Method for removing harmful elements from chinese herbal medicine ficus simplicissima lour.
A technology of harmful elements and Chinese herbal medicines, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, plant raw materials, etc., can solve problems such as restricting the export of medicinal materials, affecting the use of medicinal materials, and complexing agent residues, and achieving dual greening , The effect of maintaining the original characteristics and increasing the solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
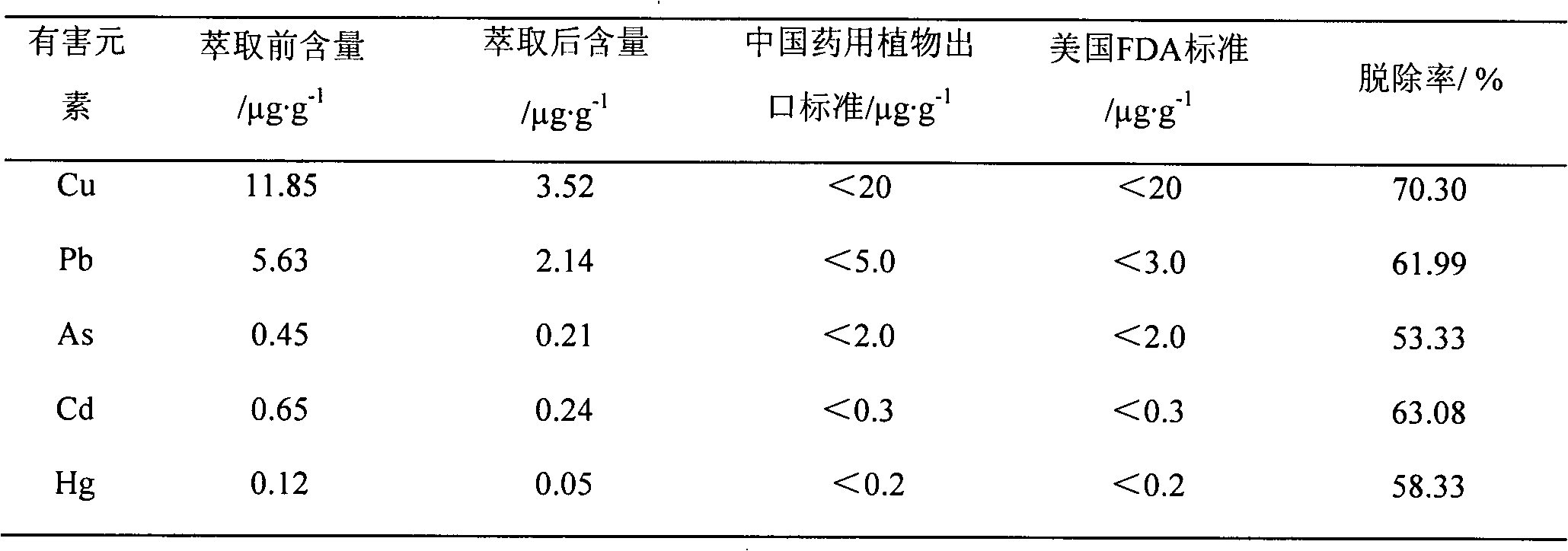
[0027] The removal of harmful elements in the Chinese medicinal material Peach quinquefolium of embodiment 1
[0028] Phosphatidylcholine, provided by Shanghai Bio-Engineering Company; food grade, purity > 95%
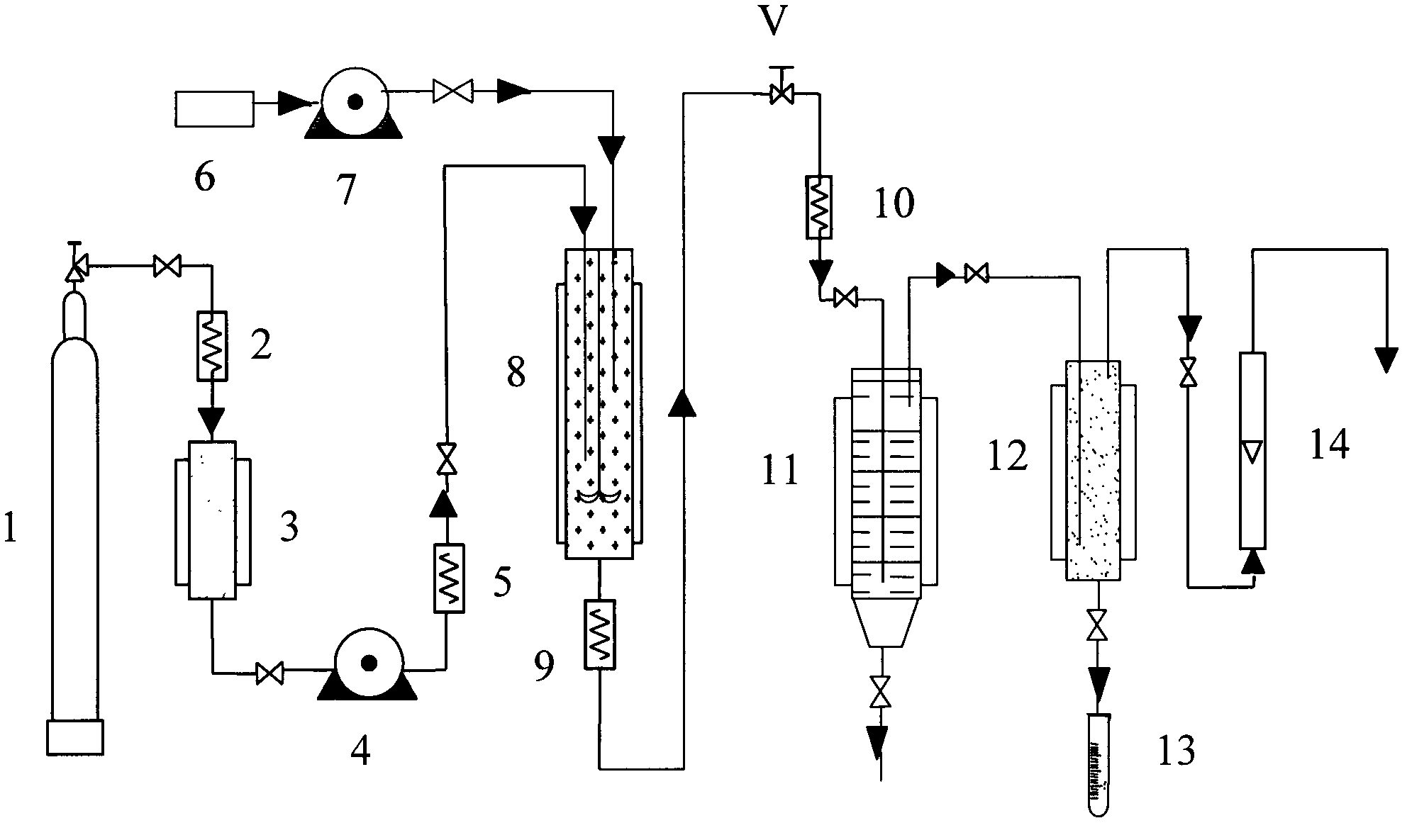
[0029] Experimental device: Jiangsu Hua'an supercritical reaction / extraction device, the capacity of the reaction kettle is 1L, the capacity of the extraction kettle is 1L, the capacity of the collection kettle is 2L, the maximum withstand pressure is 35MPa, and the maximum temperature is 368K.
[0030] Preparation method: In one embodiment, the harmful element removal method of the present invention can be completed in a supercritical reaction / extraction device, and the flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown. The specific steps are: mix 20g of phosphatidylcholine [x(PC)=1.5×10 -3 ] dissolved in 200mL ethanol [x(CH 3 CH 2 OH)=0.21], placed in the reactor (8), capped. Simultaneously take by weighing 200g 20~40 order five-finger peach medicinal material granules,...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Harmful element extraction process under the different surfactant dosages of embodiment 2
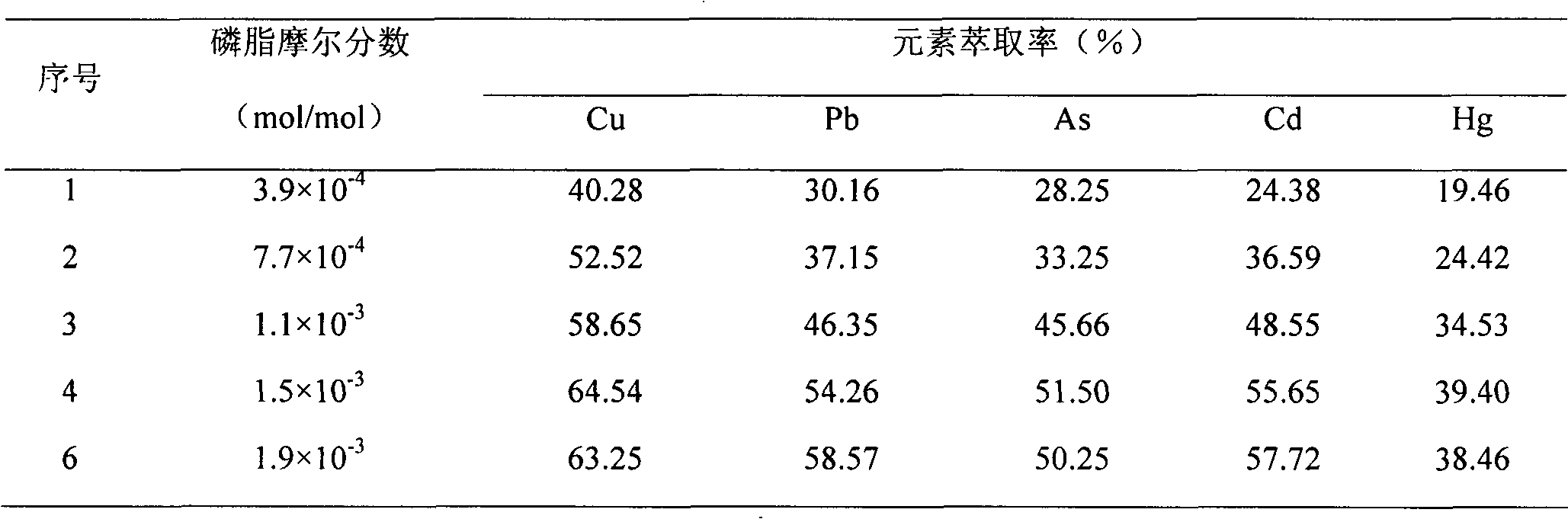
[0039] This example investigates the effect of microemulsions formed with different surfactant dosages on the element extraction process. Control x(PC) is 3.9×10 -4 ~1.9×10 -3 ,, the amount of ethanol and water are respectively set to x(CH 3 CH 2 OH)=0.21 and x(H 2 O)=0.19, under pressure 15MPa, temperature is 323K, balance reaction 1h, form supercritical microemulsion. Harmful elements in medicinal materials were extracted according to the method of Example 1, the element extract was collected, the content of elements in the extract was measured, and the extraction rate was calculated. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0040] The impact of table 2 phospholipid dosage on the extraction of harmful elements
[0041]
[0042] The results of this example show that when x(PC) is lower than 3.9×10 -4 At this time, micelles cannot be formed, and the desorption effect on el...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The extraction process of harmful elements under the different cosurfactant dosages of embodiment 3
[0044] This example investigates the influence of different ethanol dosages on the extraction process of harmful elements. Control the amount of ethanol x(CH 3 CH 2 OH) is 0.05~0.27, x(PC)=1.5×10 -3 , the amount of deionized water x(H 2 O)=0.19, under pressure 15MPa, temperature is 323K, balance 1h, form supercritical microemulsion. Harmful elements in medicinal materials were extracted according to the method of Example 1, the element extract was collected, the content of elements in the extract was measured, and the extraction rate was calculated. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0045] The results of this example show that in the absence of co-surfactants, phospholipids in supercritical CO 2 Solubility is very small, can not solubilize water to form microemulsion. After adding ethanol, the phospholipids and supercritical CO 2 intermolecular interactions. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com