Method for preparing plant-based polyether polyol by straw liquefaction
A technology based on polyether and polyol, which is applied in the field of straw liquefaction to prepare plant-based polyether polyol, which can solve the problems of complex liquefaction products, slow liquefaction speed, unfavorable utilization, etc., to improve liquefaction efficiency, increase contact area, and benefit The effect of the osmotic reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
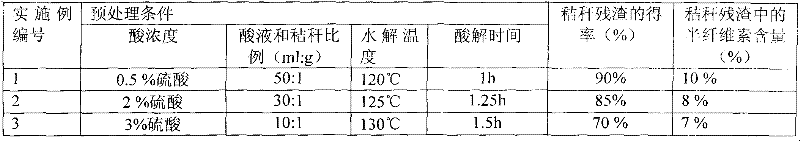
[0020] Crush the corn stalks to 2-3cm first, then remove the stone and sand, dry the moisture of the stalks at a temperature of 80-100 ℃ to below 5%, and finally crush the dried corn stalks to the particle size for the second time with a grinder Spare below 0.3mm. Add 0.5% dilute sulfuric acid to the crushed straw and hydrolyze it at 120°C to 130°C for 1 hour. The ratio of the volume of dilute sulfuric acid used (ml) to the mass of straw (g) is 50:1; after the reaction, filter the obtained solid After the material is dried, it is the straw residue of acid hydrolysis. The quality of the straw residue is 90% of the original straw, and the measured hemicellulose content in the straw residue is 10%.
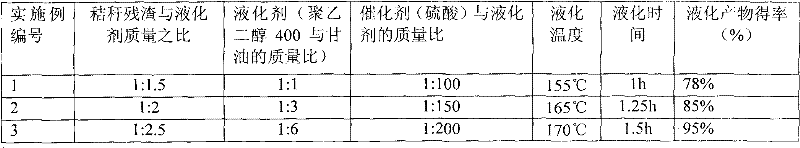
[0021] Weigh 150g of polyethylene glycol 400 and 150g of glycerin into a three-necked flask, and raise the temperature to 120°C, then add 200g of straw residue and 3g of sulfuric acid, start the magnetic stirring paddle to mix the materials, and continue to heat up to 155°C, and kee...
Embodiment 2
[0023] The pretreatment steps of stalks in the present embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference being that corn stalks are hydrolyzed with 2% dilute sulfuric acid at 125° C. for 1.25 h, the volume of dilute sulfuric acid used (ml) and the quality of corn stalks ( g) The ratio is 30:1. The mass of the corn stalk residue is 85% of the original stalk, and the measured hemicellulose content in the corn stalk residue is 8% (see Table 1).
[0024] The liquefaction steps of stalks in this example are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the mass ratio of corn stalk residue to liquefaction agent is 1:2, the mass ratio of catalyst to liquefaction agent is 1:150; the liquefaction temperature is 165 ℃, liquefaction time 1.25h. The mass of the straw liquefaction product was measured to account for 85% of the amount of material added (see Table 2 for details).
Embodiment 3
[0026] The pretreatment steps of stalks in the present embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference being that corn stalks are hydrolyzed with 3% dilute sulfuric acid at 130° C. for 1.5 h, the dilute sulfuric acid volume (ml) used and the corn stalks quality ( g) The ratio is 10:1. The mass of the corn stalk residue is 70% of the original stalk, and the measured hemicellulose content in the corn stalk residue is 7% (see Table 1 for details).
[0027] The liquefaction steps of stalks in this example are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the mass ratio of corn stalk residue to liquefaction agent is 1:2.5, the mass ratio of catalyst to liquefaction agent is 1:200; the liquefaction temperature is 170 ℃, liquefaction time 1.5h. The mass of straw liquefaction products accounted for 95% of the amount of material added (see Table 2).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com