New botrytis cinerea gene related to pathogenicity and application of new botrytis cinerea gene
A botrytis cinerea and gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of botrytis cinerea that are prone to drug resistance, environmental pollution, pesticide residues, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
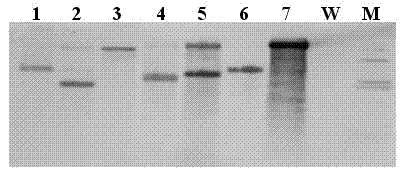
[0033] Example 1 Bcdp1 Obtaining of Gene T-DNA Insertion Mutants
[0034] The mutant involved in the present invention is obtained by Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation method (ATMT).
[0035] 1.1 Cultivation of Agrobacterium. Pick a single colony of Agrobacterium and place it in LB liquid medium (containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin and 50 μg / mL rifampicin), shake it at 120 rpm at 28°C for 48 h, take 1 mL of the bacterial liquid at 4°C Centrifuge at 10000 rpm for 1 min and discard the supernatant. Wash twice with induction medium (IM), dilute to OD600≈0.15 with IM medium, add AS at a final concentration of 200-400 μM, and activate at 28°C for about 7 h at 180 rpm.
[0036] 1.2 Collection of conidia of Botrytis cinerea. Wash the conidia of Botrytis cinerea from the PDA plate cultured for about 7 days with 10 mL of sterilized distilled water, filter through two layers of gauze, count with a hemocytometer, and dilute the spore concentration with sterile water to 10...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Screening and Stability Detection of Pathogenicity Loss Mutants
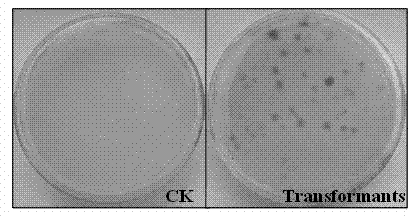
[0040] The T-DNA insertion mutant library of Botrytis cinerea was screened by in vitro fruit inoculation. First select fresh tomatoes of the same size and scrub the fruit with 75% alcohol for surface disinfection. At the same time, the rejuvenated Botrytis cinerea wild-type BC22 and transformants were cultured for 3 days, and the colonies were punched out with a puncher to get a 5 mm-diameter plate from the edge of the colony, and they were symmetrically inoculated on tomato fruits (without wounds). The tomato fruit was put into a moisturizing tank, and the condition was investigated after 6 days. The difference in pathogenicity of the strains was evaluated according to the size of the lesion area. The mutant Bct89 that lost the pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea was subcultured in PDA medium (containing hygromycin 100 μg / mL) for 15 generations, and the pathogenicity of each generation was te...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Biological studies of mutants
[0042] Botrytis cinerea wild-type strain BC22 and mutant strain Bct89 were rejuvenated. After rejuvenation, they were respectively inoculated on PDA medium. After 3 days of cultivation, the wild-type and mutant strains with a diameter of 9 mm were punched on the edge of the colony. , cultured at 20°C for 10 days, observed the colony shape, color, measured growth rate, spore production, etc.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com