Method for adjusting the rotor position of an electrically commutated motor
A technology of rotor position and rotor, which is applied in the direction of electronically commutated motor control, electronic commutator, monitoring commutation, etc., can solve the problem of discontinuous and strong amplitude torque change, and achieve the effect of reducing computing power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
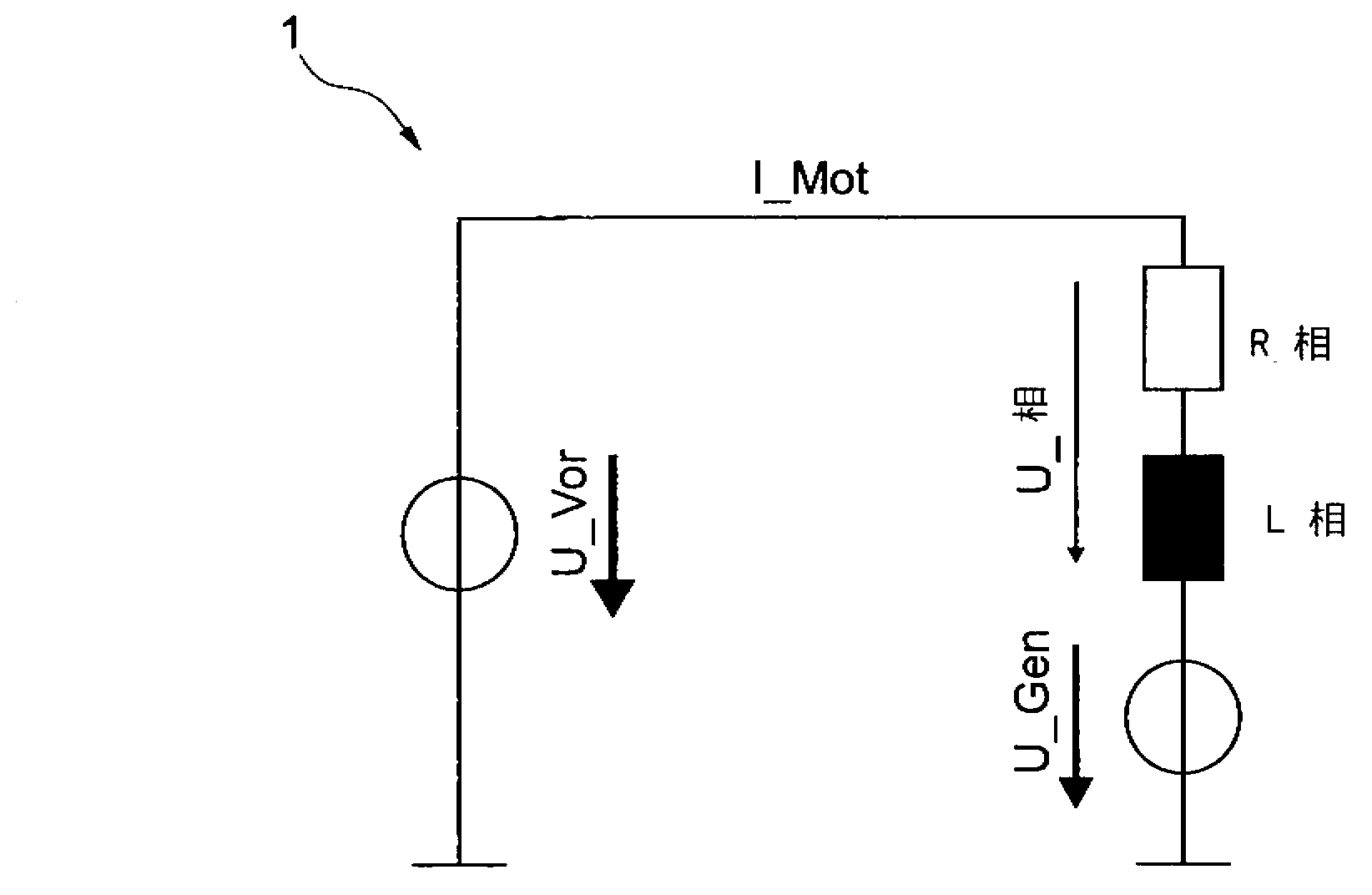
[0023] figure 1 An alternative circuit diagram is shown for a phase of an electrically commutated electric machine 1 , which is designed as a brushless direct current motor (BLDC motor). Such electric machines are used, for example, to actuate clutches in motor vehicles. This is an alternating current machine which is operated with an alternating current which is induced by three alternating voltages shifted by 120° and which generates a rotating field. The electric machine has three AC coils, one of the three AC voltages being applied to each coil. The connections of the coils are referred to here as phases. Here, each coil is an impedance, which is characterized by an L-phase (inductive reactance) and an R-phase (reeller widerstand).
[0024] At high rotational speeds, the motor current I-Mot lags behind the motor voltage U-Gen due to the motor inductance L-phase. In order to determine the position of the motor rotor with an accuracy of at least 1 degree, the motor curre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com