Oxide superconductor and production method for same
A technology of oxide superconducting layer and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of cable/conductor manufacturing, superconducting magnet/coil, chemical instruments and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as increased resistance and decreased critical current characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1)
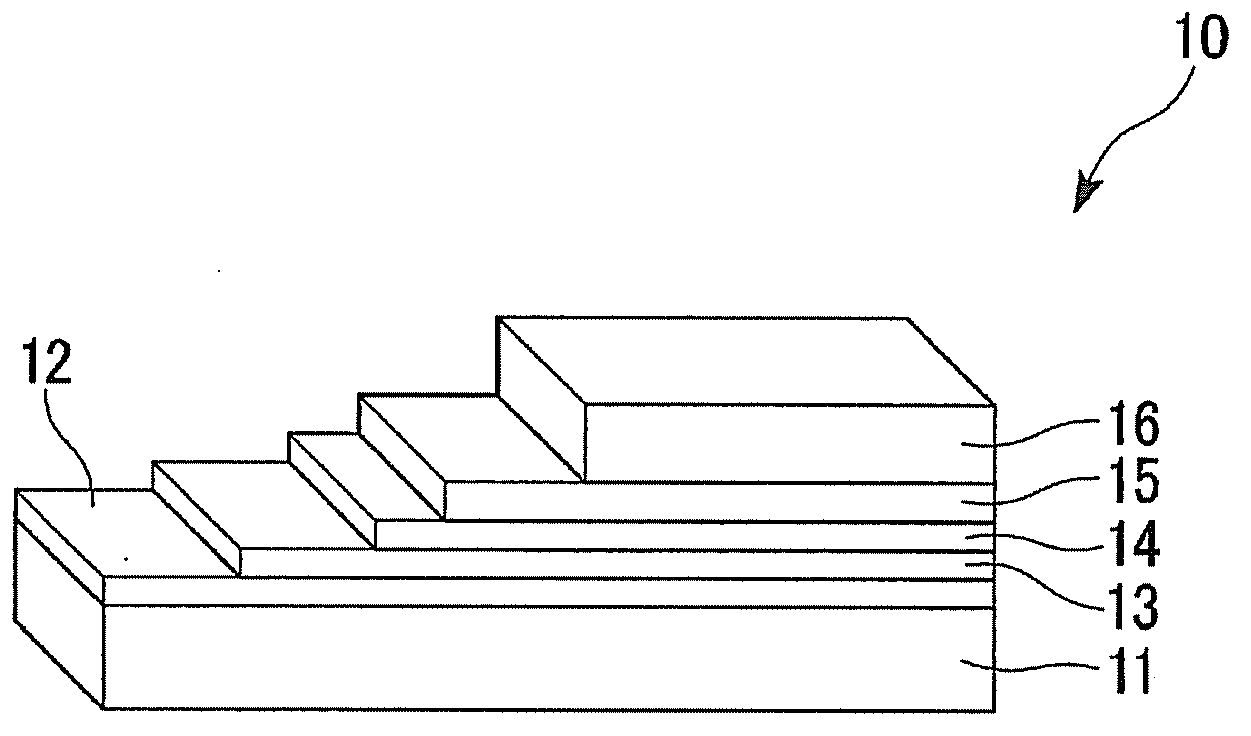
[0082] Using the sputtering method, Al was applied to a strip-shaped substrate made of HASTELLOY C276 (Haynes International, Inc. registered trademark) with a width of 5 mm and a thickness of 0.1 mm. 2 o 3 (Anti-diffusion layer; film thickness 150nm) film formation. Next, use ion beam sputtering method to make Y 2 o 3 (bed layer; film thickness 20nm) film formation. Next, MgO (middle layer; film thickness: 10 nm) was formed on the bed layer by ion beam assisted deposition (IBAD method). Then, the CeO 2 (Cover layer: film thickness 500nm) film formation.
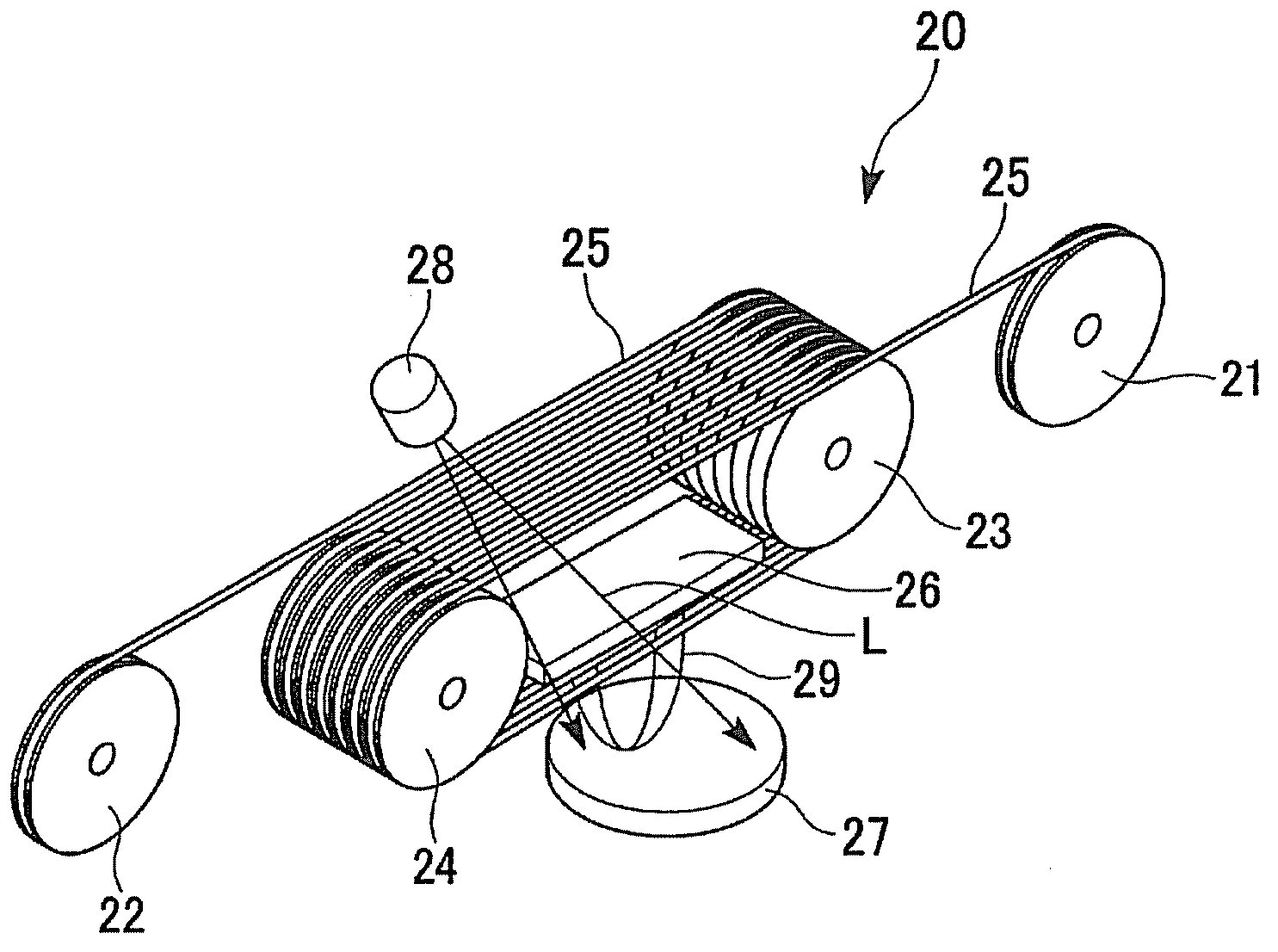
[0083] Next, use figure 2 The shown laser evaporation device 20 utilizes the pulsed laser deposition method (PLD method), on Ce 2 An RE123-based oxide superconducting layer with a film thickness of 1.0 μm was formed on the O layer, and Ag (stabilizing layer) with a thickness of 10 μm was sputtered on the oxide superconducting layer to prepare an oxide superconductor. It should be noted that the film formation of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0090] (Example 2: Tb 4 o 7 Incorporation studies)
[0091] As a target, use the GdBa 2 Cu 3 o y Tb was mixed into the powder in Table 1 4 o 7 The oxide superconductors of Samples 1 to 6 were produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the oxide superconducting layer was formed by sintering the sintered body obtained by sintering the powder.
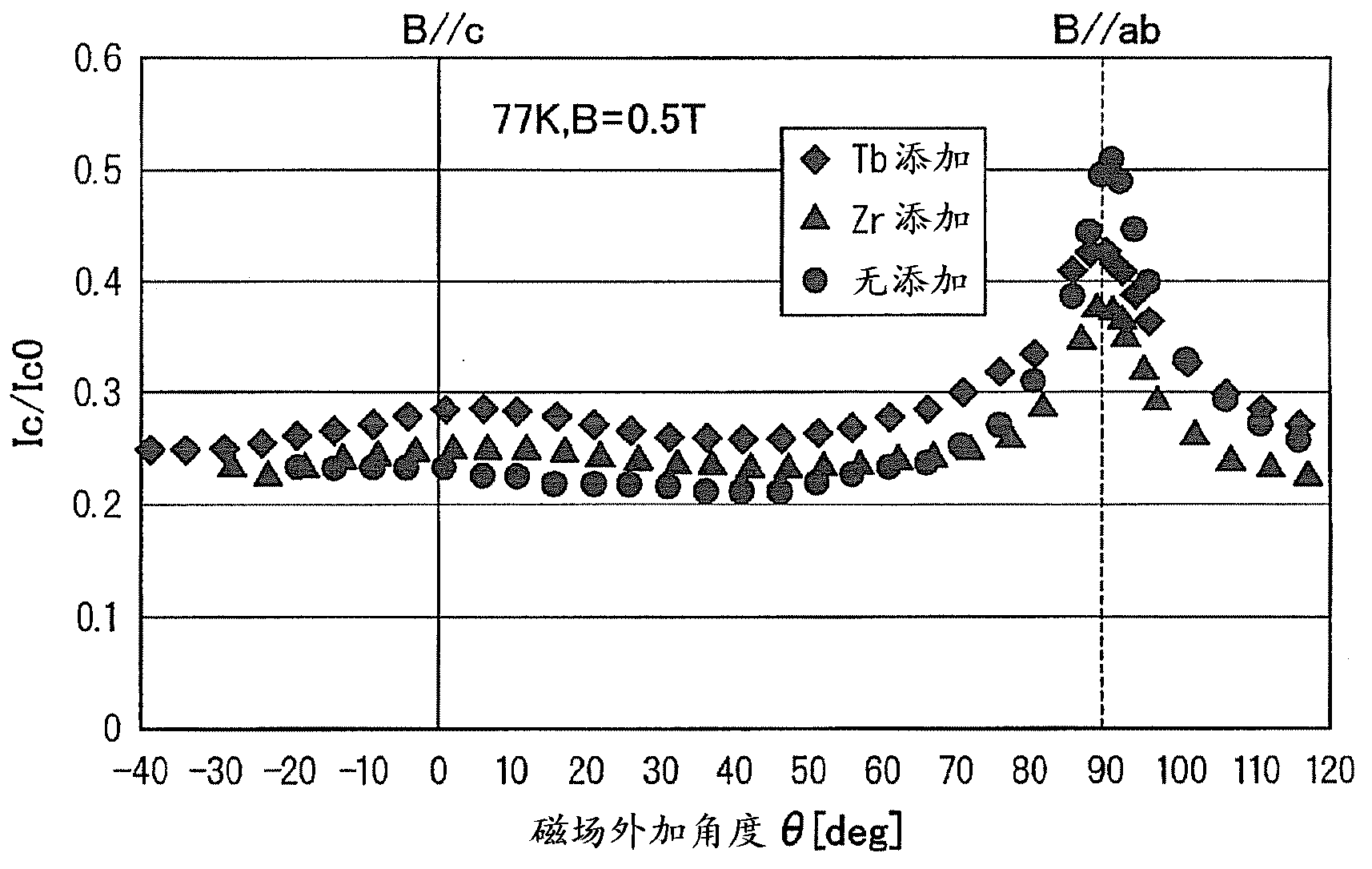
[0092] The critical current Ic0 of the obtained oxide superconductors of Samples 1 to 6 was measured at the liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) and without a magnetic field (0T). The critical current Ic was also measured when a magnetic field of 0.5T was applied at a magnetic field angle of θ=45° (45° to the c-axis) at the temperature of liquid nitrogen (77K). For the oxide superconductors of Samples 1 to 6, the rate of change of critical current Ic / Ic0 at a magnetic field application angle θ=45° was calculated. Record the results in Table 1.
[0093] Table 1
[0094]
[0095] As can be seen from the results shown ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com