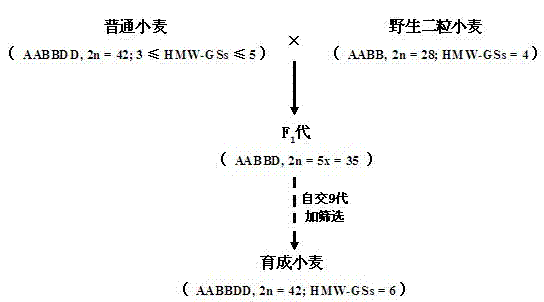
Cultivation method of common wheat capable of stably expressing six HMW-GS (High Molecular Weight-Glutenin Subunits)
A technology of HMW-GS and stable expression, applied in the field of common wheat cultivation, can solve the problems of lack of molecular structure analysis, lack of stable expression, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
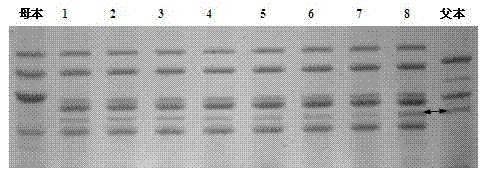
[0038] Example 1 SDS-PAGE detection to obtain HMW-GS results
[0039] Extraction solution composition: 62.5 mM Tris-HCl (pH=6.8), 10% (v / v) glycerol, 2% (w / v) SDS, 0.002% (w / v) bromophenol blue, 3.0% (v / v) β-mercaptoethanol;
[0040] Resolving gel buffer (2.5 L): dissolve 378g Tris, 25g SDS, 95g boric acid, add water to make up to 2.5L, pH value is 8.9.
[0041] Stacking gel buffer: 1.0 M Tris-HCL, pH=6.8, 10% (W / V) SDS.
[0042] Electrophoresis buffer: dilute the separation gel buffer 10 times
[0043] Polyacrylamide gel composition:
[0044] Stacking Gel (3%) Separating Gel (10%)
[0045] 40% acrylamide, ml 0.375 2.5
[0046] 2% methylene bisacrylamide, ml 0.2 0.52
[0047] Resolving gel buffer, ml 0 1
[0048] Stacking gel buffer, ml 0.62 0
[0049] 10%SDS (W / V), ml 0.04 0
[0050] 10% (W / V) ammonium persulfate, ml 0.05 0.09
[0051] TEMED, μl 5 4.2
[0052] h 2 O, ml 3.7 5.9
[0053] Use amphiphilic glutenin subunits as a control, electrophoresis at a cons...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Chromosome number detection in somatic cells
[0058] The seeds of the hybrid progeny were germinated at a constant temperature of 25°C, and the roots were taken, and the root tips were frozen in an ice-water mixture for 24 hours. Carnot's Ⅰ fixative solution (alcohol: glacial acetic acid = 3:1) was fixed for 24 h and then transferred to 70% ethanol for storage. Put the root tip in 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid and dissociate it in a constant temperature water bath at 60 °C for 6-8 minutes, stain with Schiff reagent, and perform regular compression with modified phenol fuchsin to observe the chromosomes of somatic cells. Observe 50 cells, statistical data.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Genomic DNA extraction
[0060] Genomic DNA of common wheat, wild emmer and hybrid offspring was extracted by 2×CTAB method, and the extraction steps were as follows:
[0061] (1) Take 2 g of fresh young leaves, grind them into fine powder with liquid nitrogen, add 2×CTAB extract (2% CTAB, 1.4 M NaCl, 0.1 M Tris-HCl pH=8.0, 0.1 M EDTA pH=8.0, add 2% β-mercaptoethanol) 15 ml before use and mix well;
[0062] (2) Place in a water bath at 65°C for 30-45 minutes, during which time shake gently to mix. After cooling to room temperature, add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), mix gently until the supernatant becomes milky, and centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 min.
[0063] (3) Take the supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol, and ice-bath for 2 h to precipitate DNA;
[0064] (4) Hook up the DNA, wash it twice with 70% ethanol, wash it once with absolute ethanol, and dissolve the air-dried DNA in an appropriate amount of 1×TE solution wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com