Method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of cattle PPARGC1A genes
A single nucleotide polymorphism and nucleotide technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as lack of research and gaps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
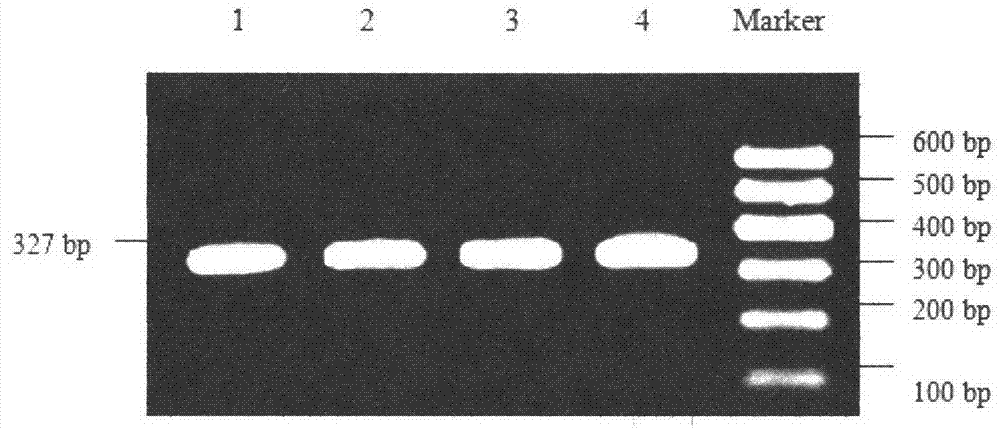
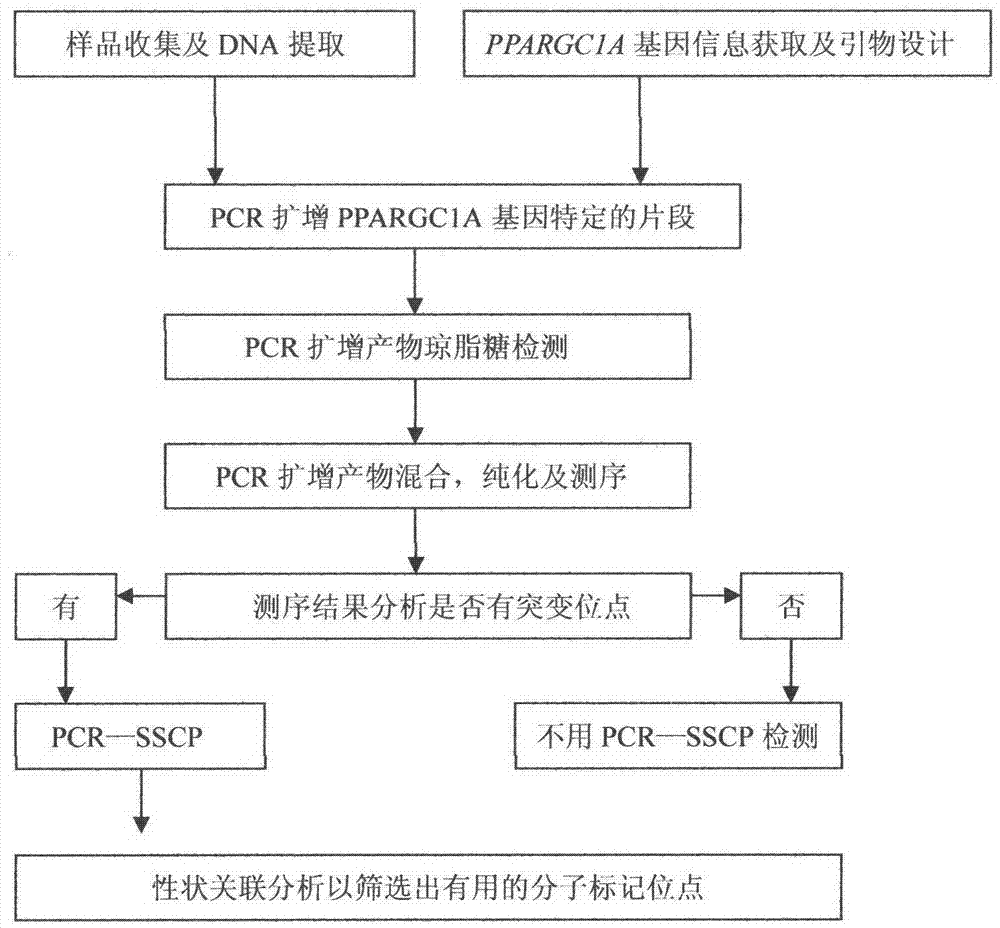
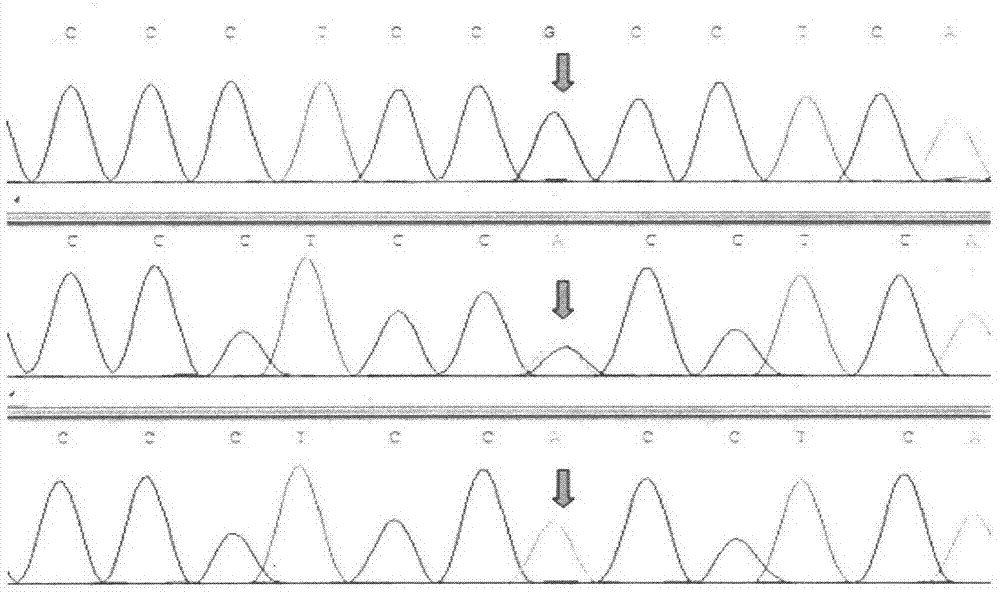
[0026] In the present invention, primers are firstly designed according to the PPARGC1A gene sequence (GenBank Accession No. NC_007304) published by NCBI, and the genomic DNAs of three cattle breeds are respectively used as templates for PCR amplification, and the PCR products are mixed, purified, and sequenced. Then, carry out sequencing map analysis and sequence comparison to screen out SNP sites; secondly, carry out PCR-SSCP detection of polymorphic sites in the tested population; finally, carry out statistical analysis of population genetics according to the genotypes detected in the population The association analysis with growth traits screened out the molecular markers closely related to the growth traits of cattle. The present invention will be described in detail below, which is an explanation of the present invention rather than a limitation.
[0027] Cloning of Partial DNA Sequence of PPARGC1A Gene of I Local Yellow Cattle Breed
[0028] 1. Cattle sample collection...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com