Double-channel anodic stripping voltammetry
An anodic stripping voltammetry, dual-channel technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, etc., to achieve satisfactory detection results, convenient operation, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035]This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0036] (1) Prepare 0.1 g·L -1 Cd(II), Pb(II) standard solution, when used, dilute this solution to 10 mg·L -1 , prepare 0.1 mol L with ultrapure water -1 Acetic acid buffer solution (pH 4.5), as a supporting electrolyte solution for detecting Cd(II) and Pb(II); prepare 0.1 mol L -1 As(III) standard solution, dilute this solution to 0.01 mmol·L when using -1 , 0.1 mmol·L -1 , 1 mmol·L -1 and 10 mmol·L -1 , prepare 0.5 mol·L with ultrapure water -1 Sulfuric acid solution is used as a supporting electrolyte solution for detecting As(III); of course, neutral phosphate buffer solution or BR buffer solution with a pH of 1.81 to 8.95 can also be used as a supporting electrolyte solution for detecting As(III).
[0037] (2) Channel 1 and channel 2 were detected by a three-electrode system, the working electrode of channel 1 was a glassy carbon electrode, the working electrode of channel 2 was a gold electrode, the reference e...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0044] (1) The preparation of Cd(II), Pb(II) standard solution and As(III) standard solution is the same as in Example 1, and 0.1 mol L is prepared with ultrapure water -1 Acetic acid buffer solution (pH 4.5) as a supporting electrolyte solution;
[0045] (2) Channel 1 and channel 2 are detected by a three-electrode system respectively. The working electrode of channel 1 is a glassy carbon electrode with pre-mercury coating, the working electrode of channel 2 is a gold electrode, and the reference electrode of channel 1 and channel 2 is saturated with calomel. Electrode (SCE), counter electrode, platinum plate electrode, wash each electrode, beaker and magnetic stirrer with water; then connect the line, fix the position of the beaker, each electrode and magnetic stirrer, and then add 10 mL of 0.1 mol ·L -1 Acetate buffer, connected to channel 1 and channel 2;
[0046] Preparation of the pre-mercury-coated glassy carbon ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The difference between this example and Example 2 is that in step (4), first take the water sample to be tested - tap water, filter it under reduced pressure with a 0.22 mm filter membrane, add 50 μL of water sample to the supporting electrolyte solution, and then use the standard addition Law.
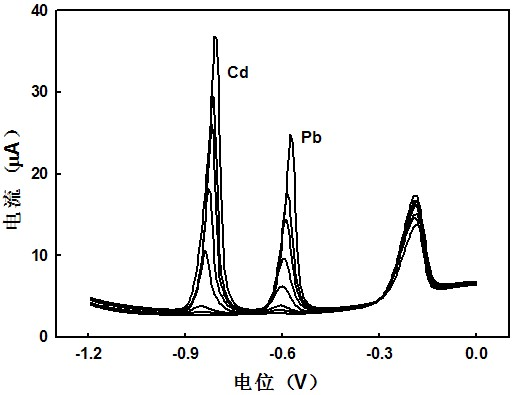
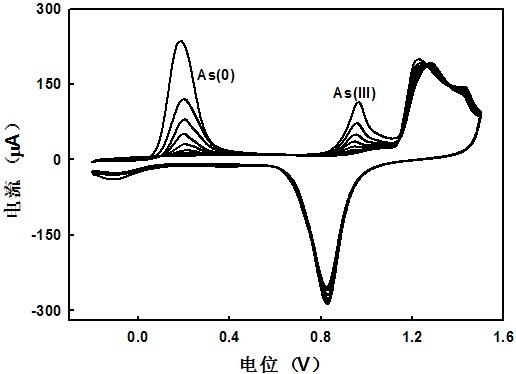
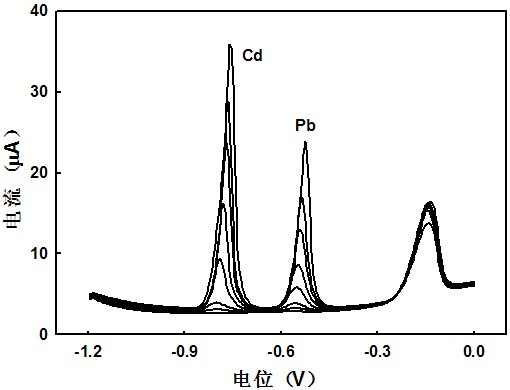
[0053] Analysis of measurement results: no obvious lead, cadmium and arsenic oxidation peaks in blank tap water, adding 1, 5, 10, 30, 50 and 70 ppb of Pb(II), Cd(II) (final concentration) and 0.01, 0.03 , 0.05, 0.08 and 0.1 μmol L -1 After As(III) (final concentration), the oxidation peaks of lead, cadmium and arsenic appeared, the oxidation peak potential of Cd(0) to Cd(II) was about -0.635 V vs SCE, and the oxidation peak potential of Pb(0) to Pb(II ) is about -0.465 V vs SCE, the oxidation peak potential of As(0) to As(III) is about 0.035 V vs SCE, and the oxidation peak potential of As(III) to As(Ⅴ) is about 0.695 V vs SCE, the peak currents of the oxidation peaks of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com