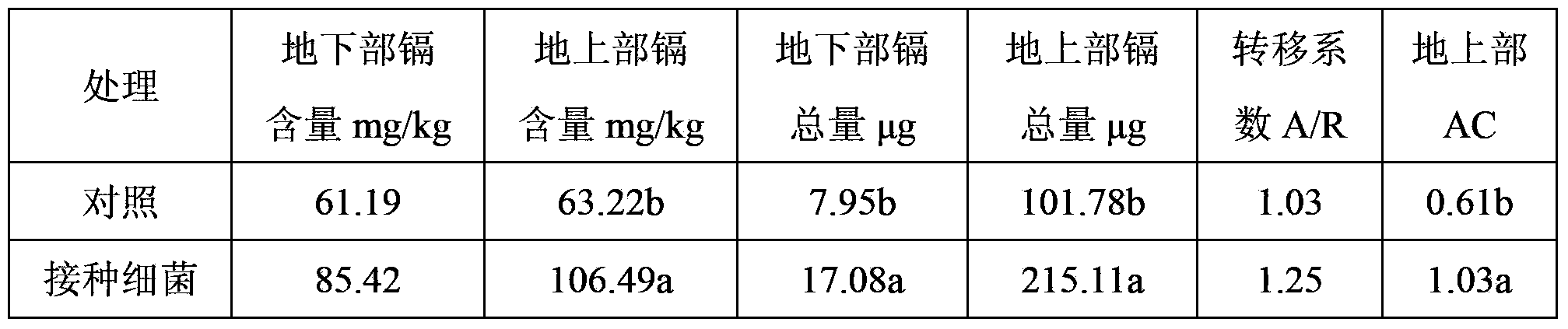
[0044] Example 3 The joint enrichment of cadmium in soil by Semen chinensis-cadmium-tolerant bacteria
[0045] First, Klebsiella sp. (Klebsiella sp.) DE2 used for inoculation in Example 1 was activated, the strain was activated using solid LB medium, cultured at 30°C for 24h, picked colonies and inserted into bean sprouts juice medium, 30°C, 150r / min shaking culture for 48h to prepare the fermentation liquid, and dilute the bacterial liquid to a concentration of 1×10 with the blank bean sprouts juice medium 8 CFU / mL, spare.
[0046] Plastic pots with a diameter of about 15 cm were used in the test, and each pot was filled with about 2 kg of soil. The heavy metal cadmium was added into the pot in the form of a solution and mixed evenly to prepare 100 mg / kg of cadmium-contaminated soil. Adjust the water content of the soil in the pot to about 70% to 85% of the maximum water holding capacity. After a week of natural balance, transplant the seedlings of the 4-6 leaf stage with b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com