Preparation method of powder high-speed steel material
A high-speed steel and powder technology, which is applied in the field of powder high-speed steel material preparation, can solve the problems of reduced mechanical properties, complex sintering process, high sintering temperature, etc., and achieve the effects of lower sintering temperature, easy process control, and expanded sintering temperature range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
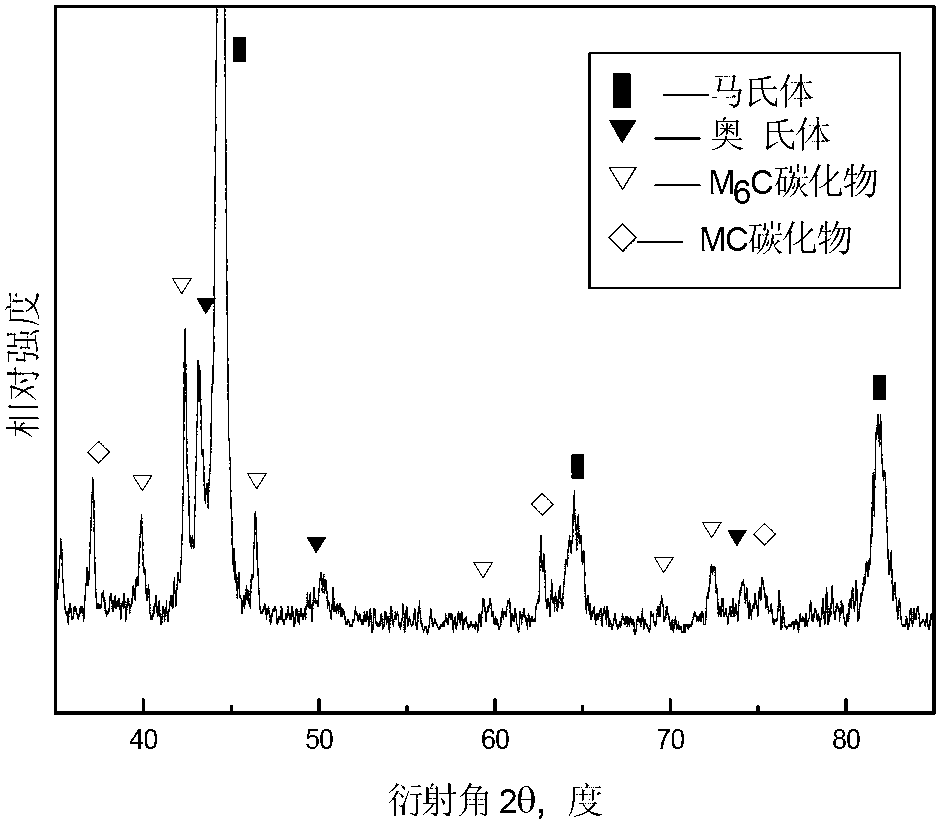
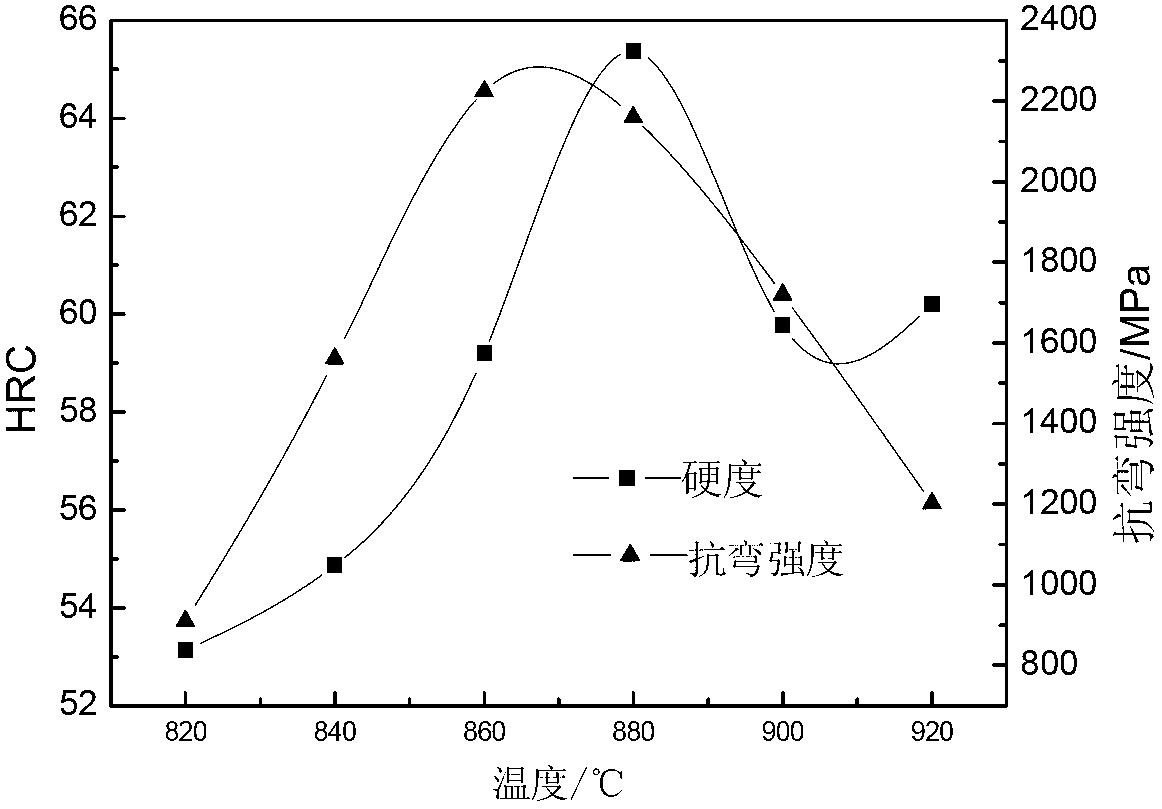
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, powder high-speed steel is prepared according to the following steps:
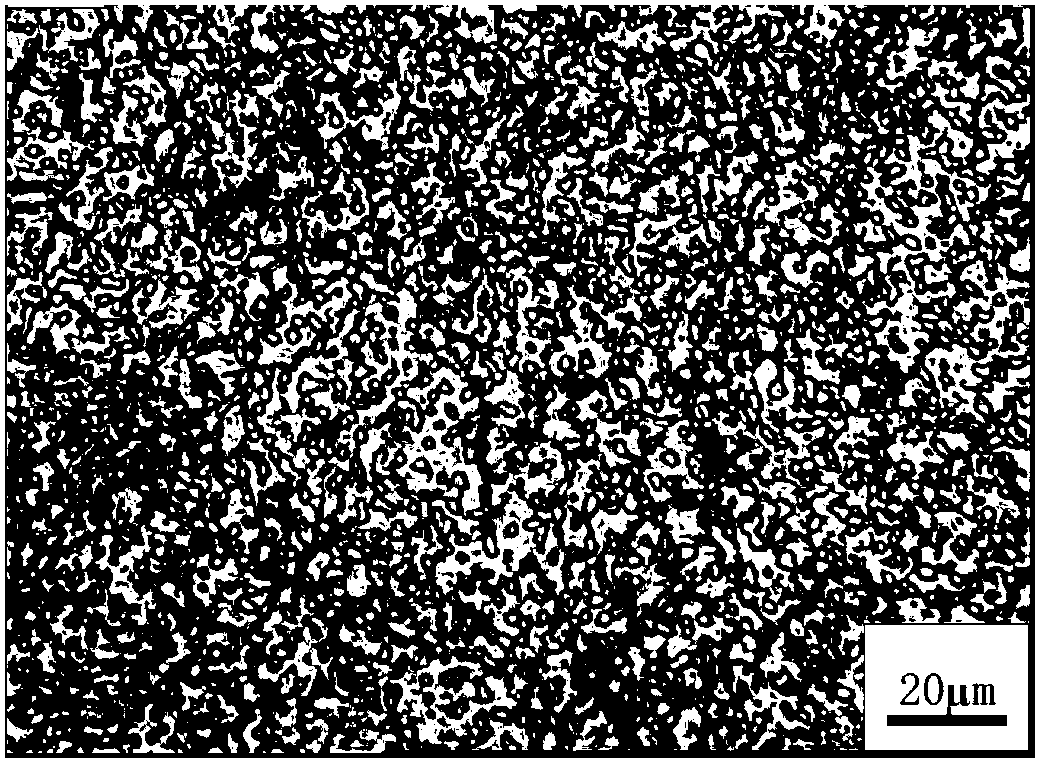
[0024] (1) The master alloy powder and additives were placed in a planetary mixer and mixed for 8 hours at a speed of 120 rpm. The master alloy is M3:2 high-speed steel powder with low carbon content; the additive is carbon powder, and its content relative to the master alloy is 0.15-0.25wt% of carbon powder in terms of mass percentage.
[0025] (2) The high-speed steel powder is vacuum sintered in a spark plasma sintering furnace at a sintering temperature of 870-890°C for 10 minutes. The vacuum sintering process is divided into four stages: ① After applying a pressure of 30MPa to the powder, vacuumize the vacuum to lower than 10Pa, then raise the temperature to 500℃ at a faster heating rate (average 20℃ / min); ② use 10℃ / min The heating rate is raised to the sintering temperature; ③keep at the sintering temperature for 10 minutes (the allowable temperature change o...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: The differences between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 are: no carbon powder is added, and the sintering temperature is 890-910°C. Others are the same as in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3 Embodiment and Embodiment 1 :,;1,3,,550℃。 other and Embodiment 1 。 Embodiment 59~62HRC。 Embodiment 4
[0029] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the high-speed steel is directly placed in a box-type tempering furnace for tempering after sintering, and the quenching heat treatment process is omitted; the tempering time is 1 hour, the tempering times are 3 times, and air cooling , the tempering temperature is chosen to be 550°C. Others are the same as in Embodiment 1. The implementation hardness is reduced to 59-62HRC. Embodiment four: the difference between this embodiment and embodiment three is: when cooling with the furnace, nitrogen gas is charged with a pressure of 0.04 MPa to accelerate cooling. Others are the same as the third embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com