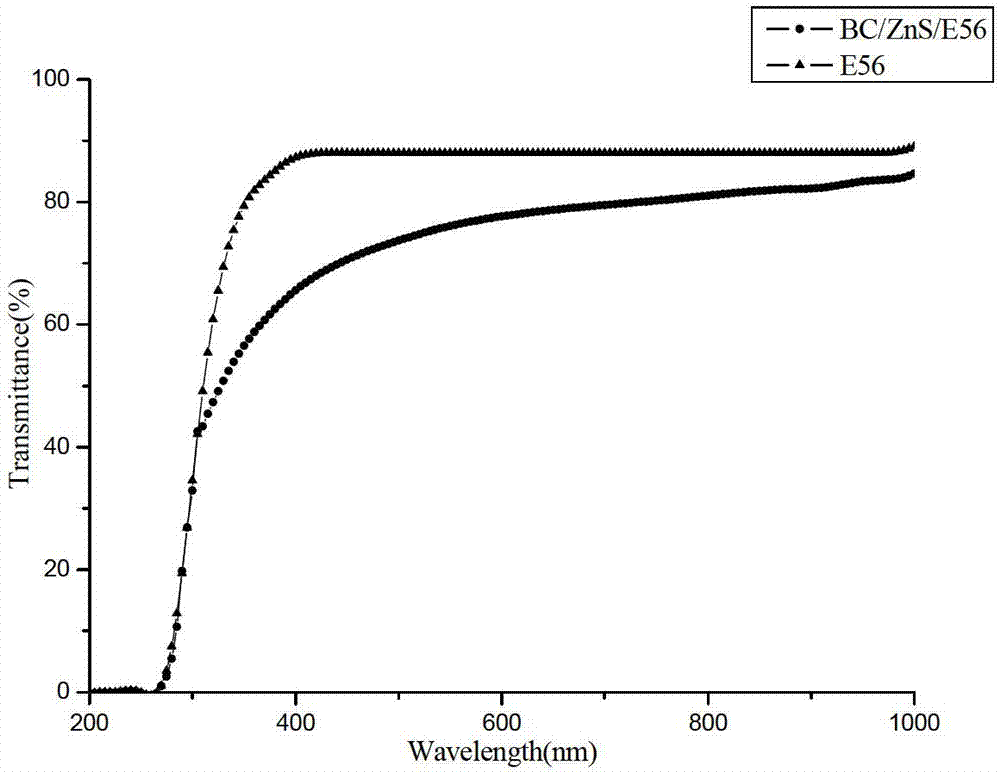
Bacterial cellulose base optical thin film and preparation method thereof
A bacterial cellulose-based optics technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of volume shrinkage affecting the mechanical properties of materials, reducing the refractive index of materials, and restricting applications, so as to increase the refractive index and thermo-optic stability , excellent thermal and light stability, and the effect of ensuring light transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] 1) Cut the bacterial cellulose film produced by Acetobacter xylinum into small pieces with a size of 4cm×5cm×0.5cm, place it in a 1% NaOH alkaline solution with a mass concentration of 1% for 3 hours, and then rinse it repeatedly with deionized water to neutral;
[0056] 2) Immerse the bacterial cellulose film in 0.05mol / L zinc acetate solution for 24 hours at room temperature and magnetic stirring until the adsorption equilibrium;
[0057] 3) Add thioacetamide, wherein the molar ratio of thioacetamide to zinc acetate is 3:1;
[0058] 4) Adjust the pH value of the reaction system to 2, and then react at 90°C for 2 hours under the protection of nitrogen;
[0059] 5) Take out the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, wash and backwash it with deionized water until neutral, and obtain a bacterial cellulose wet membrane composited with zinc sulfide nanoparticles;
[0060] 6) Perform solvent exchange treatment on the obtained bacterial cellulose wet film of composite zinc ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] 1) Cut the bacterial cellulose film produced by Acetobacter acetogenes into small pieces with a size of 4cm×5cm×0.5cm, place it in a 3% NaOH alkaline solution with a mass concentration of 2 hours for magnetic stirring, and then rinse it repeatedly with deionized water to neutral;
[0065] 2) Immerse the bacterial cellulose film in a 0.1mol / L zinc chloride solution for 20 hours at room temperature and under magnetic stirring until the adsorption equilibrium;
[0066] 3) Add thioacetamide, wherein the molar ratio of thioacetamide to zinc chloride is 3:1;
[0067] 4) Adjust the pH value of the reaction system to 2, and then react at 80°C for 3 hours under the protection of nitrogen;
[0068] 5) Take out the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, wash and backwash it with deionized water until neutral, and obtain a bacterial cellulose wet membrane composited with zinc sulfide nanoparticles;
[0069] 6) Perform solvent exchange treatment on the obtained bacterial cellulose ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The bacterial cellulose film produced by Acetobacter acetogenes was cut into small pieces with a size of 4cm×5cm×0.5cm, placed in a 5% NaOH alkali solution with a mass concentration of 5% and magnetically stirred for 2 hours, and then washed repeatedly with deionized water until medium sex;
[0073] 2) Immerse the bacterial cellulose film in a 0.15mol / L zinc sulfate solution for 16 hours at room temperature and under magnetic stirring until the adsorption equilibrium;
[0074] 3) Add thioacetamide, wherein the molar ratio of thioacetamide to zinc sulfate is 2:1;
[0075] 4) Adjust the pH value of the reaction system to 3, and then react at 70°C for 4 hours under the protection of nitrogen;
[0076] 5) Take out the reacted bacterial cellulose membrane, wash and backwash it with deionized water until neutral, and obtain a bacterial cellulose wet membrane composited with zinc sulfide nanoparticles;
[0077] 6) Perform solvent exchange treatment on the obtained bacterial ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com