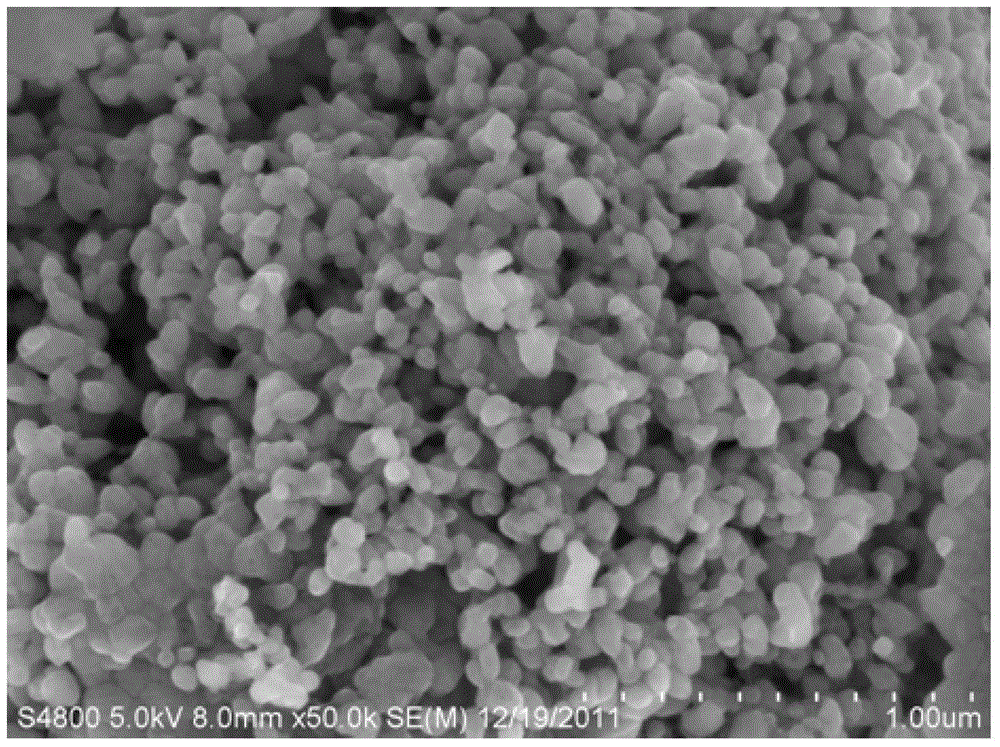
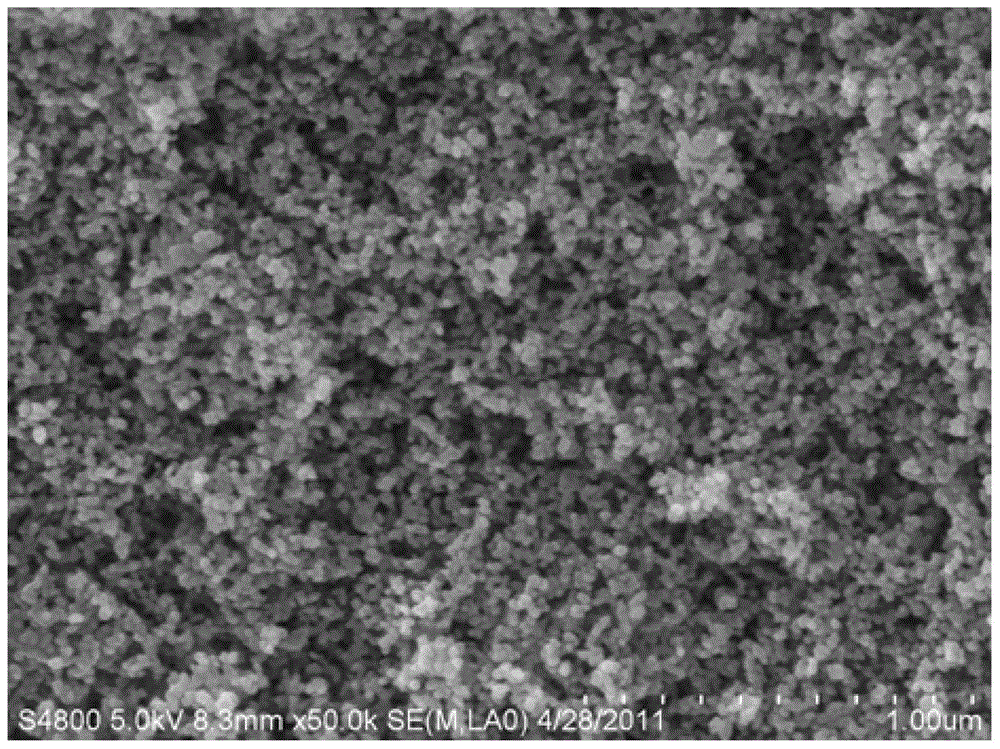
Micro-chemical preparation method of nano-iron phosphate and nano-iron phosphate
A nano-iron phosphate and micro-chemical technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the complicated use of rotating packed bed reactors, time-consuming auxiliary operations, discontinuous processes, etc. problems, to achieve precise control of reaction process conditions, reduce the degree of manual intervention, and achieve the effect of residence time distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] A microchemical preparation method of nano-iron phosphate, comprising the steps of:
[0036] 1) According to Fe:P=1:0.8-1.2, dissolve soluble iron salt and phosphate in deionized water respectively, and the solution concentration is 0.1-1mol / L. The final volume fraction of preferred iron salt solution and phosphate solution is identical; The purity of described soluble iron salt and phosphate is preferably analytical pure; Any one or any two of preferred iron trichloride, iron nitrate, iron sulfate in soluble iron salt More than one combination; the soluble phosphate is preferably any one of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate or any combination of two or more.
[0037] 2) Weigh the theoretically generated 1wt.%-10wt.% surfactant of iron phosphate and dissolve it in the iron salt solution; the surfactant is preferably cetyl t...
Embodiment 1
[0043] Dissolve soluble ferric chloride (analytical pure) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (analytical pure) in deionized water respectively according to Fe:P=1:1.1, the solution concentration is 0.6mol / L, ferric chloride solution and diphosphate The final volume fraction of ammonium hydrogen solution is the same.
[0044] Weigh the theoretically generated 1wt.% ferric phosphate surfactant and dissolve it in the ferric chloride solution; at the same time, add ammonia water dropwise to the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution to adjust the pH to 8.5.
[0045] Adjust the speed of the mechanical pump to 60 rpm, and add the ferric chloride solution and the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution to the microchemical system at the same time at the same flow rate to carry out the aforementioned step 4), and react for 30 minutes to obtain a beige suspension liquid. Then filter and separate the obtained suspension, wash 4 times with deionized water, and dry it into powder in a const...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Soluble ferric chloride (analytical pure) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (analytical pure) were respectively dissolved in deionized water according to Fe:P=1:1.2, the solution concentration was 0.1mol / L, ferric chloride solution and diphosphate The final volume fraction of ammonium hydrogen solution is the same.
[0048] Weigh 10wt.% of theoretically produced ferric phosphate surfactant and dissolve it in the ferric chloride solution; at the same time, add ammonia water dropwise to the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution to adjust the pH to 10.
[0049] Adjust the speed of the mechanical pump to 300 rpm, and add the ferric chloride solution and the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution to the microchemical system at the same time at the same flow rate to carry out the aforementioned step 4), and react for 10 minutes to obtain a beige suspension liquid. Then the obtained suspension was separated by filtration, washed 5 times with deionized water, and dried into po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com