Method for industrializedly recovering zinc and manganese in waste dry cells
A dry cell and waste technology, which is applied in the field of environmentally friendly recycling and production of waste dry cells, can solve the problems of complex process, high recycling cost and difficult control, and achieve the effects of simple process, high recovery rate and low production cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
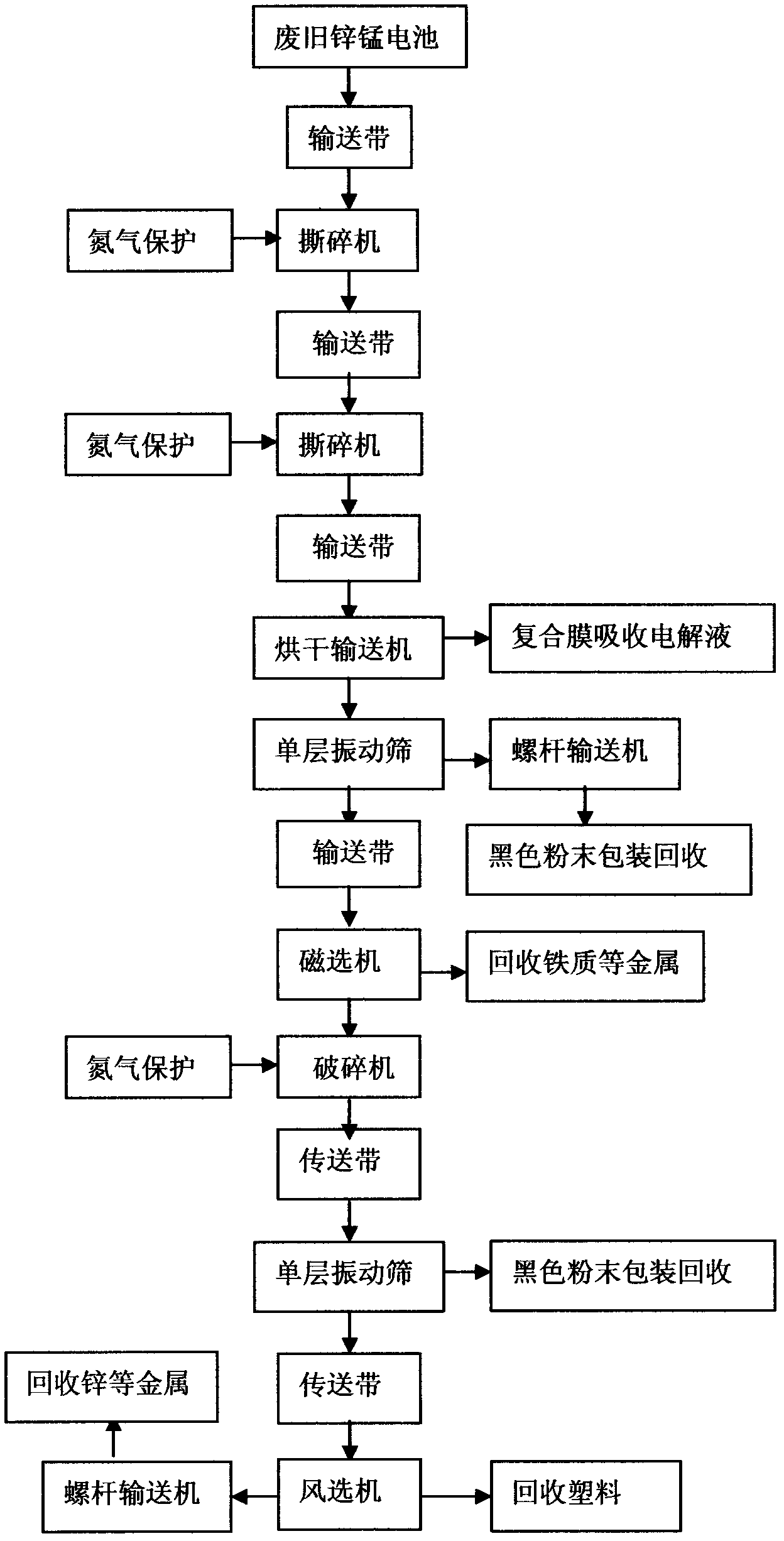
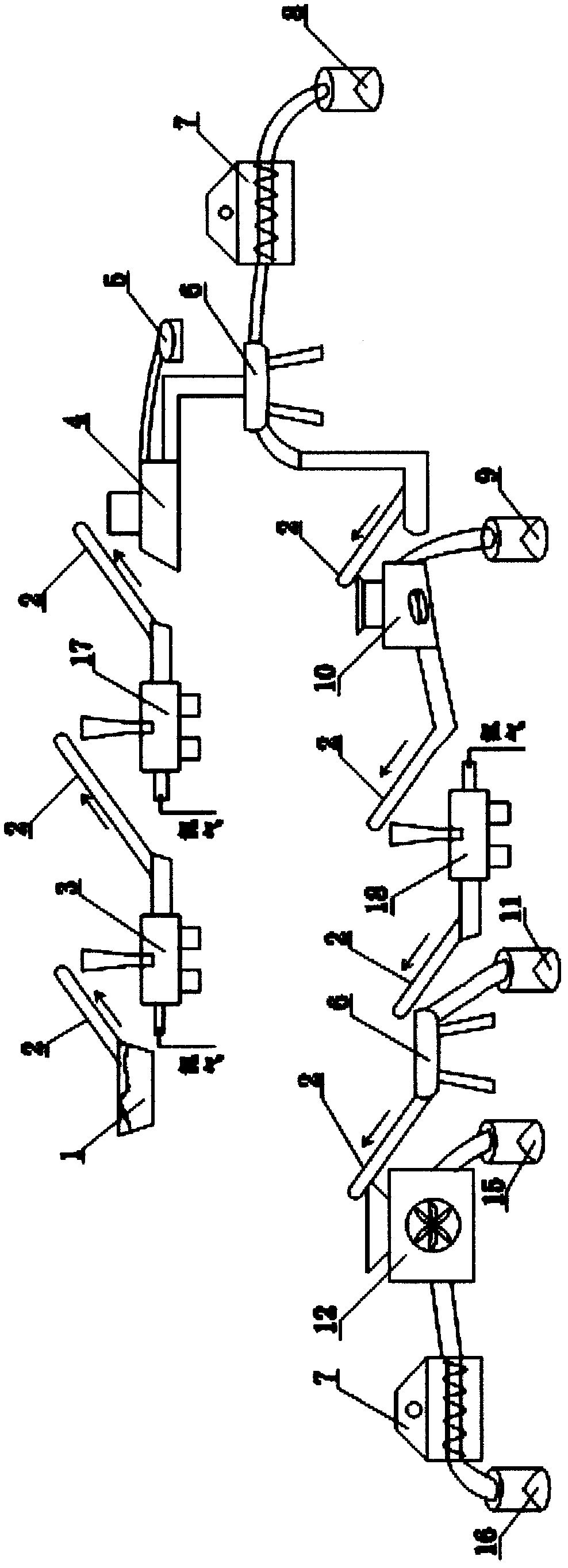
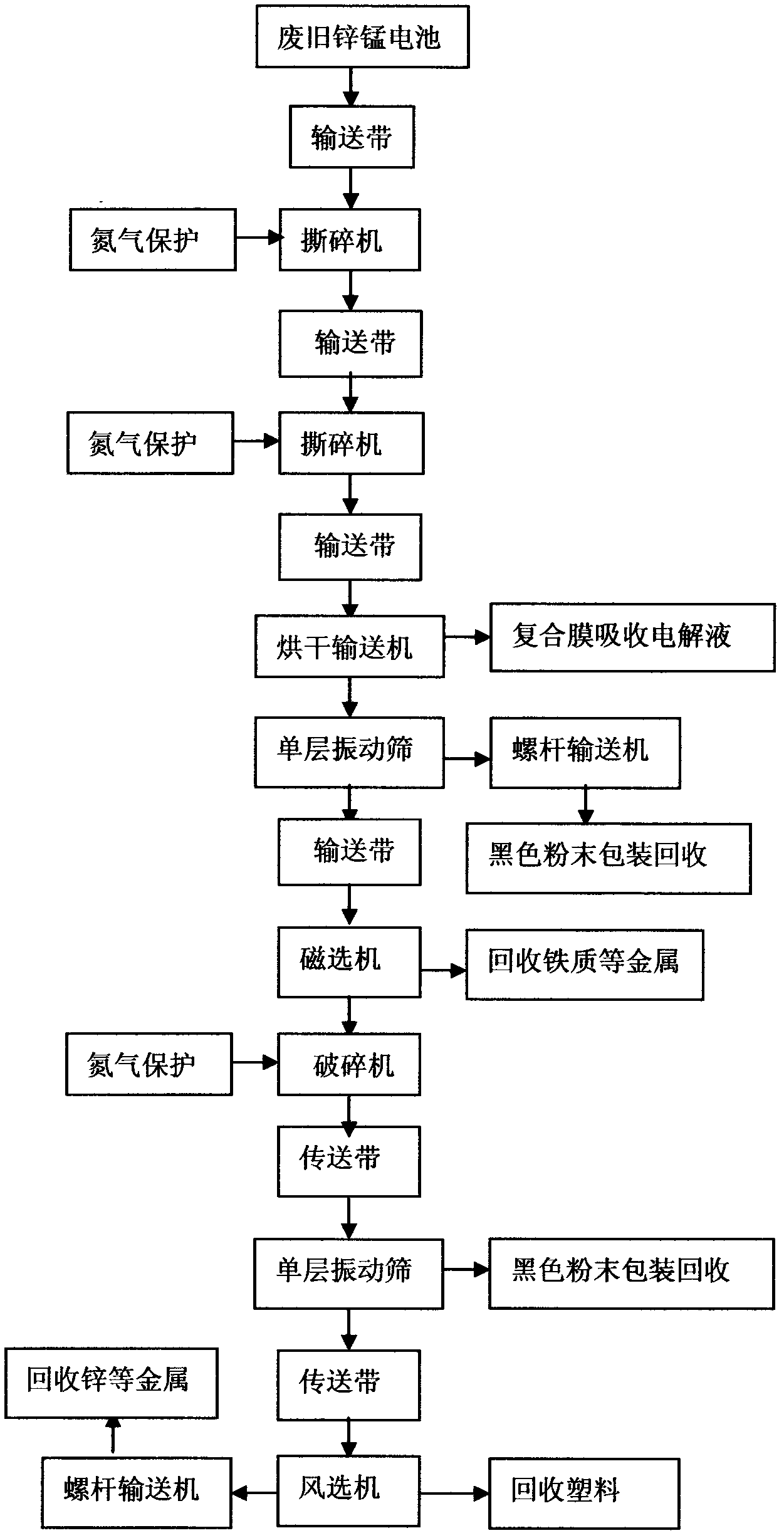
[0038] Embodiment 1: In the first step, take 0.2 tons of waste dry batteries, use the starter to put 0.2 tons of waste batteries into the bottom of the conveyor belt, start the climbing skirt conveyor belt, and transport 0.2 tons of waste batteries into the first shredder At the same time, inject nitrogen into the first shredder (playing a protective role), and the first shredder is also connected to the dust collector for dust removal; the first shredder crushes the zinc-manganese battery for the first time at the maximum crushing rate for about 1 hour Finally, the fragments whose size is less than 20mm account for more than 93%. At this time, the fragments with a crushing size of more than 20mm are screened out through the mesh screen, and the fragments below 20mm are not broken and put aside. After the first crushing, until the size of the broken pieces is less than 20mm, stop the first shredder, complete the primary crushing, and enter the next crusher for crushing.
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: Take 0.15 tons of waste batteries, use the starter to put 0.15 tons of waste batteries into the bottom end of the conveyor belt, start the climbing skirt belt conveyor belt, and transport 0.15 tons of waste batteries into the first shredder, and follow-up steps Same as embodiment one.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is the same as the first three steps of the above two embodiments, the difference is that the air separator is used to select the plastic, and then the magnetic separator is used to select the metal;
[0046] The fourth step is to use the conveyor belt to transport the remaining fragments to the third crusher for three-stage crushing, and at the same time inject nitrogen into the third crusher, and the third crusher is connected to the dust collector to remove dust; the third crusher crushes the remaining fragments until the fragments The size below 8mm accounts for 98%, stop crushing, and then use the conveyor belt to transport to the single-layer vibrating screen. The oversize left by the single-layer vibrating screen is driven by the conveyor belt to enter the air separator to maintain the wind speed of the air separator. Reach 3m / s, separate out the plastic, and recycle the packaged plastic.
[0047] The fifth step is to drive the debri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com