A kind of antibacterial polypeptide and its preparation method and application
A technology of antibacterial peptides and antibacterial drugs, which is applied in the field of preparation of antibacterial peptides and the antibacterial peptides, can solve the problems of low content of antibacterial peptides, difficulty in extraction, high cost, etc., and achieve the effect of less drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The preparation of embodiment 1 antibacterial polypeptide
[0030] Escherichia coli DH5α was purchased from Treasure Bioengineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd., methanol yeast (Pichia pastoris) GS115, and expression vector pPIC9K was purchased from Invitrogen.
[0031] Inoculate a single colony of GS115 in 5ml YPD (1% yeast extract, 2% tryptone, 2% D-glucose) liquid medium, culture overnight at 28-30°C, transfer 100μl to 50ml YPD medium to continue the cultivation, Stop culturing when the OD600 is between 1.1 and 1.3, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 5min, collect the bacteria, then wash twice with ice-cold deionized water and D-sorbitol, and finally add 1ml of pre-cooled 1M D-sorbitol, Aliquot 200 μl per tube into spare methanolic yeast GS115 competent cells, use immediately or store at -70°C.
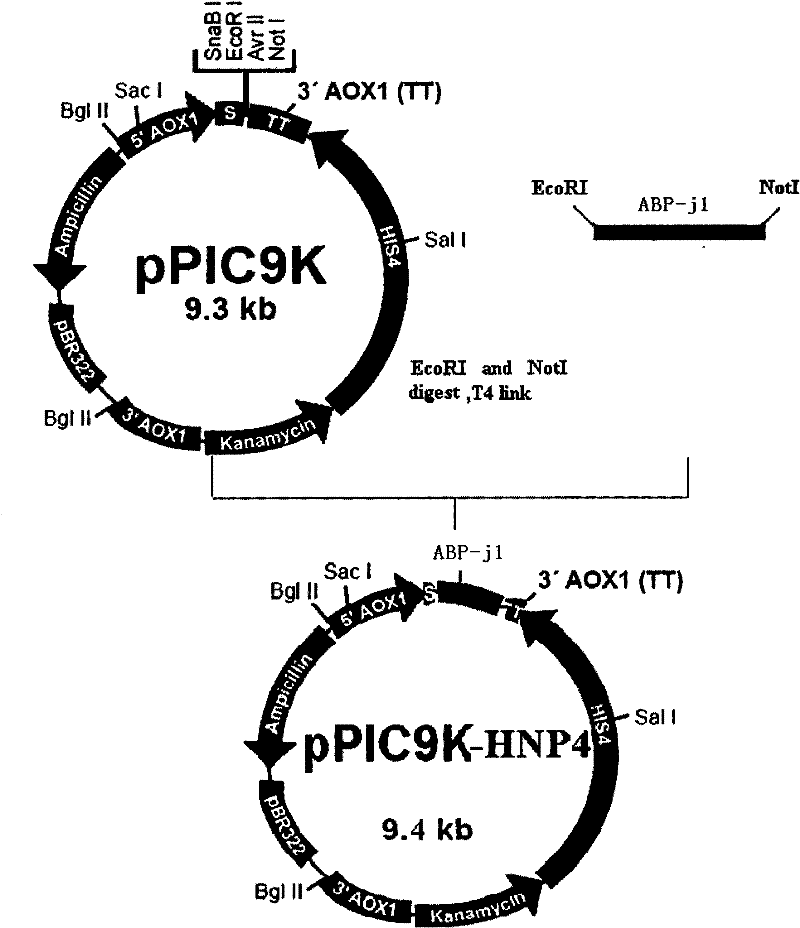
[0032] According to the ABP-j1 nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID No.1) and the restriction endonuclease site characteristics on the Pichia pastoris expression vector pPIC9K, by artificial synthes...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The thermostability test of embodiment 2 antibacterial polypeptide
[0038] Take 1ml of each yeast expression supernatant and place them in water baths at 40, 60, 80 and 100°C for 10, 20, and 30 min respectively. Use the untreated yeast expression supernatant as a control, and standard Staphylococcus aureus as an indicator bacterium. The antibacterial effect of the samples before and after treatment was determined by the diameter of the inhibition zone. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and the average value was taken as the measurement result.
[0039] Table 1 The diameter of inhibition zone of yeast expression supernatant against standard Staphylococcus aureus after heat treatment
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] Note: The control is the diameter of the inhibition zone of the yeast expression supernatant without heat treatment.
[0043] The results in Table 1 show that the effects of different heating temperatures and times on the antibacterial effect of the yeas...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Antimicrobial polypeptide challenge protection test
[0045] The virus strain is Escherichia coli K88.
[0046] Determination of median lethal dose (LD50) Escherichia coli K88 was inoculated in nutrient broth containing 0.5% glucose, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, and the OD650 value was 0.765. The mice were injected intraperitoneally with doses of 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, and 0.25 mL, respectively, and 5 mice were inoculated with each dose, and the death conditions were observed and recorded.
[0047] Table 2 The death of mice inoculated with different doses of bacterial solution
[0048] Dosage (ml / piece)
[0049] With the increase of the inoculum amount, the number of death of mice increased linearly. Calculated by Reed and Meunch method, the median lethal dose (LD50) of the bacterial solution to mice is 0.142mL.
[0050] Divide 30 mice into 4 groups, namely blank control group, virus strain control group, empty vector yeast supernatant control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com