Method for improving write margin of static random access memory (SRAM)
A static random, write redundant technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as reducing hole mobility, increase equivalent resistance, and improve write redundancy , the effect of reducing the potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in combination with principle diagrams and specific operation examples.
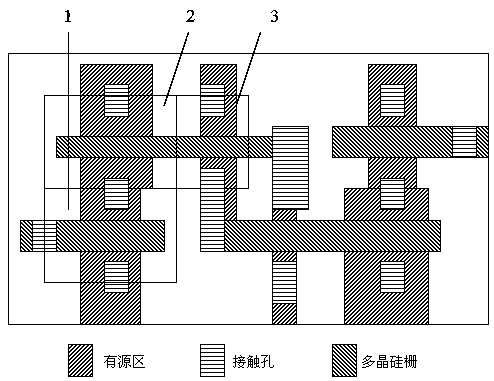
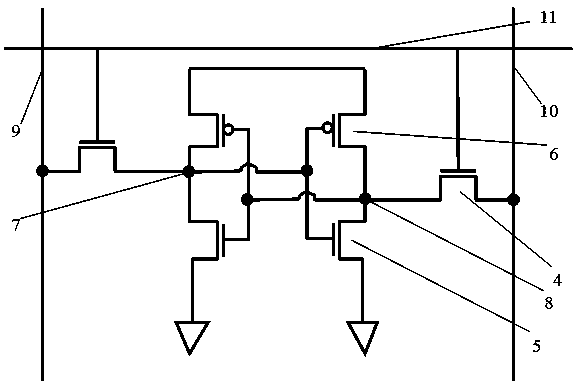
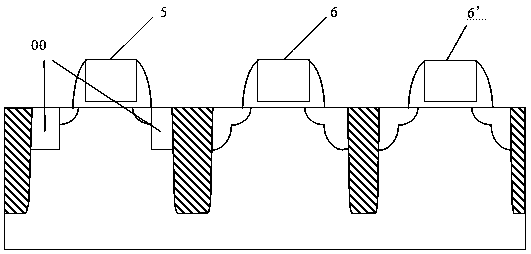
[0025] Such as Figure 4 Shown, the present invention improves the method for SRAM writing redundancy, and it comprises the following steps:
[0026] A SRAM substrate 0 is provided, and the substrate 0 includes sequentially adjacent NMOS regions 5, a first PMOS region 6 and a second PMOS region 6', and the first NMOS region 5 is used to prepare common NMOS devices, control transistors and pull-down tube, the first PMOS area is used to prepare a common PMOS device, and the second PMOS area is used to prepare a pull-up tube;
[0027] A shallow trench isolation region (STI) is respectively formed between the NMOS region 5, the first PMOS region 6 and the second PMOS region 6';
[0028] Simultaneously, a silicon carbide epitaxial formation process that generates tensile stress is adopted for the NMOS region 5 and the second PMOS region 6', and si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com