Pullulanase, pullulanase producing strain and application of pullulanase
A pullulanase and strain technology, applied in the field of biological enzymes, can solve the problems of high price, no screening of pullulanase-producing strains, and limited application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
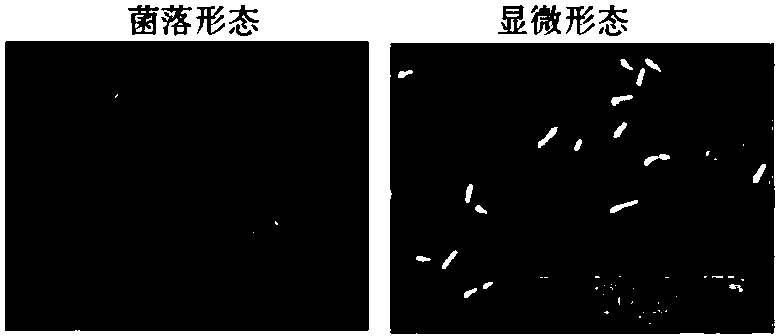
[0030] Example 1: Screening, isolation and identification of pullulanase-producing strains
[0031] Take 10 g of soil sample and put it into a conical flask filled with 90 mL of sterile water and glass beads, shake it for 30 min to fully disperse the sample, draw 100 μL of culture solution and dilute it, and spread it on the mixture with pullulan as the only Plate enriched medium with carbon source was cultured in a 30°C incubator for 48 h. Two single colonies of different shapes were picked from the enrichment medium and inoculated on the strain isolation medium, and the picked single colonies were streaked repeatedly. Subsequently, the colonies purified by streaking on the plate were inoculated into the enzyme-producing seed medium, and cultured with shaking at 30 °C for 24 h to obtain a bacterial suspension. The bacterial suspension was inserted into the enzyme-producing fermentation medium with 4% inoculum, and cultured with shaking at 30 °C for 48 h; the supernatant wa...
Embodiment 2
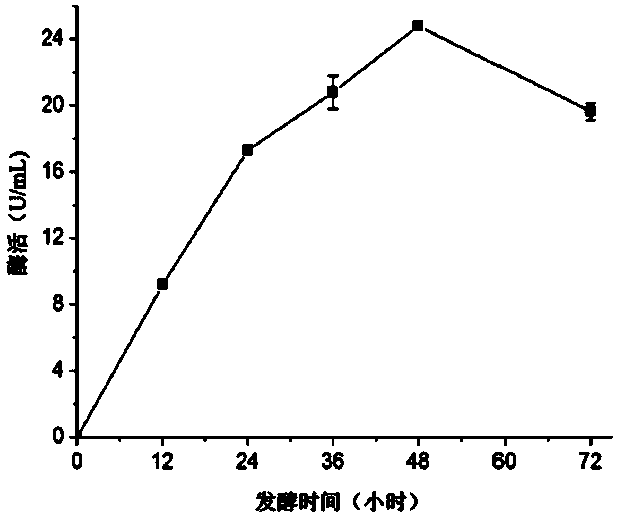
[0033] Example 2: Aeromonas sp . As fermentation condition optimization
[0034] The pullulanase of the As strain is an inducible enzyme and needs to be expressed under substrate-inducing conditions. Therefore, when optimizing the conditions for the production of pullulanase by the As strain, soluble starch was used as the enzyme-producing inducer. After the As strain was isolated and purified, a single colony was picked and inoculated in 25 mL of seed medium, and cultured with shaking at 30 °C for 16–18 h; then 2 mL was transferred into 50 mL of fermentation medium, and incubated for 30 ℃. Cultivate with shaking at ℃ for 48 h, and take the supernatant to measure the enzyme activity. Adjust the pH value of the fermentation medium (pH 6.5 and pH 7.5) and fermentation temperature (30 ℃ and 37 ℃), measure the activity of pullulanase in the fermentation broth every 12 h, and establish the conditions for high-yield pullulanase of strain As .
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Aeromonas sp . Preliminary Purification of Pullulanase from As Fermentation Supernatant
[0036] Aeromonas sp . After the As strain was fermented for 48 h, 20 μL of the fermentation supernatant was used to detect protein expression bands by 12% SDS-PAGE. Take 30 mL of fermentation supernatant, concentrate it to 1 mL by ultrafiltration with Amicon ultrafiltration tube (molecular weight 30 KDa), the buffer solution is 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), take 20 μL for SDS-PAGE detection, and detect the first Specific activity of pullulanase after one ultrafiltration (U / mg protein). For the second ultrafiltration purification, Amicon ultrafiltration tubes with a molecular weight cut-off of 50 KDa and 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) were used. The final volume after ultrafiltration was 800 μL, and 20 μL was taken out for SDS-PAGE detection (such as Figure 4 ), while measuring the specific activity of pullulanase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com