Novel welding method for laser welding of magnesium alloy
A technology of laser welding and welding method, which is applied to laser welding equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, welding equipment and other directions, can solve the problems of limiting the application of laser welding technology, low utilization rate of laser welding energy, and increasing equipment cost. The effect of improving energy utilization, improving mechanical properties, and increasing energy transmission efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
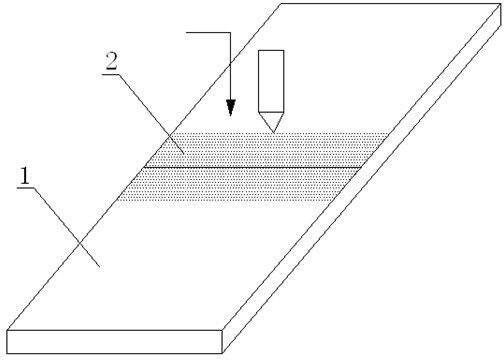
[0024] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of magnesium alloy laser welding using the method of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the novel welding method for magnesium alloy laser welding in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0025] 1) Fully grind SiO first 2 Activator powder, then to SiO 2 Add acetone to the active agent powder to make it into a paste; grind and clean the surface of the magnesium alloy to be welded with ethanol to remove oxides and oil stains;
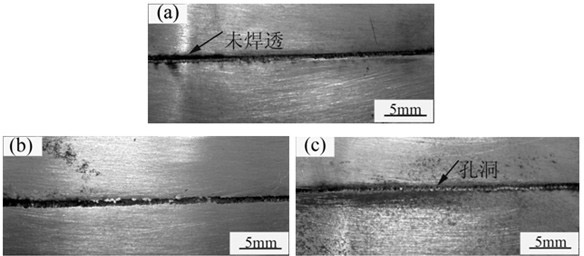
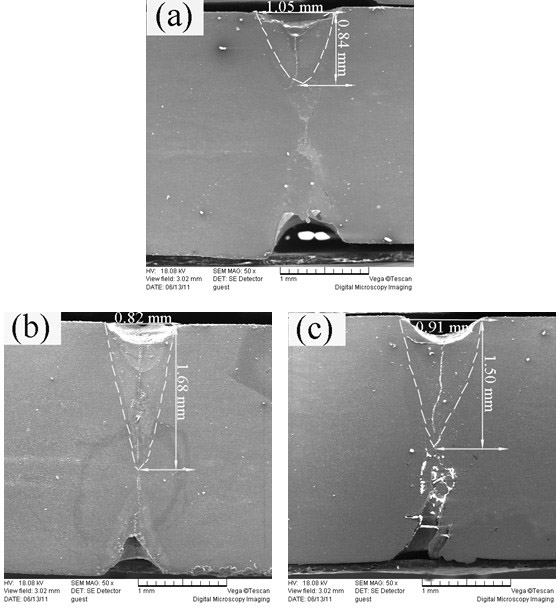
[0026] 2) Use a flat brush to shake the paste SiO 2 The active agent is evenly coated on the surface of the magnesium alloy to be welded to form SiO 2 active agent coating ( figure 1 Among them, 1 is magnesium alloy, 2 is SiO 2 active agent coating); the paste SiO 2 The coating amount per unit area of the active agent on the surface of the magnesium alloy to be welded is 1 mg / cm 2 , the paste SiO 2 The coating width of the active agent on the surface of the magnesium alloy to be wel...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference between the novel welding method for magnesium alloy laser welding of this embodiment and embodiment 1 is only that: the paste SiO 2 The coating amount per unit area of the active agent on the surface of the magnesium alloy to be welded is 2mg / cm 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference between the novel welding method for magnesium alloy laser welding of this embodiment and embodiment 1 is only that: the paste SiO 2 The coating amount per unit area of the active agent on the surface of the magnesium alloy to be welded is 3mg / cm 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com