Strain of bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria and application thereof in producing heparinase I
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and engineering bacteria, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, lyase, etc., can solve the problem of no successful expression of heparanase Ⅰ, and achieve high activity and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
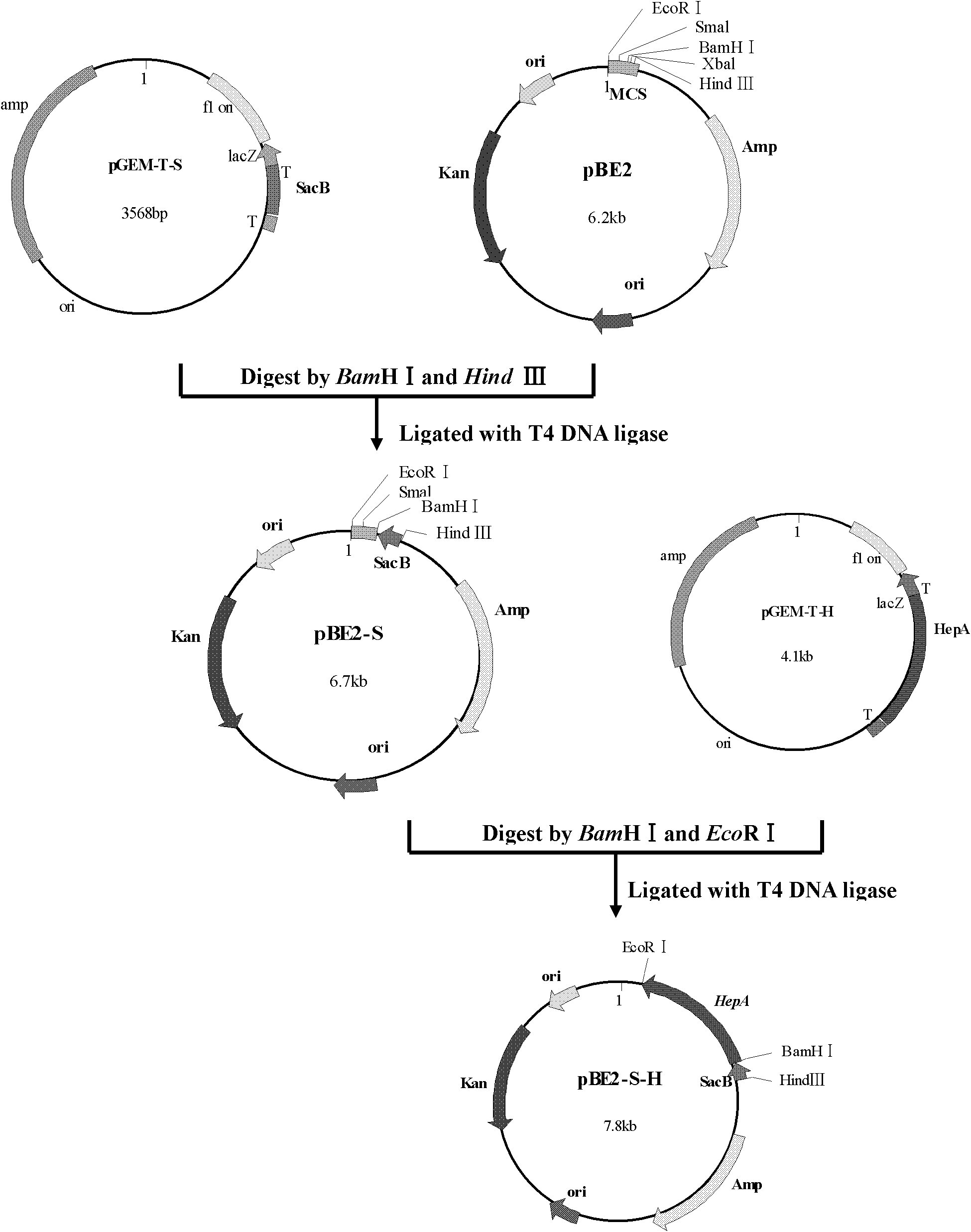
[0030] Example 1 Construction of Bacillus subtilis WB600 (pBE2-S-H), an engineering bacterium of Bacillus subtilis expressing recombinant heparanase I.
[0031] 1. Acquisition of heparanase Ⅰ gene from Flavobacterium heparinus
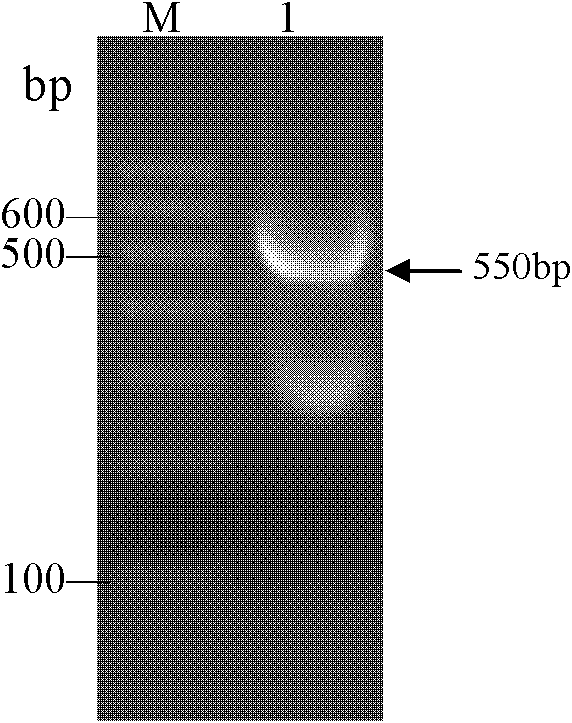
[0032] Extract the genomic DNA of Flavobacterium heparinus DSMZ 2366, design a pair of primers H1 and H2 according to the gene sequence of heparinase Ⅰ, conduct conventional polymerase chain reaction, amplify the gene sequence of Flavobacterium heparinus heparinase Ⅰ, and obtain a DNA fragment of 1100bp (See figure 2 ), the product was cloned into pGEM after amplification and purification -T Easy vector, constructed into recombinant plasmid HepA / pGEM -T Easy, the sequence determination results show that the obtained heparanase I gene sequence and the GenBank number are EU541216.1 The nucleotide sequence of the 1st-1089th base of the 5'-end (shown in SEQ ID NO.2) totally agree. The two primers are:
[0033] H1: 5′CG GGATCC CAGCAAAAAAAAATCCGGTA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com