A sintering method for an oxide superconducting powder rod and a method for preparing a superconducting wire rod by using the powder rod sintered by using the sintering method
A sintering method and technology for superconducting wire rods, which are used in cable/conductor manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc. to achieve the effects of low defect rate, high critical current density, and high filling factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The superconducting precursor powder referred to in the present invention contains five metal elements of bismuth, lead, strontium, calcium and copper and has a stoichiometric ratio Bi:Pb:Sr:Ca:Cu=1.9:0.3:2:2.1:3 Superconducting powder prepared by solid state reaction method or spray drying method.
[0032] Using the above superconducting precursor powder as raw material, according to figure 1 The method steps shown in the flow chart of manufacturing oxide superconducting wires are to prepare Bi2223 superconducting wires. The first is the pretreatment of the precursor powder. Specifically, the precursor powder is roasted at 800°C in the atmosphere for 10 hours, and then ground to reduce the particle size of the powder to 1-2 μm. The phase composition of the powder after pretreatment is Bi2212(Bi2Sr2Ca1Cu2Ox) The main phase contains a small amount of CaPbO4, 3321, CuO, 14:24AEC, 1:1AEC and other second phases. Then the powder is pressed into a powder rod with a diamete...
Embodiment 2
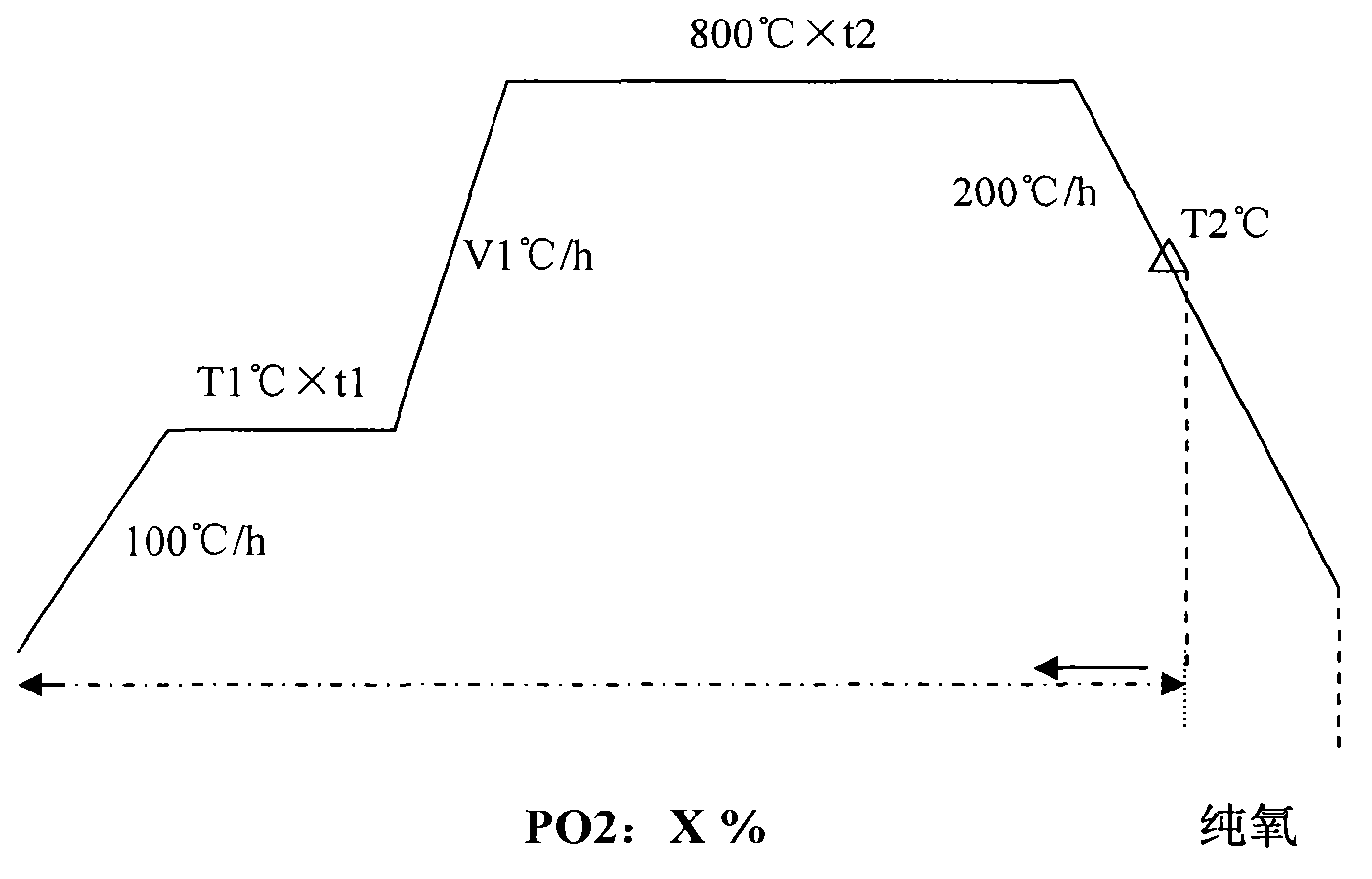
[0035] Obtain powder rod by the method identical with embodiment 1, carry out powder rod sintering then, control atmosphere in the furnace is 5% O2 / N2 balance gas, with the rate of 100 DEG C / hour heating up, be 400 DEG C to T1 and carry out insulation, The holding time t1 is 2 hours. After the holding time, until 800°C, use V1 to raise the temperature at a rate of 200°C / hour, and at 800°C, keep holding time t2 for 5 hours, then cool down to 500°C at 200°C / hour, and The atmosphere in the furnace is switched to 99.999% high-purity oxygen, and then the temperature is lowered to 100°C at 600°C / hour, and the furnace is taken out, and then single-core, multi-core drawing, preliminary rolling and deformation heat treatment are carried out according to the same follow-up steps as in Example 1. Made (Bi, Pb) 2223 high temperature superconducting tape.
Embodiment 3
[0037] According to the same method as in Example 1, the powder rods were prepared, and then the powder rods were sintered. The atmosphere in the furnace was controlled to be 8.5 O2 / N2 balance gas, and the temperature was raised at a rate of 100°C / hour, and the temperature was kept at 300°C until T1 was kept. The time is 5 hours. After the heat preservation is over, until 800°C, use V1 to raise the temperature at a rate of 100°C / hour, and keep it at 800°C for 5 hours, then cool down to 650°C at 200°C / hour, and switch the atmosphere in the furnace to 99.999 % of high-purity oxygen, then cooled to 100°C at 600°C / hour, and then released from the furnace, and then carried out single and multi-core drawing, preliminary rolling and deformation heat treatment according to the same subsequent steps as in Example 1 to make (Bi, Pb) 2223 high temperature superconducting tape.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com