Direct liquid cooling method for light emitting didoes and light emitting diode package utilizing method
A technology of light-emitting diodes and light-emitting diodes, which is applied in the field of cooling and heat dissipation, can solve the problems of reducing heat conduction efficiency, decreasing light energy efficiency, and fluorescent pink temperature difference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
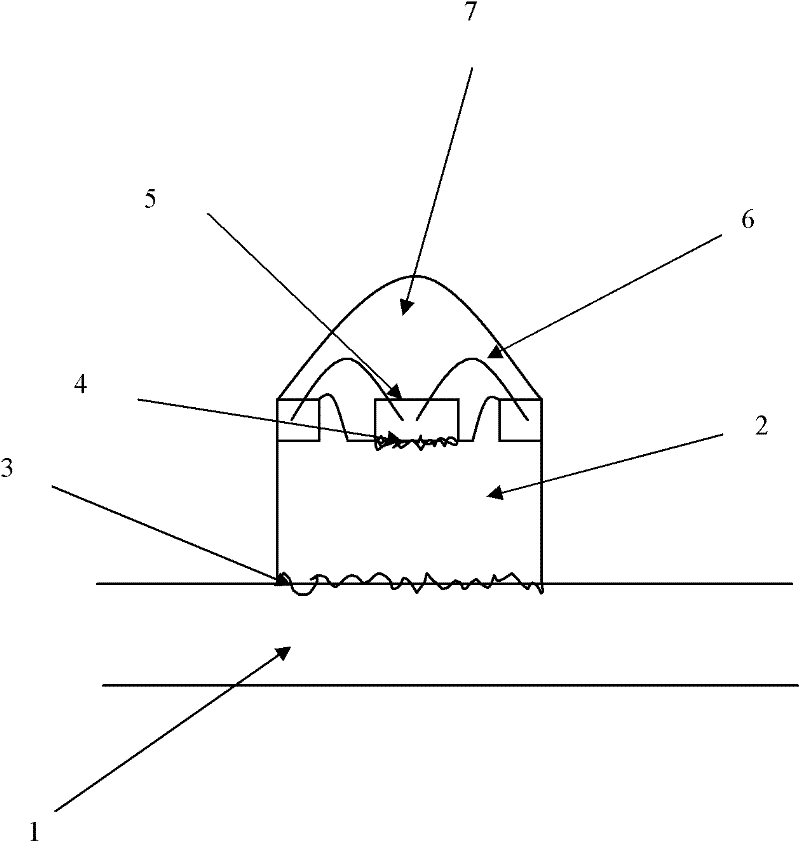
[0027] figure 1 A cross-section of existing heat dissipation techniques for light-emitting diodes is illustrated. Such as figure 1 As shown in , the reference numeral 1 denotes the aluminum substrate; the reference numeral 2 denotes the heat sink; the reference numerals 3 and 4 denote the silver paste; the reference numeral 5 denotes the LED chip; the reference numeral 6 denotes the wire; the reference numeral 7 denotes the silica gel phosphor.
[0028] As mentioned in the background technology, the heat dissipation technology of the light-emitting diodes in the prior art cannot ensure sufficient heat dissipation of the light-emitting diodes, which will lead to the accumulation of heat in the light-emitting diode chip, the current will continue to rise, and the light decay will continue to occur, and the phosphor powder will Long-term thermal decomposition results in light attenuation and color temperature differences.
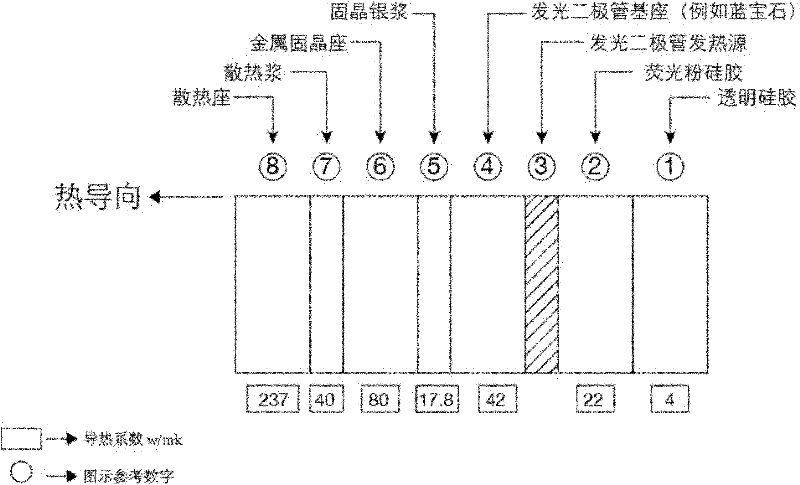
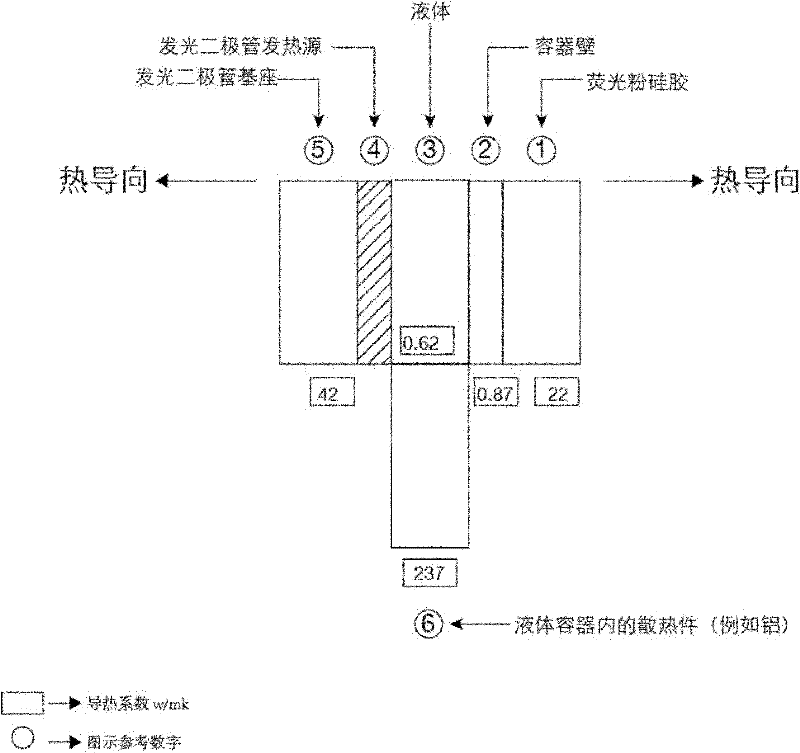
[0029] figure 2 The heat conduction relationship of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com