Preparation method and application of nanometer particles of taxane drugs
A taxane and nanoparticle technology, which is applied in the directions of drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, and inactive medical preparations, can solve the problems of long-circulating nanoparticles without a preparation process, immaturity and the like, and achieves low histamine levels. Release effect, low viscosity, low toxicity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Implementation example 1: Preparation of TPGS emulsified paclitaxel nanoparticles
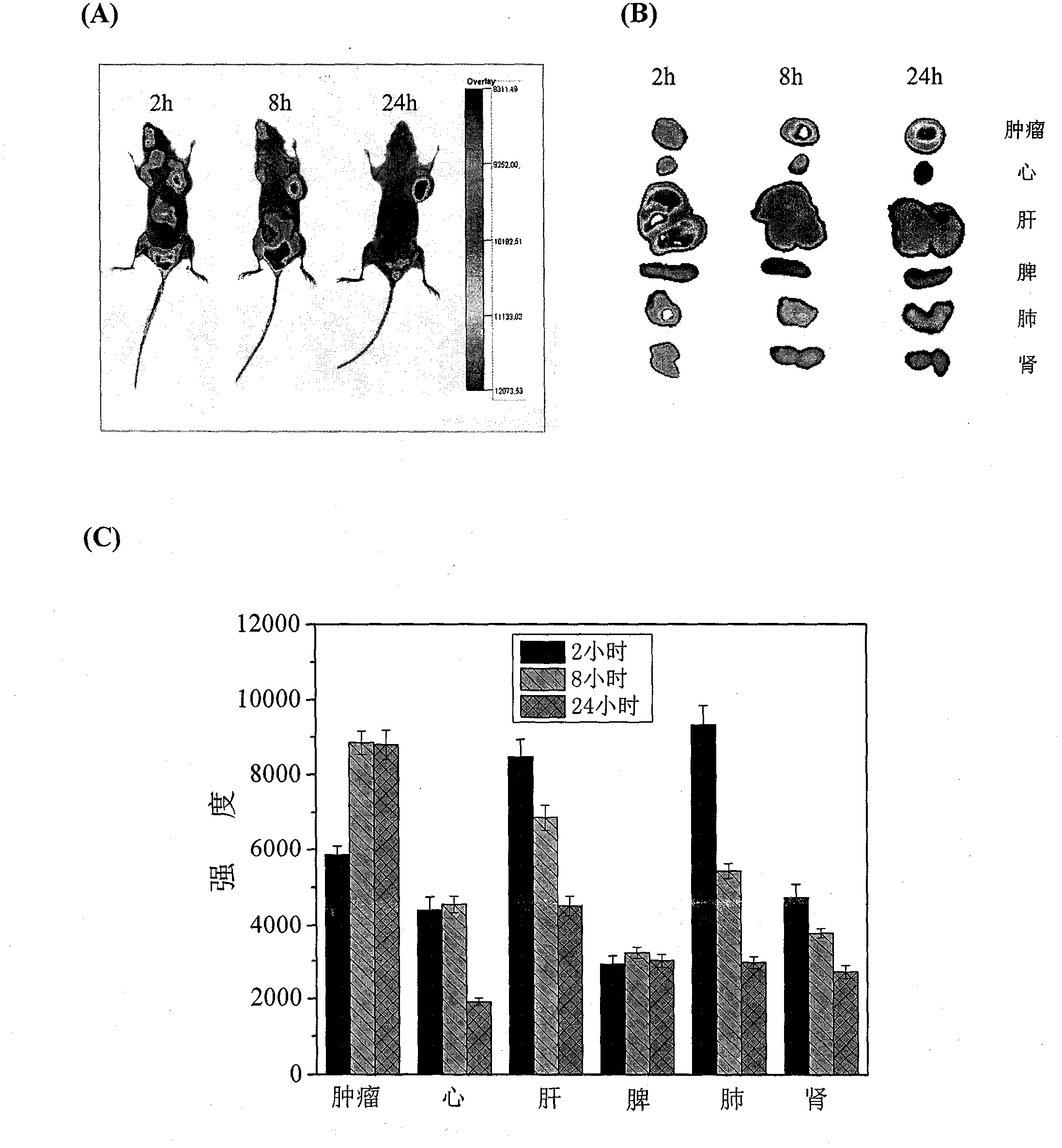
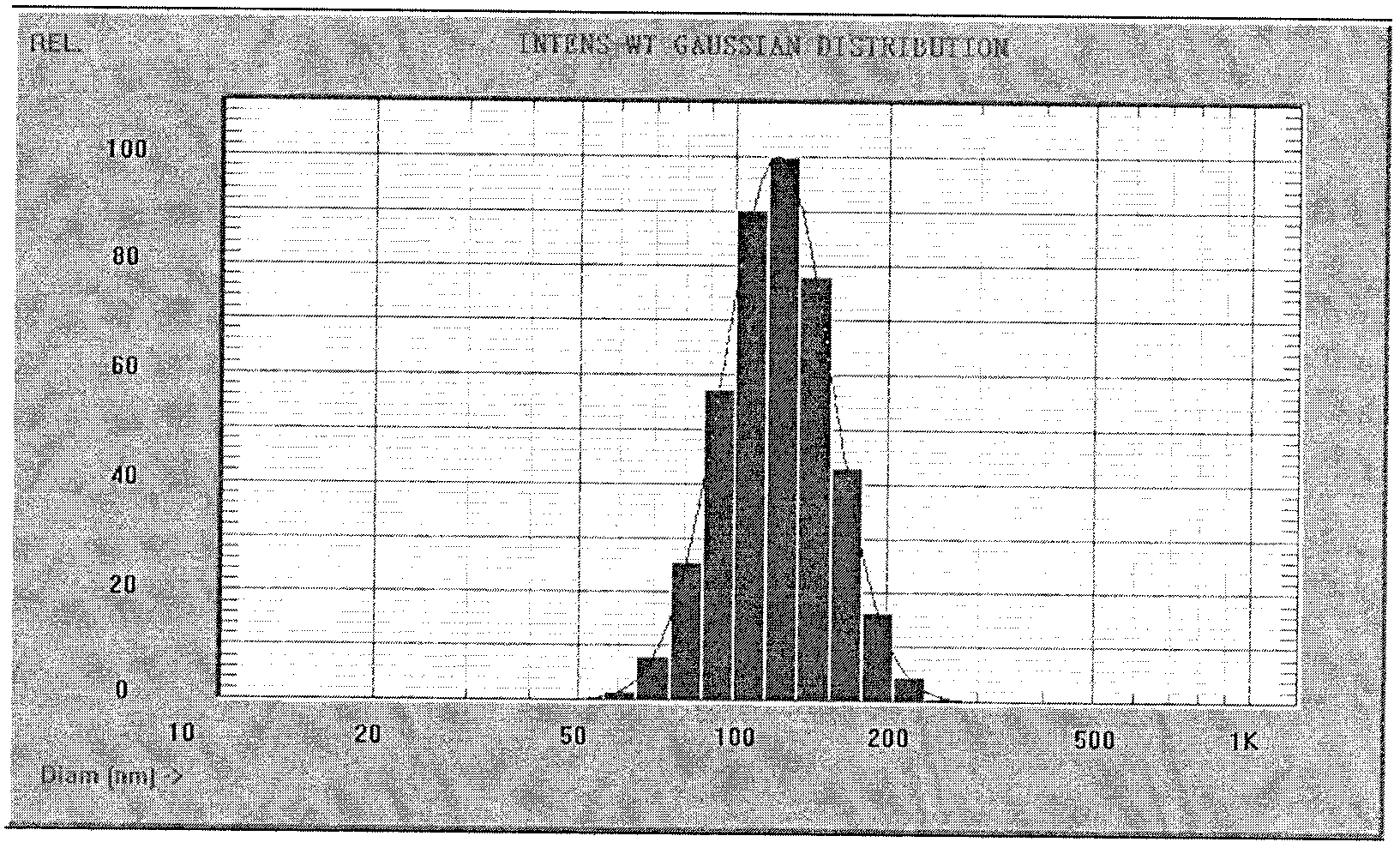
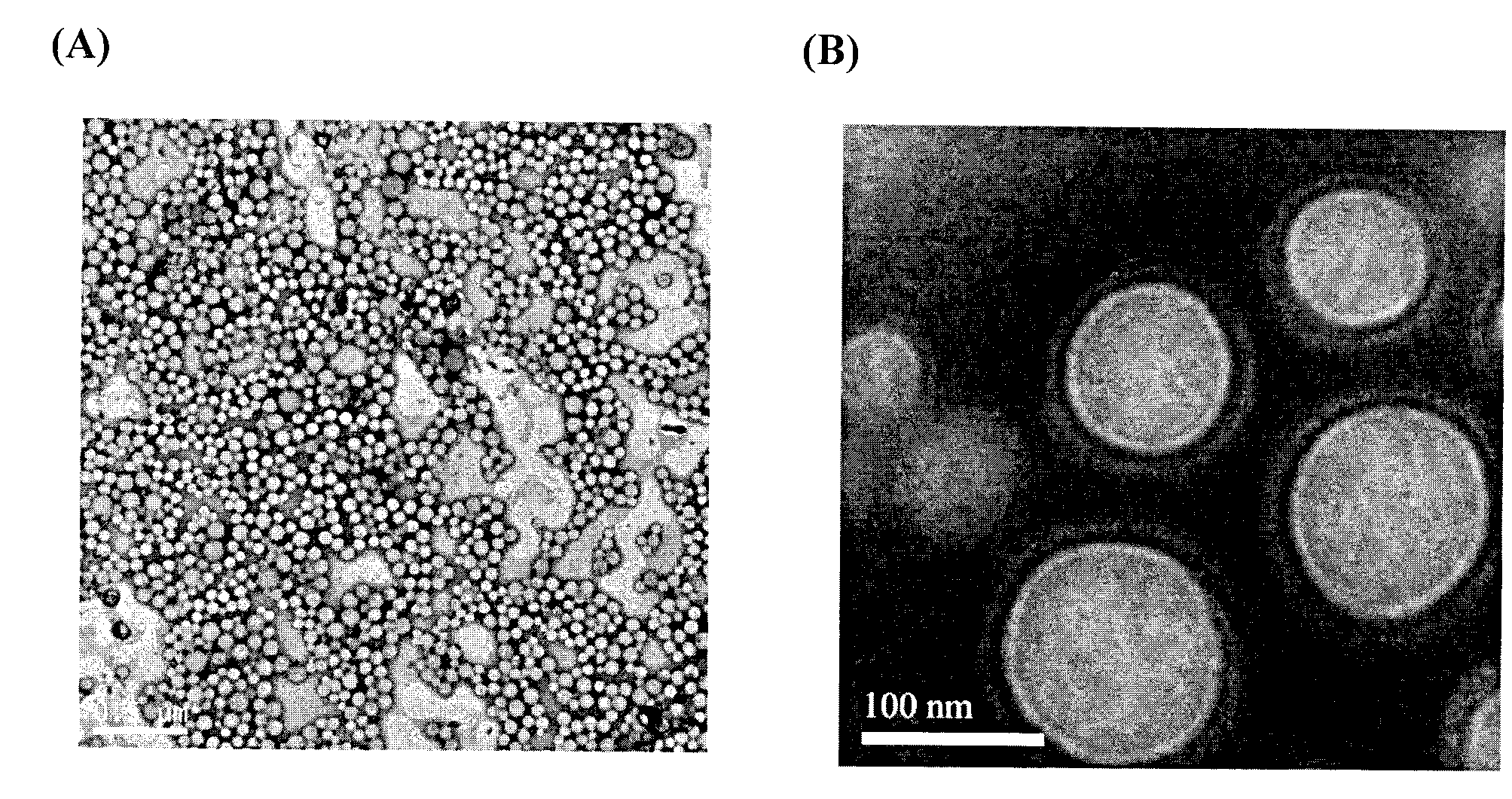
[0036] 80mg PLGA (50:50, molecular weight 45000) and 8mg paclitaxel were dissolved in 20mL acetone solvent as oil phase, 240mgTPGS was dissolved in 40mL water and ethanol volume ratio is 1: 1 in the cosolvent of 1 forming mixed solution; Drop into the mixed solution containing TPGS at a speed of 1 min, and form a light blue nanoemulsion under low-speed stirring at 300 r / min. After the addition is completed, transfer the nanoemulsion to a rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent by vacuum rotation to obtain nanoparticles. The average particle size measured by the laser dynamic scattering instrument is 105.1±2.3nm, and the particle size distribution is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the particle size distribution coefficient PDI is 0.047±0.025, and the encapsulation efficiency of nanoparticles is 92.5±2.2%. The morphology of the prepared nanoparticles was analyzed by transmission e...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Implementation example 2: Preparation of TPGS emulsified paclitaxel nanoparticles
[0038] 80mg PLGA (50:50, molecular weight 15000) and 8mg paclitaxel were dissolved in 20mL acetone solvent as oil phase, 240mgTPGS was dissolved in 40mL water and ethanol volume ratio is 1: 1 in the co-solvent of ethanol to form mixed solution; Drop into the mixed solution containing TPGS at a speed of 1 min, and form a light blue nanoemulsion under low-speed stirring at 300 r / min. After the addition is completed, transfer the nanoemulsion to a rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent by vacuum rotation to obtain nanoparticles. The average particle size measured by the laser dynamic scattering instrument is 102.3±2.4nm, the particle size distribution coefficient PDI is 0.073±0.012, and the encapsulation efficiency of the nanoparticles is 85.2±2.4%.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Implementation example 3: Preparation of TPGS emulsified paclitaxel nanoparticles
[0040] 80mg PLGA (50:50, molecular weight 100000) and 8mg paclitaxel were dissolved in 20mL of acetone solvent as the oil phase, 240mgTPGS was dissolved in 40mL of water and ethanol with a volume ratio of 1:1 to form a mixed solution; the oil phase was dissolved in 1mL / Drop into the mixed solution containing TPGS at a speed of 1 min, and form a light blue nanoemulsion under low-speed stirring at 300 r / min. After the addition is completed, transfer the nanoemulsion to a rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent by vacuum rotation to obtain nanoparticles. The average particle size measured by the laser dynamic scattering instrument is 109.1±2.2nm, the particle size distribution coefficient PDI is 0.062±0.018, and the encapsulation efficiency of the nanoparticles is 86.4±2.1%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com