Multi-wavelength micro illumination device
A lighting device and light beam technology, applied in microscopes, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of multiple pulse lasers out of synchronization, limited number of wavelengths, low energy density, damage, etc., to overcome sample degeneration or even damage, and overcome the number of wavelengths Limited, overcoming desynchronization effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
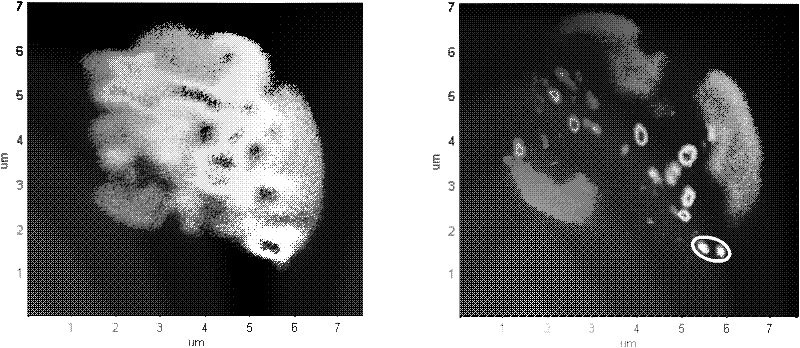
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
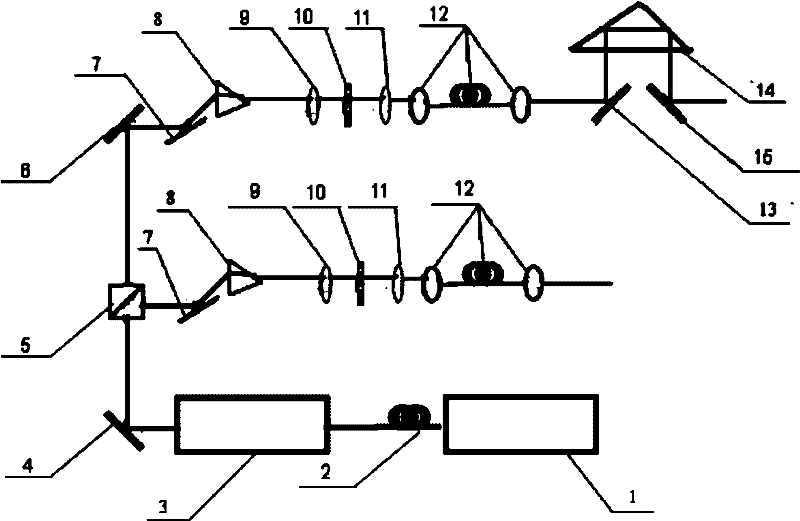
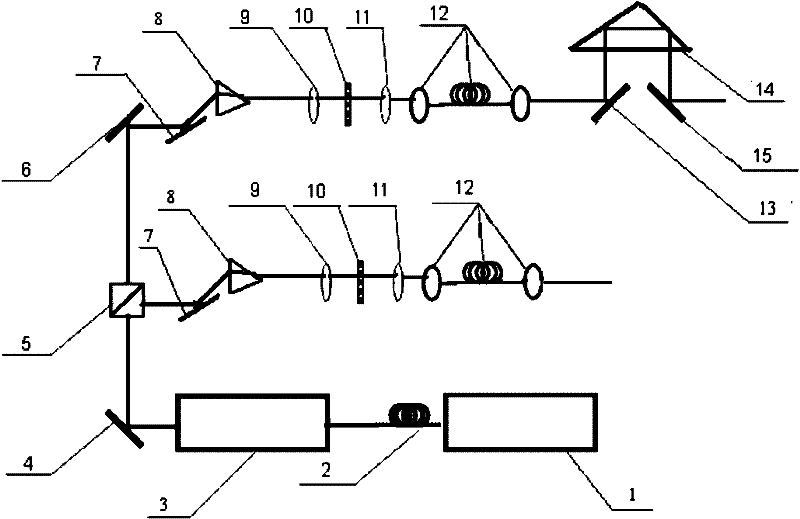
[0016] Embodiment 1, micro-illumination device
[0017] In the microscopic illumination device provided by the present invention, the laser light source output by the picosecond pulse laser 1 is incident on the nonlinear photonic crystal fiber 2 to obtain a broadband laser light source; the pulse laser output by the broadband laser light source is incident on the acousto-optic modulator 3 Above, the repetition frequency of the output laser pulse can be controlled by controlling the repetition frequency of the radio frequency pulse of the acousto-optic modulator 3, and a laser pulse beam with a suitable repetition frequency is obtained; the laser beam is coupled into the beam splitter 5 through the mirror 4 to obtain Two parallel output beams; each output beam is coupled into a wavelength selector through a reflector 7, and the wavelength selector is composed of a dispersion prism 8, a lens a9, a spatial light modulator 10, and a lens b11, and the wavelength selector is used to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com