New method for preprocessing high-salt dye wastewater
A technology for dye wastewater and pretreatment, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing accumulation probability, alleviating hardening and pollution, and low cost and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
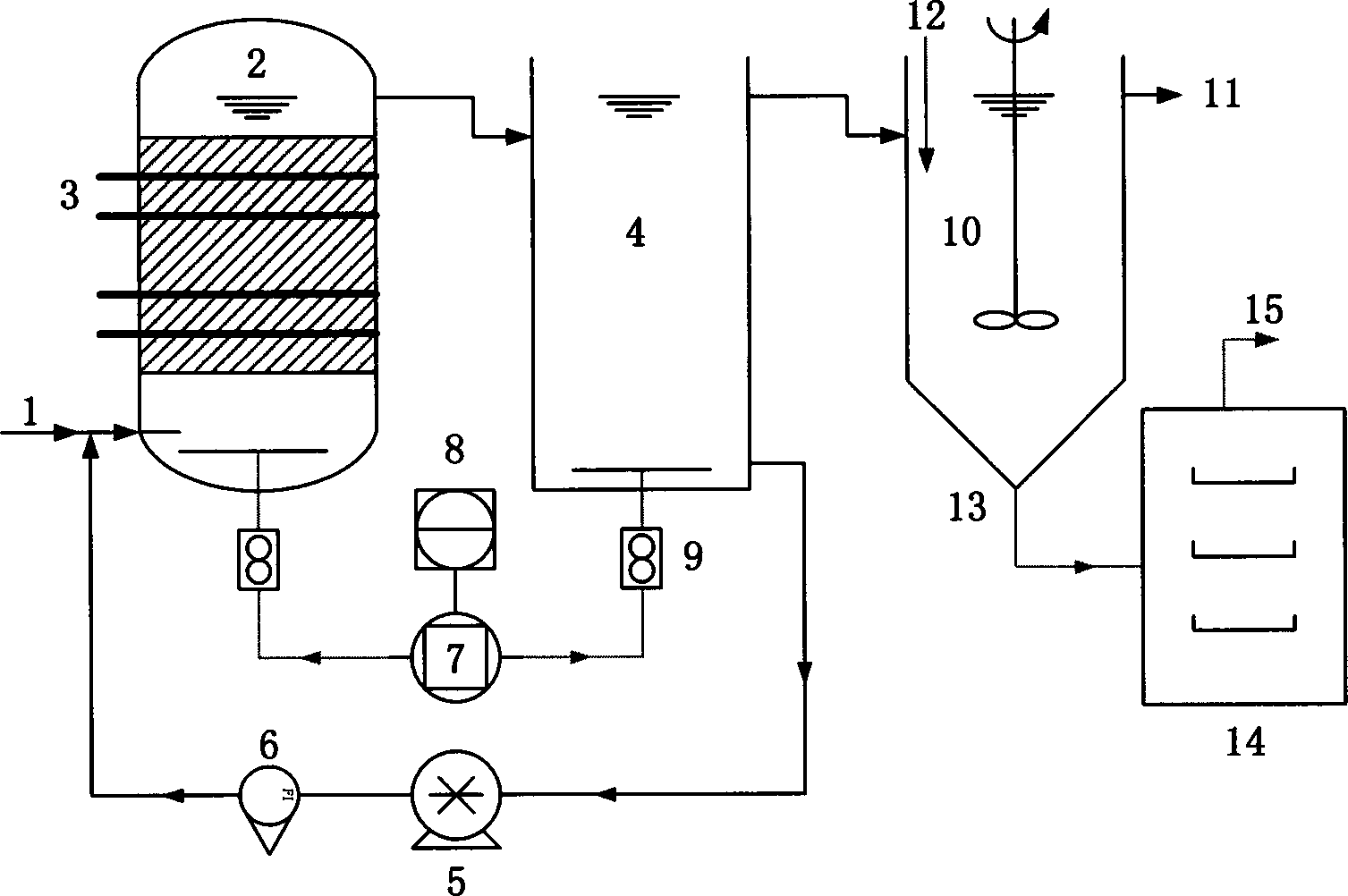
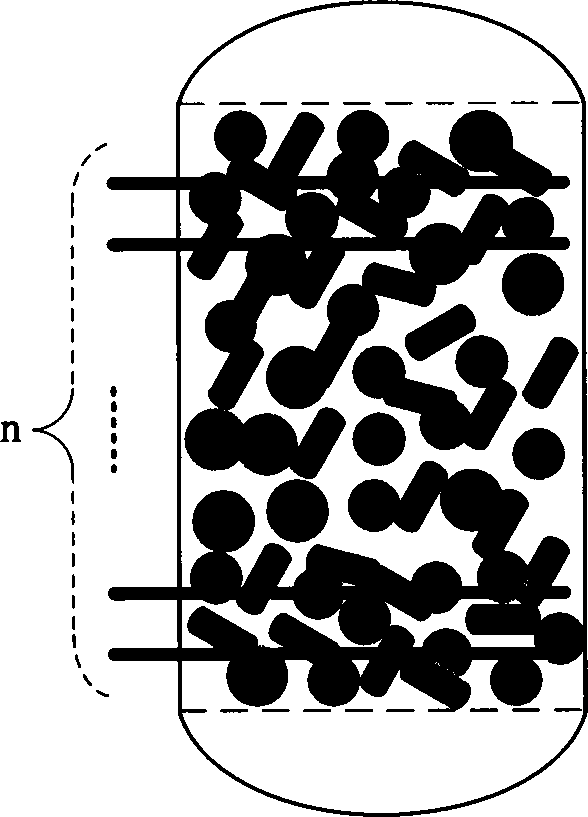
[0022] Using an integrated micro-electrolysis reactor to treat the actual leather dye wastewater of an enterprise in Tianjin, the water quality is: the appearance is dark black, the chroma is ≈100,000 (diluted multiples); the salt content (calculated as NaCl) = 9.0-10.0%; COD = 4200.0~4500.0mg / L; pH=5.5~6.0; SS=1800.0~1900.0mg / L. Under the technical conditions of solid-liquid ratio = 50.0%, aeration rate = 80.0L / h, reflux rate = 16.0L / h, load voltage = 20.0v and residence time = 24h, the effluent water quality: chromaticity ≈ 200 (diluted times), the chromaticity removal rate is 99.8%; COD is within 700.0mg / L, the dye removal rate reaches 83.9%; energy consumption (EC COD )≈21.9(kWh kg -1 COD). The effluent can enter the follow-up biochemical pool to complete the advanced treatment and discharge up to the standard.
Embodiment 2
[0024] The actual wastewater of a dyestuff company in Tianjin was treated with an integrated micro-electrolysis reactor. The water quality is as follows: the appearance is dark red, the chroma is ≈2000 (dilution factor); the salt content (calculated as NaCl) is ≈5.0%; COD=1500.0~1600.0 mg / L; pH=5.5~7.5; SS=0.38~0.44mg / L. Under the technical conditions of solid-liquid ratio = 50.0%, aeration rate = 80.0L / h, return flow rate = 16.0L / h, load voltage = 9.0v and residence time = 5h, the effluent water quality: chromaticity ≈ 50 (diluted times), the chromaticity removal rate reaches 97.5%; COD is within 185.0mg / L, the dye removal rate reaches 88.1%; energy consumption (EC COD )≈2.18(kWhkg -1 COD). The effluent can be discharged after moderate dilution or enter the subsequent membrane separation unit for reuse.
Embodiment 3
[0026] The actual wastewater of a dyestuff company in Tianjin was treated with an integrated micro-electrolysis reactor. The water quality is: dark red in appearance, chroma ≈130,000-140,000 (dilution multiple); salt content (calculated as NaCl) ≈13.0-14.0%; COD =28,000.0~30,000.0mg / L; pH=5.0~6.0; SS=800.0~900.0mg / L; TDS=1700.0~1800.0mg / L. Under the technical conditions of solid-liquid ratio = 50.0%, aeration rate = 80.0L / h, reflux rate = 16.0L / h, load voltage = 18.0v and residence time = 42h, the effluent water quality: chromaticity ≈ 500 (diluted times), the chromaticity removal rate reaches 99.5%; the COD is within 10050.0mg / L, the dye removal rate reaches 64.1%; the energy consumption (EC COD )≈47.9(kWh kg -1 COD). After the effluent is diluted, it enters the subsequent membrane separation unit for advanced treatment.
[0027] It can be seen that, compared with the current micro-electrolysis or enhanced micro-electrolysis method, the new method of pretreatment of high-s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com