Bidirectional and symmetrical high-speed overvoltage protective device
A technology for overvoltage protection devices and devices, which is applied in the fields of electric solid state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid state device components, etc., to achieve the effect of improving protection capability, superiority and capability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
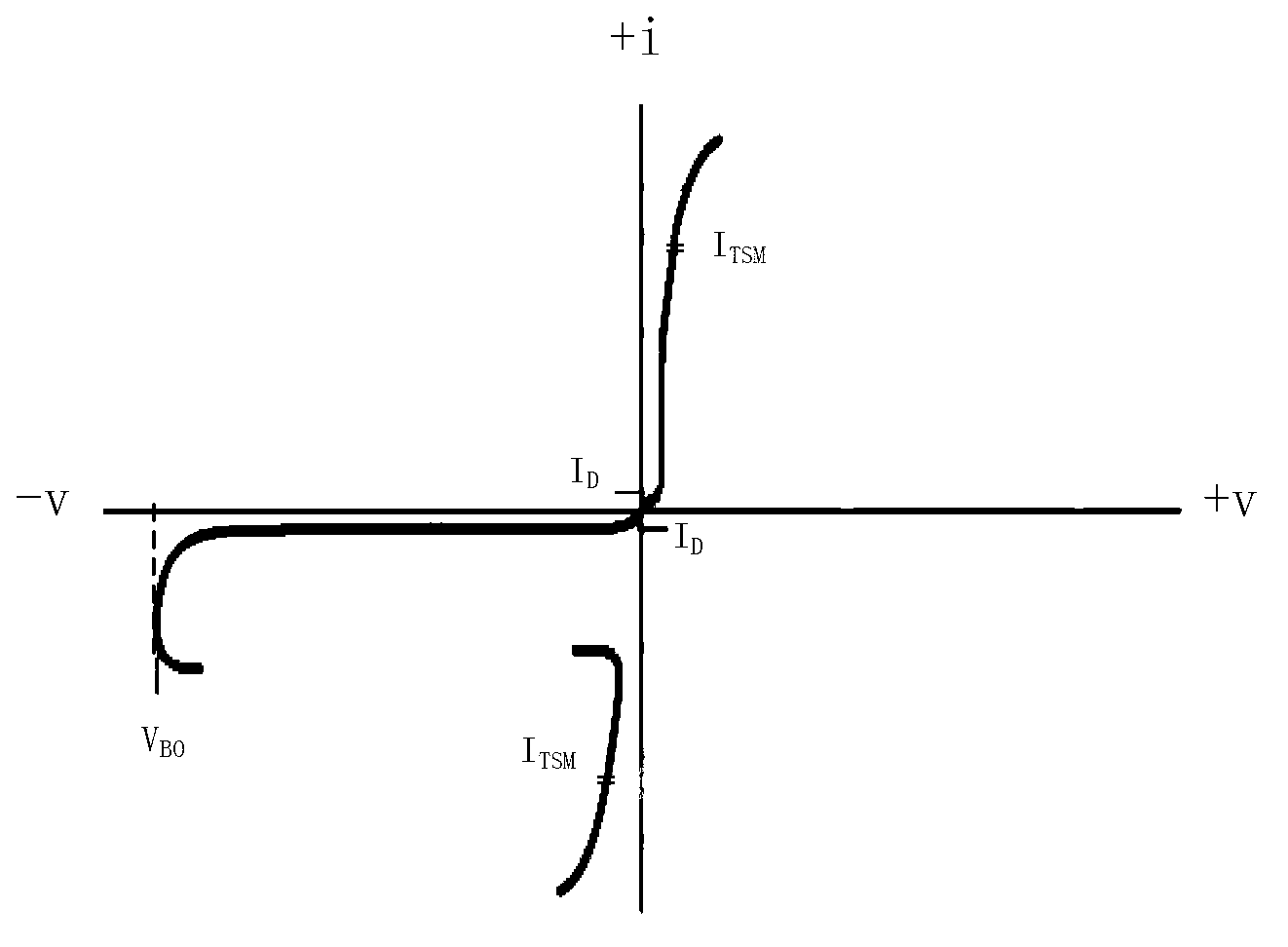
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
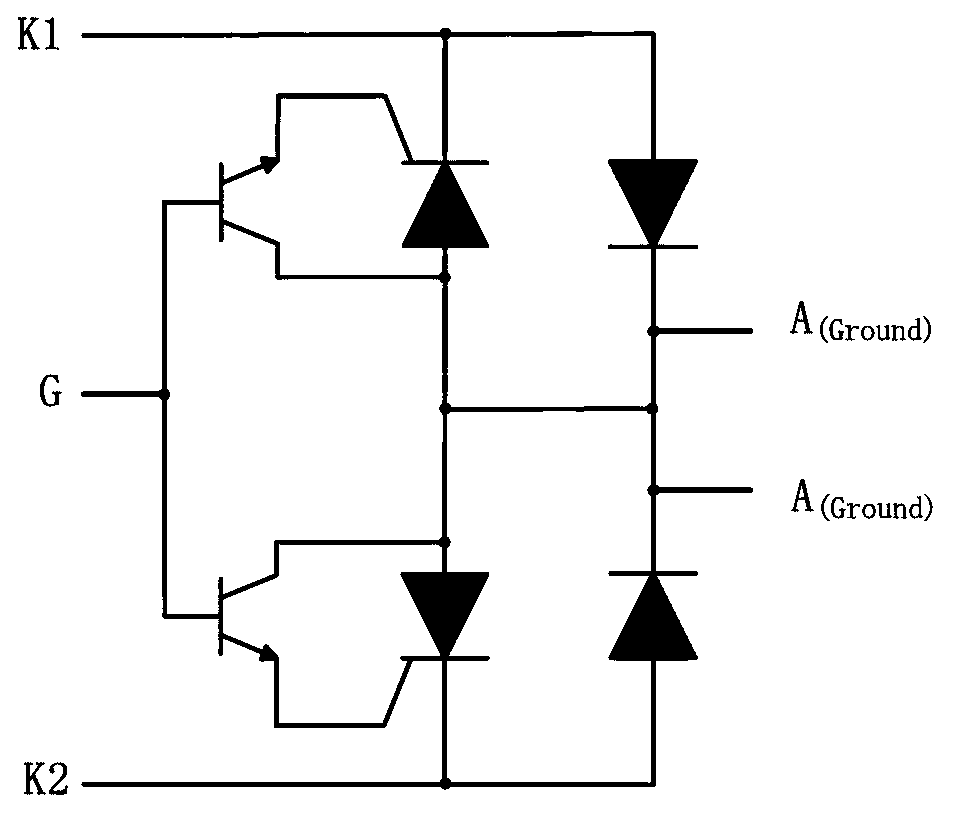
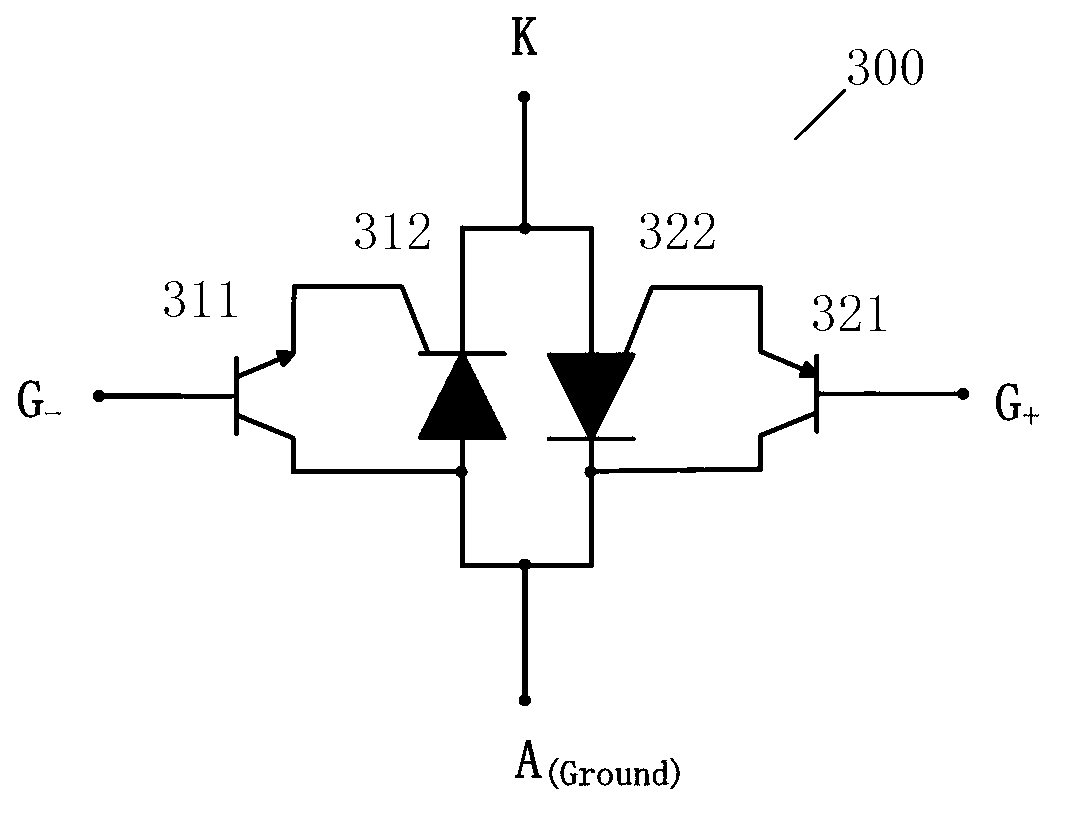
[0072] image 3 A schematic diagram of an overvoltage protection circuit 300 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown. The overvoltage protection circuit 300 includes an NPN transistor 311 and an NPNP thyristor 312 as well as a PNP transistor 321 and a PNPN thyristor 322 . The emitter and the collector of the NPN transistor 311 are respectively connected to the control electrode and the anode of the NPNP transistor 312 , and the emitter and the collector of the PNP transistor 321 are respectively connected to the control electrode and the cathode of the PNPN transistor 322 . The base of the NPN transistor 311 is used as the negative overvoltage reference potential port G of the protection circuit – , the base of the PNP transistor 321 serves as the forward overvoltage reference potential port G of the protection circuit + . The anode of the NPNP thyristor 312 and the cathode of the PNPN thyristor 322 are connected as the ground port A (Ground) of the prot...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of an overvoltage protection circuit 400 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention is shown. The overvoltage protection circuit 400 includes a first protection unit and a second protection unit, and each protection unit has image 3 structure shown. The first protection unit includes an NPN transistor 411 and an NPNP thyristor 412 and a PNP transistor 421 and a PNPN thyristor 422 . The emitter and the collector of the NPN transistor 411 are respectively connected to the control electrode and the anode of the NPNP transistor 412 , and the emitter and the collector of the PNP transistor 421 are respectively connected to the control electrode and the cathode of the PNPN transistor 422 . The second protection unit includes an NPN transistor 431 and an NPNP thyristor 432 and a PNP transistor 441 and a PNPN thyristor 442 . The emitter and the collector of the NPN transistor 431 are respectively connected to the control electrode and t...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The chip structure of the overvoltage protection device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 .
[0080] Refer below Figure 6A and Figure 7A The chip structure of the N-type chip 600 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The N-type chip includes a combination of two sets of NPN transistors and NPNP thyristors in the overvoltage protection device 400 . Figure 6A shown on the N-type semiconductor substrate 9 N A top view of the semiconductor chip of the N-type chip 600 fabricated on Figure 7A for Figure 6A N-type chip 600 shown along the B 1 -B 1 Longitudinal section view of the line. As shown in the figure, an N-type chip 600 includes a transistor region 10 of two NPN transistors N Two NPNP thyristor regions 11 each comprising an NPNP thyristor located in the middle of the chip N are respectively formed on both sides of the transistor region. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com