Probe detection system
A detection system and probe technology, which is applied in the field of probe microscopy, can solve problems such as inability to obtain accurate results and consider the transient mode of the cantilever, and achieve the effect of minimizing the transient effect and making the transient effect convenient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
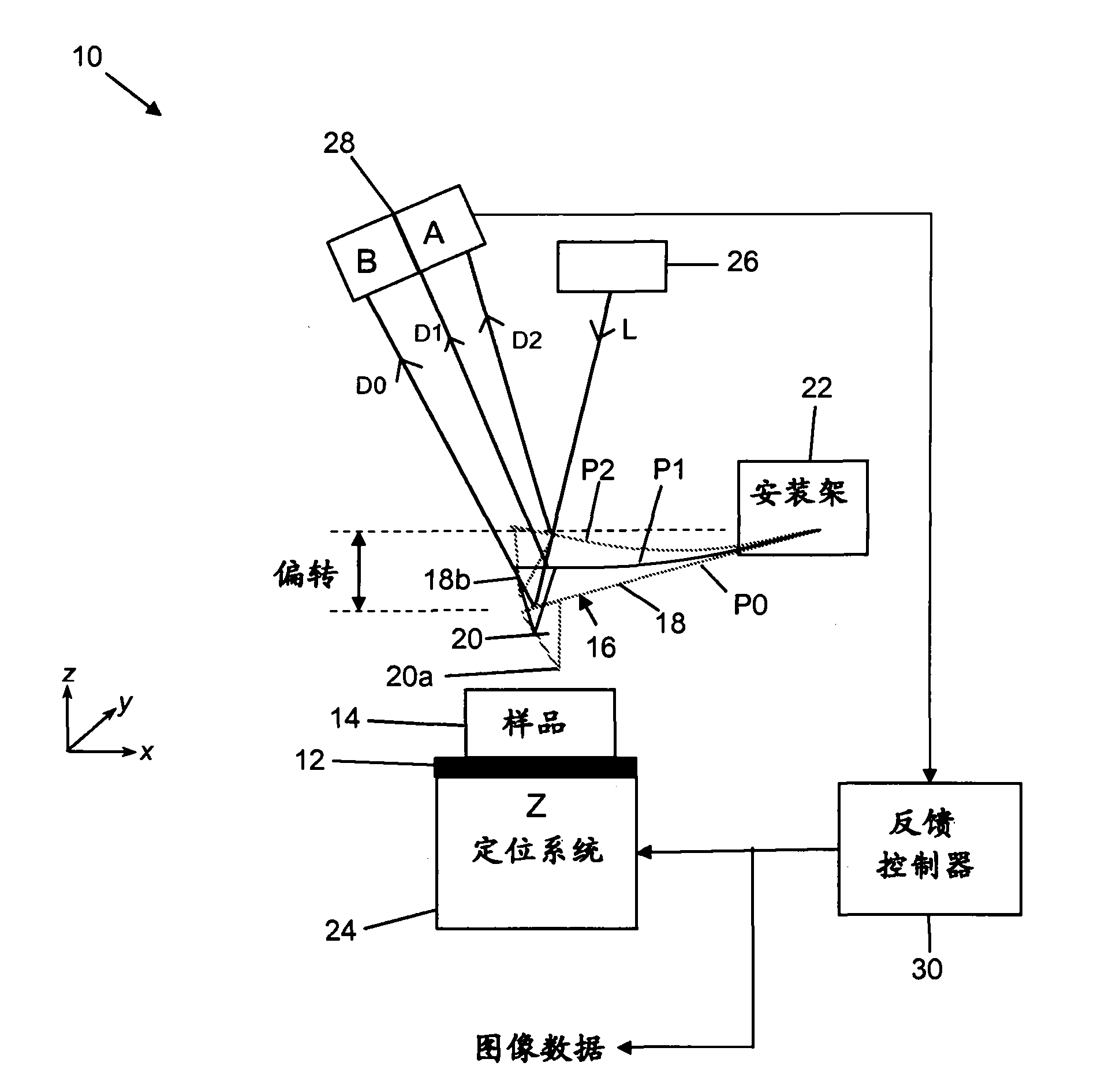
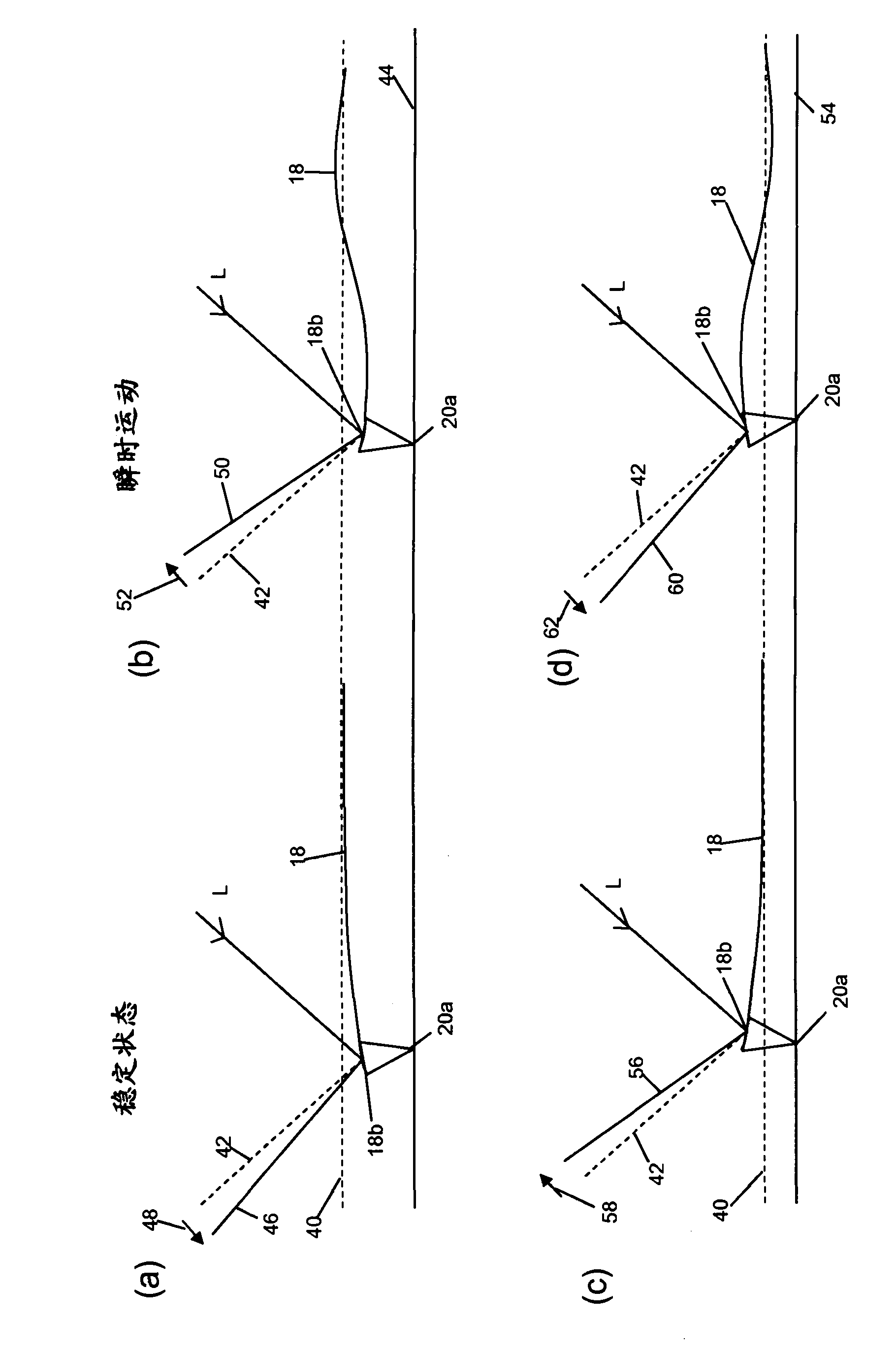
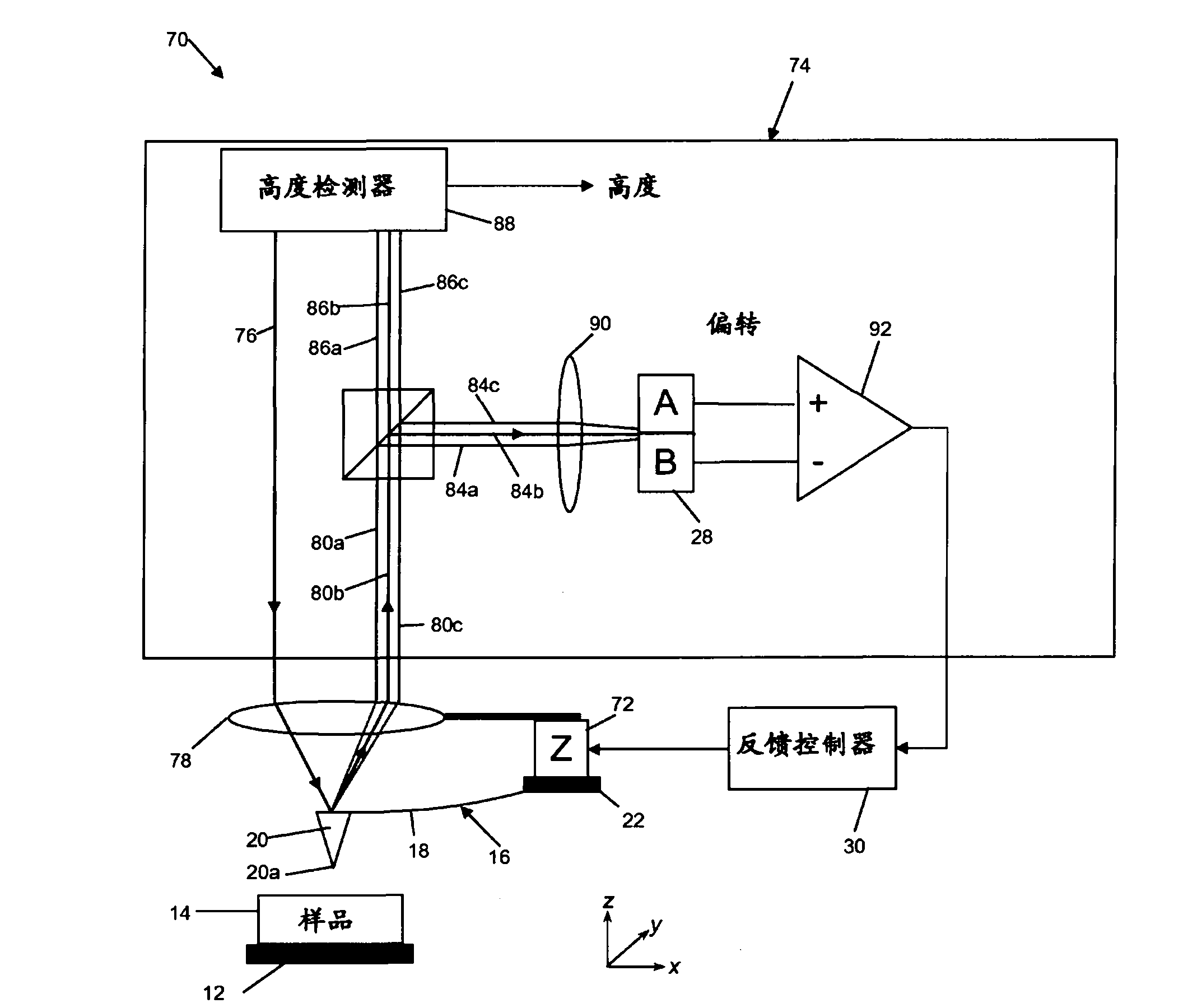
[0111] refer to image 3 , schematically illustrates an embodiment of an AFM, indicated generally at 70, utilizing a first embodiment of a detector constructed in accordance with an aspect of the invention. Elements in common with the prior art AFM described earlier with reference to FIG. 1 are given the same reference numerals. Accordingly, the illustrated AFM apparatus includes a movable stage 12 adapted to accommodate a sample 14 whose surface is to be inspected by a probe 16 . Probe 16 includes cantilever beam 18 and needle tip 20 that tapers toward point 20 a and is positioned toward one end of cantilever beam 18 . The other end of the cantilever beam 18 is supported by a mounting bracket 22 .
[0112] One or more drive motors (72, not shown) are used to drive the sample 14 (together with the stage 12) and / or the probe 16 so that they can be moved relative to each other in three dimensions, namely the x, y and z directions. scan each other. As is conventional in the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com