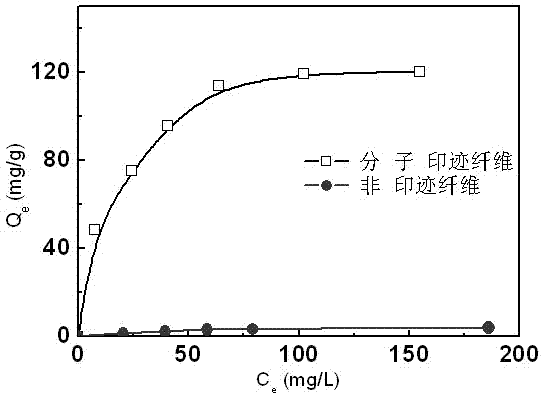
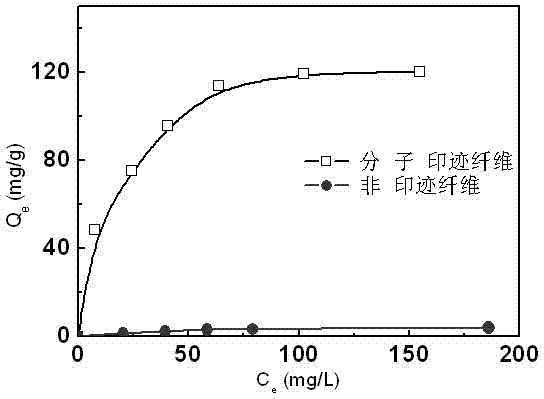
A molecularly imprinted fiber material and its preparation method
A technology of molecular imprinting and fiber materials, applied in fiber treatment, chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of low-molecular imprinting materials, unfavorable, high grafting rates, etc., to promote development and application, fast adsorption Effect of speed, high mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Weigh 20 g of the pretreated polypropylene fiber and put it into a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, and seal it with a silica gel membrane. It is irradiated with cobalt 60 gamma rays, the radiation dose is controlled to 48KGy, and the irradiation time is 55 hours. Acrylic acid monomer and methanol are prepared into 150ml homogeneous mixed solution according to volume percentage 30:70, 5g of pre-irradiated polypropylene fiber is added according to 1:30 bath ratio (weight: volume), and 5% of activator is added salt, reacted at a temperature of 60°C for 6 hours, washed the grafted fibers with methanol to remove homopolymers and unpolymerized grafted monomers, dried in vacuum, and calculated the grafting rate to be 200%. The grafted fiber was added to 1wt.% polyethyleneimine methanol solution to react for 10h, and then washed with methanol to remove unreacted polyethyleneimine. After drying, the polyethyleneimine grafting rate was calculated to be 50%. Add polyethyleneimine gra...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Put 20 g of pretreated polypropylene fibers into a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask and seal it with a silica gel membrane. It is irradiated with cobalt 60 gamma rays, the radiation dose is controlled to 48KGy, and the irradiation time is 55 hours. According to 1:30 bath ratio (weight: volume), 5 g of pre-irradiated polypropylene fiber was added to 10 / 90 (v / v) % acrylic acid / water mixed solution, and reacted at 80 ° C for 1 hour. The grafted fibers after the reaction were washed with methanol to remove homopolymers and unpolymerized monomers, dried in vacuum, and the calculated grafting rate was 100%. The grafted fiber was added to a 30wt.% polyethyleneimine (PEI) aqueous solution to react for 8 hours, and then washed with methanol to remove unreacted polyethyleneimine. After drying, the polyethyleneimine grafting rate was calculated to be 60%. Add polyethyleneimine grafted fiber to 100ppm zinc nitrate solution, add the fiber to 10% glutaraldehyde ethanol solution to react f...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Weigh 20 g of the pretreated polyacrylonitrile fiber and put it into a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, and seal it with a silica gel membrane. It is irradiated with cobalt 60 gamma rays, the radiation dose is controlled to 48KGy, and the irradiation time is 55 hours. Acrylic acid monomer and methanol are formulated into a homogeneous mixed solution at a ratio of 20:80 by volume, 5 g of pre-irradiated polyacrylonitrile fibers are added at a bath ratio of 1:30 (weight: volume), and activator Moore is added at a rate of 5%. salt, reacted at a temperature of 60° C. for 6 hours, washed the grafted fibers after reaction with methanol to remove homopolymers and unpolymerized monomers, dried in vacuum, and calculated the grafting rate to be 100%. The grafted fiber was added to 1wt.% polyethyleneimine methanol solution to react for 10h, and then washed with methanol to remove unreacted polyethyleneimine. After drying, the polyethyleneimine grafting rate was calculated to be 40%. Ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com