Method for detecting sulfamethazine in animal-derived food
A sulfamethazine, animal-derived technology, applied in the fields of food safety testing and analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of high price and poor selectivity, and achieve the effects of low cost, small sample volume and good adsorption performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Preparation of sulfamethazine molecularly imprinted polymer and preparation of solid phase extraction column:
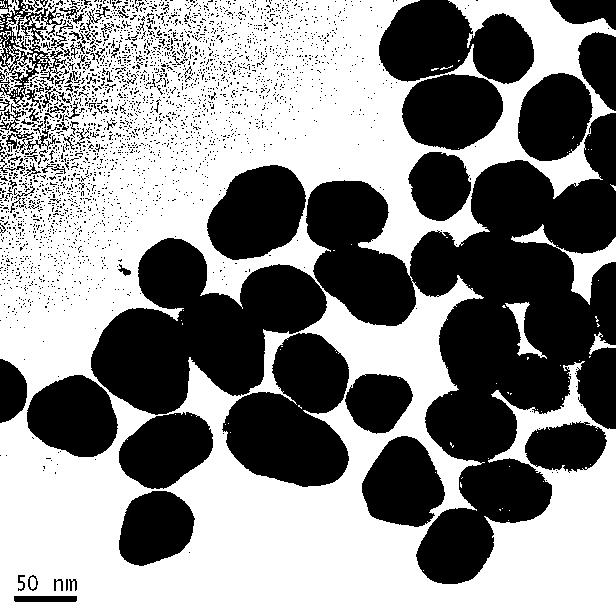
[0039] In a glass container, the template molecule sulfamethazine (SM2) 0.278 g (1 mmol), the functional monomer methacrylic acid (MAA) 0.35 mL (4.0 mmol), the cross-linking agent ethylene glycol dimethyl diacrylate (EGDMA) 3.85mL (20.0 mmol) was mixed uniformly according to the molar ratio of 1:4:20, and added to 10 mL of porogen acetonitrile together, and 50 mg of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) was added, and ultrasonic treatment was performed for 10 Minutes, purged with nitrogen for 10 minutes, sealed, placed in a water bath at 60°C, and thermally initiated polymerization for 24 hours to obtain a block polymer.
[0040] The resulting massive polymer is ground by a mortar, passed through 200 mesh and 400 mesh sieves, the resulting polymer particles are in the range of 35-75 microns, wrapped with filter paper and placed in a Soxhlet ex...
Embodiment 2
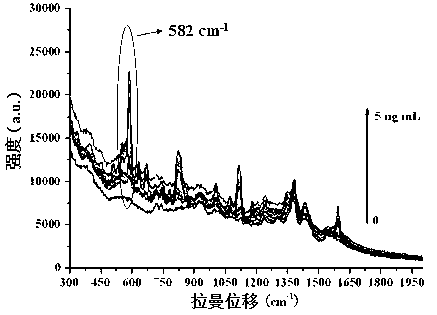
[0042] Example 2: Extraction and Raman-enhanced detection of sulfamethazine in fish samples:
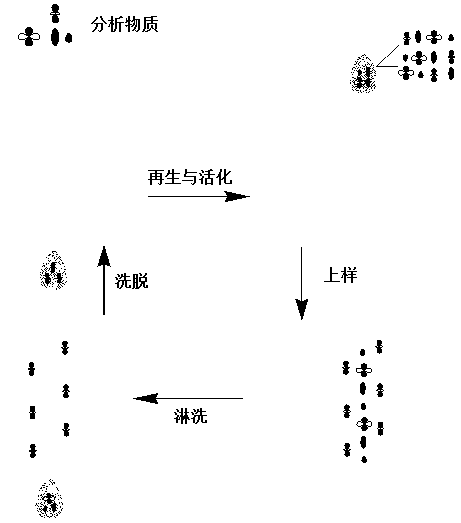
[0043] 1. Sample pretreatment and sulfamethazine extraction
[0044] The edible part of the fish sample was taken, chopped, homogenized, and stored frozen at -18°C. During the test, after the frozen sample is equilibrated to room temperature, accurately weigh 5 g of the sample, add 5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate and 25 mL of ethyl acetate, vortex for 2 minutes, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 2 minutes, and collect the ethyl acetate. ester solution. Repeat the extraction with ethyl acetate once more, combine the ethyl acetate solutions, and distill under reduced pressure at 30°C until nearly dry. Add 10% methanol to dissolve, add 3 mL of n-hexane, vortex for 2 minutes, transfer to a centrifuge tube; repeat the dissolving process, combine the mixed solution in a centrifuge tube, vortex for 2 minutes, discard n-hexane, then add 6 mL of n-hexane and repeat the operation once. Add ultrap...
Embodiment 3
[0053] A method for detecting sulfamethazine in food of animal origin, said method comprising the following steps:
[0054] (1) Synthesize the molecularly imprinted material of sulfamethazine by using the method of bulk polymerization: template molecule sulfamethazine (SM2), functional monomer methacrylic acid (MAA), cross-linking agent B in a glass container Glycol dimethyl diacrylate (EGDMA) is mixed evenly according to the molar ratio of 1:4-10:20-50, and added to the porogen together, and the initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) is added, and ultrasonic treatment For 10 minutes, pass nitrogen gas to remove oxygen for 10 minutes, seal, place in an oil bath at 60°C, and heat-initiate polymerization for 20 hours to obtain a block polymer; grind the obtained block polymer through 200 mesh and 400 mesh The obtained polymer particles are 35-75 microns, wrapped in filter paper and placed in a Soxhlet extraction reactor, extracted with methanol-acetic acid (9 / 1, v / v) mixture f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com