Cultivation and separation method for taxus stem cells
A technology of stem cell culture and separation method, which is applied in the field of plant stem cell separation, and can solve problems such as difficult super-large-volume culture, weak resistance to stress, and cell line degradation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
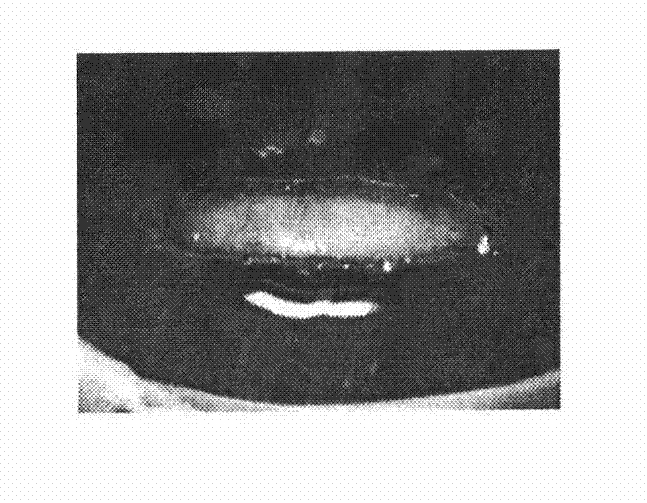
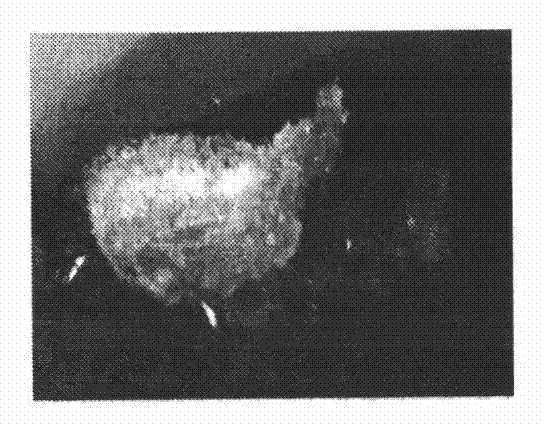
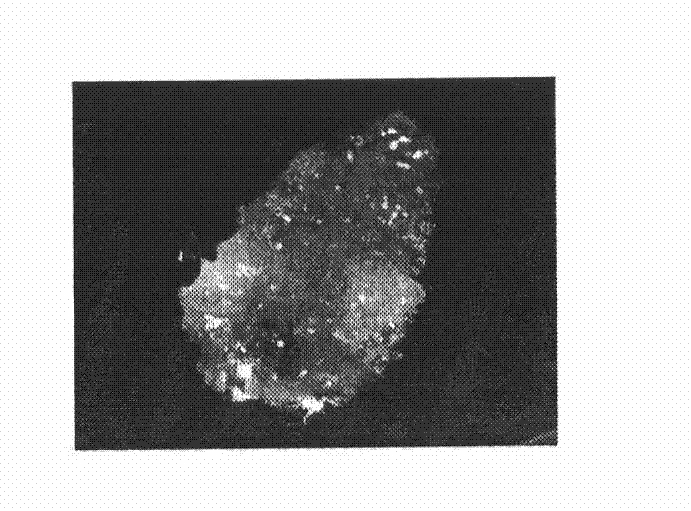
[0012] Embodiment 1: the method for cultivating and separating the stem cells of Taxus chinensis of the present invention, at first the twigs of the year with a diameter of 1 cm were sterilized with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 10 minutes, and then cut off the twigs containing Sections of exogenous cells including skin, phloem and cambium (see appendix figure 1 ), placed on B5 medium containing 0.5 mg.L-1 picloram and 0.5 mg.L-1 naphthaleneacetic acid, and cultured at 25°C in the dark. Due to the rapid division of cambium stem cells, the cambium stem cell mass naturally separates from the rest of the exogenous body (see appendix figure 2 ), this stem cell mass has a dense texture and a smoother surface. Two weeks later, the explants whose cambium proliferated significantly were taken out, and the cambium stem cells were separated and transferred to the subculture medium for culture (see appendix image 3 ). The subculture medium is B5 medium containing 0.5mg.L-1 picloram and...
Embodiment 2
[0013] Embodiment 2: First, the diameter of 1 centimeter of Taxus chinensis is sterilized with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 10 minutes, and then the exogenous shoots including periderm, phloem and cambium are cut off from the shoots. Body slices were placed on B5 medium containing 0.2 mg.L-1 picloram and 1.5 mg.L-1 naphthalene acetic acid, and cultured at 25°C in the dark; after two weeks, the explants with obvious proliferative cambium were taken out and separated The cambium stem cells were transferred to the subculture medium for culture; the subculture medium was B5 medium containing 0.2 mg.L-1 picloram and 1.5 mg.L-1 naphthalene acetic acid, which was subcultured once every two weeks. A large number of stem cells can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0014] Embodiment 3: at first the twig of the year with a diameter of 1 cm was treated with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 10 minutes, and then the exogenous twigs including the periderm, phloem and cambium were cut off from the twig. Body slices were placed on B5 medium containing 2.0 mg.L-1 picloram and 0.2 mg.L-1 naphthaleneacetic acid, and cultured at 25°C in the dark; after two weeks, the explants with obvious proliferating cambium were taken out and separated The cambium stem cells were transferred to the subculture medium for culture; the subculture medium was B5 medium containing 2.0 mg.L-1 picloram and 0.2 mg.L-1 naphthalene acetic acid, which was subcultured once every two weeks. A large number of stem cells can be obtained.
[0015] In addition, micromanipulation can be considered to isolate shoot apex growth points, root apex growth points or stem cells that form layers, and then directly culture the isolated stem cells in vitro. However, the operation of this scheme ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com