Vector host system for expressing antibiotic gene cluster and its application
An antibiotic, gene cluster technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering or microbiology, can solve the problem of slow growth of Streptomyces at room temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0052] As an embodiment of the present invention, a method for producing antibiotics is provided, comprising: transforming antibiotic synthesis gene clusters derived from room temperature and high temperature into the Streptomyces of the present invention, and then obtaining the transformed Streptomyces. The transformed Streptomyces is cultured in the culture medium, and then the target antibiotic is obtained by fermenting the transformed Streptomyces after cultivation. This provides a host bacteria platform that can grow at high temperature for heterologous expression.
[0053] Methods for introducing foreign genes or gene clusters into Streptomyces are also known to those skilled in the art, and the present invention is not particularly limited. Preferably, a method for transforming an exogenous gene or gene cluster in Streptomyces is provided, comprising: preparing protoplasts of Streptomyces, and transferring the vector containing the exogenous gene or gene cluster by Esch...
Embodiment 1
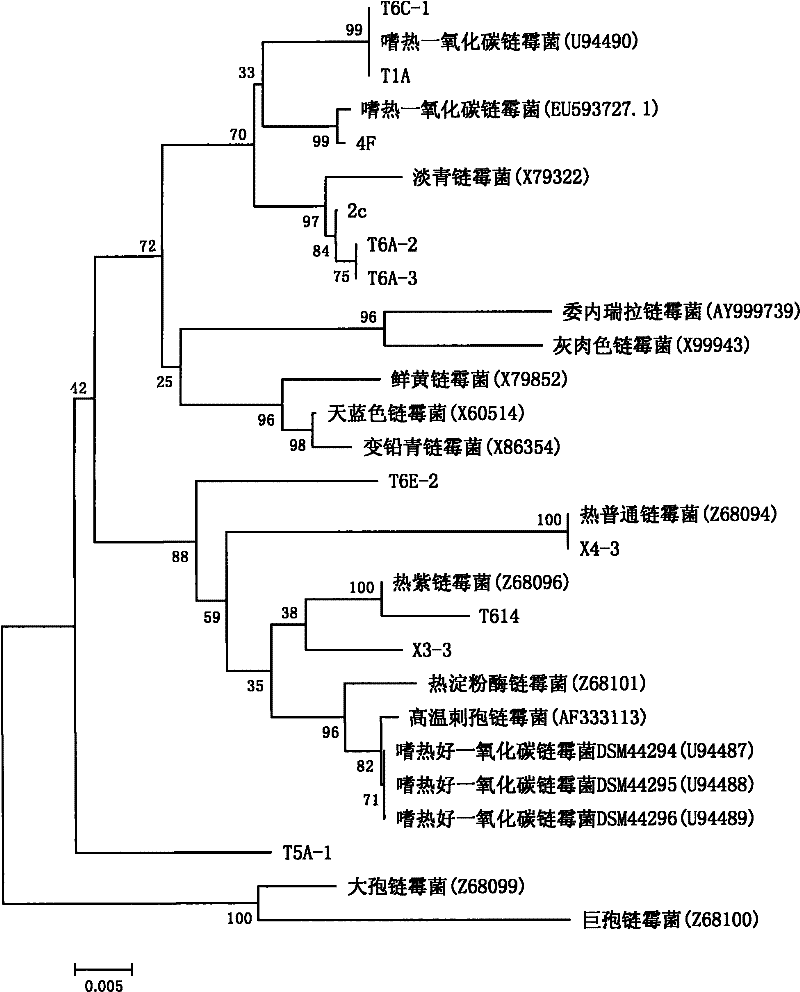
[0086] Embodiment 1, isolate and identify Streptomyces hyperthermia from soil samples of various sources
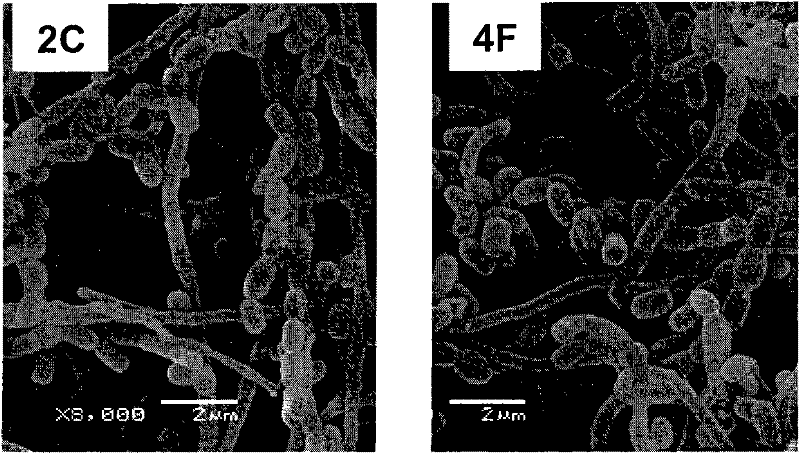
[0087] The inventor collected soil from high temperature environment sources from various places in China in summer. Streptomyces was selectively enriched and cultured with SC medium at 50°C and isolated and purified. The inventors isolated 20, 11 and 8 strains of bacteria in vegetable garden soil, weed compost and pig manure respectively. The 16S rRNA of the isolated and purified strains were amplified, cloned and sequenced. The sequence homology analysis showed that they had high homology with various Streptomyces hyperthermophilus. For example, the 16S rRNA of 2C (CCTCC M 2010091) (as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2) is 99% similar to the 16S rRNA of S. glaucescens DSM40716 (Genbank X79322.1 GI: 488843), and is 99% similar to that of S. thermocarboxydus NBRC 16323 The 16S rRNA (Genbank AB249926.1GI: 109945079) similarity was 98%. The 16S rRNA of 4F (CCTCC M 2010092) (shown as...
Embodiment 2
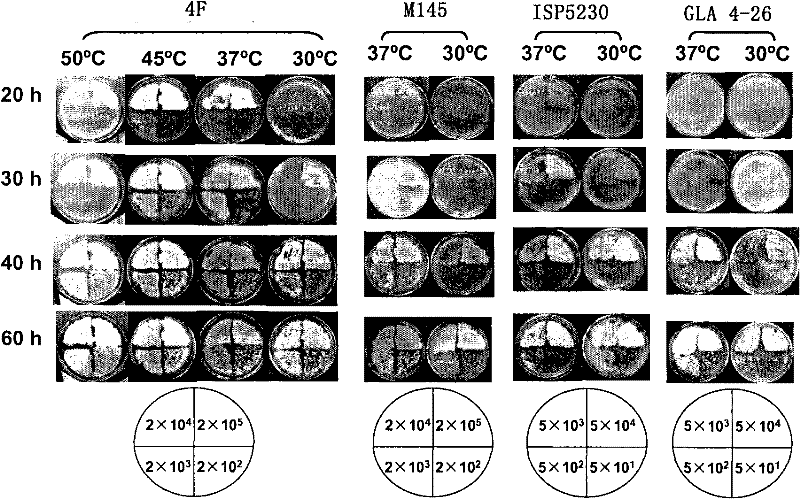
[0090] Embodiment 2, identification of 4F and 2C growth characteristics of fast-growing moderate Streptomyces thermophilus
[0091] The inventors diluted the spore suspension of the isolated Streptomyces hyperthermicus strain 10 times serially, spread it on MS medium, cultured it at 30, 37, and 45°C respectively, and took pictures and recorded observations at different time points . Such as image 3 showed that 4F grew in the temperature range of 30-50°C, respectively, while the 3 strains of mesophilic Streptomyces grew at 30°C and 37°C. 4F grows very slowly at 55°C, M145, ISP5230 and GLA 4-26 cannot grow at 45°C and 50°C. Thus 4F belongs to Streptomyces moderate thermophilus.
[0092] 4F can start sporulation in 20 hours on MS medium at 37°C and 45°C, while M145, ISP5230 and GLA 4-26 have almost no visible signs of growth at this time. The growth of 4F at 37°C or 45°C was significantly better than that at 30°C or 50°C, and ISP5230 began to produce spores at about 30 hours...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com