High-temperature-resistant gene engineering bacterium for producing extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharide and application thereof
A technology of water-insoluble polysaccharides and genetically engineered bacteria, which is applied in the application field of selectively plugging high-permeability layers of high-temperature oil reservoirs, high-temperature-resistant extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharide-producing genetically engineered bacteria, and improving oil recovery. Problems such as the limitation of the scope of application in the mine field and the different performance of wild strains, etc., to achieve the effect of improving oil recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1, the construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0040] Step 1: Screening of Parental Strains
[0041] The screening method of the recipient strain JD is as follows: according to the conventional strain screening method, the water sample collected from Jilin Oilfield is diluted 10000 times, spread on the agar plate containing 4% (v / v) molasses, and cultivated at 30°C for 24h , the isolated single colonies of various microorganisms were placed in 50mL 4% molasses liquid medium, and anaerobically cultured at 30°C for 1 day to judge the production of insoluble polymers. After repeated isolation and purification, a strain was obtained JD bacteria producing water-insoluble polymers. The strain can utilize monosaccharides to synthesize extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharides at a temperature lower than 37°C.
[0042] The screening method of the donor bacteria GW is as follows: According to the conventional strain screening method, the produced water...
Embodiment 2
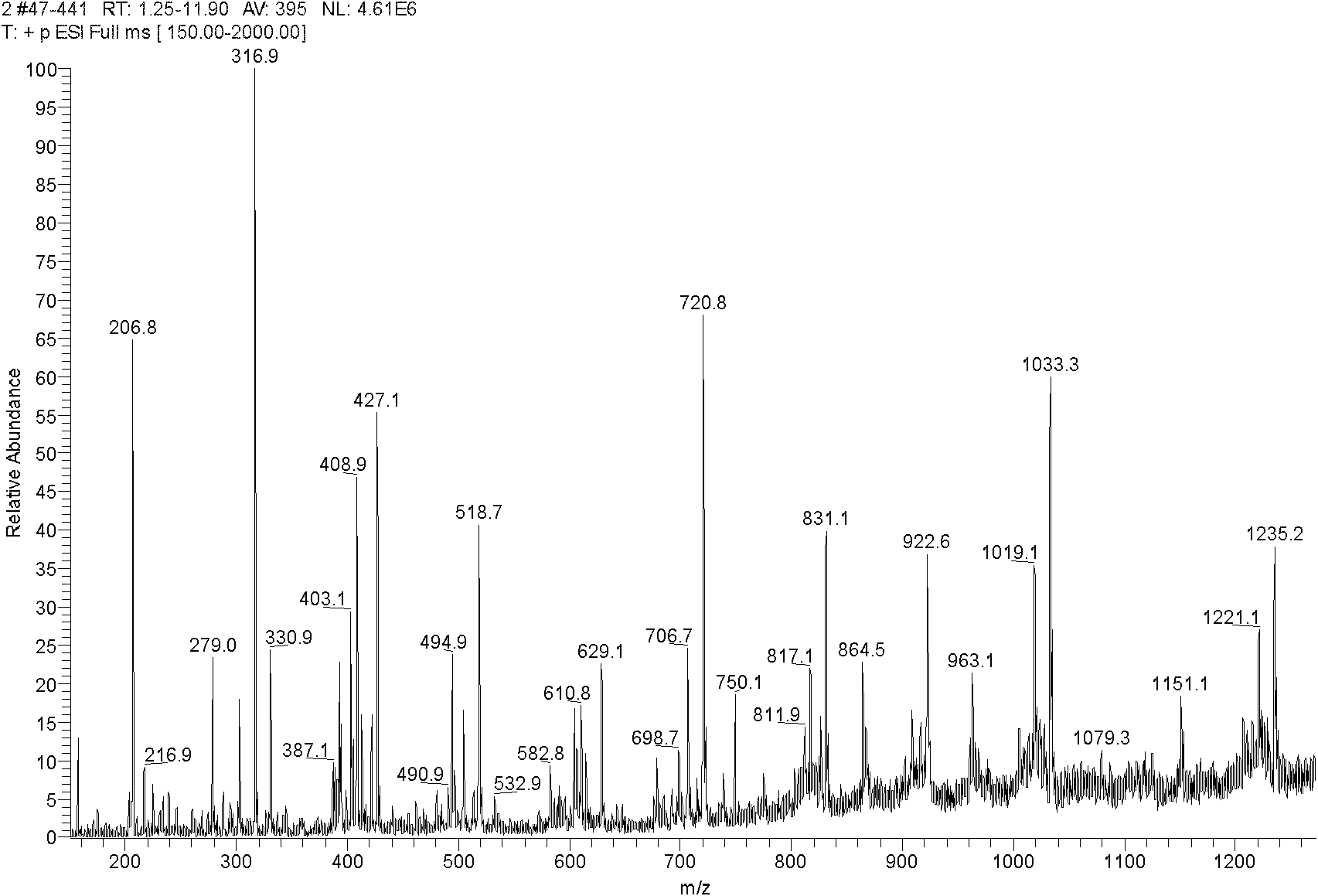
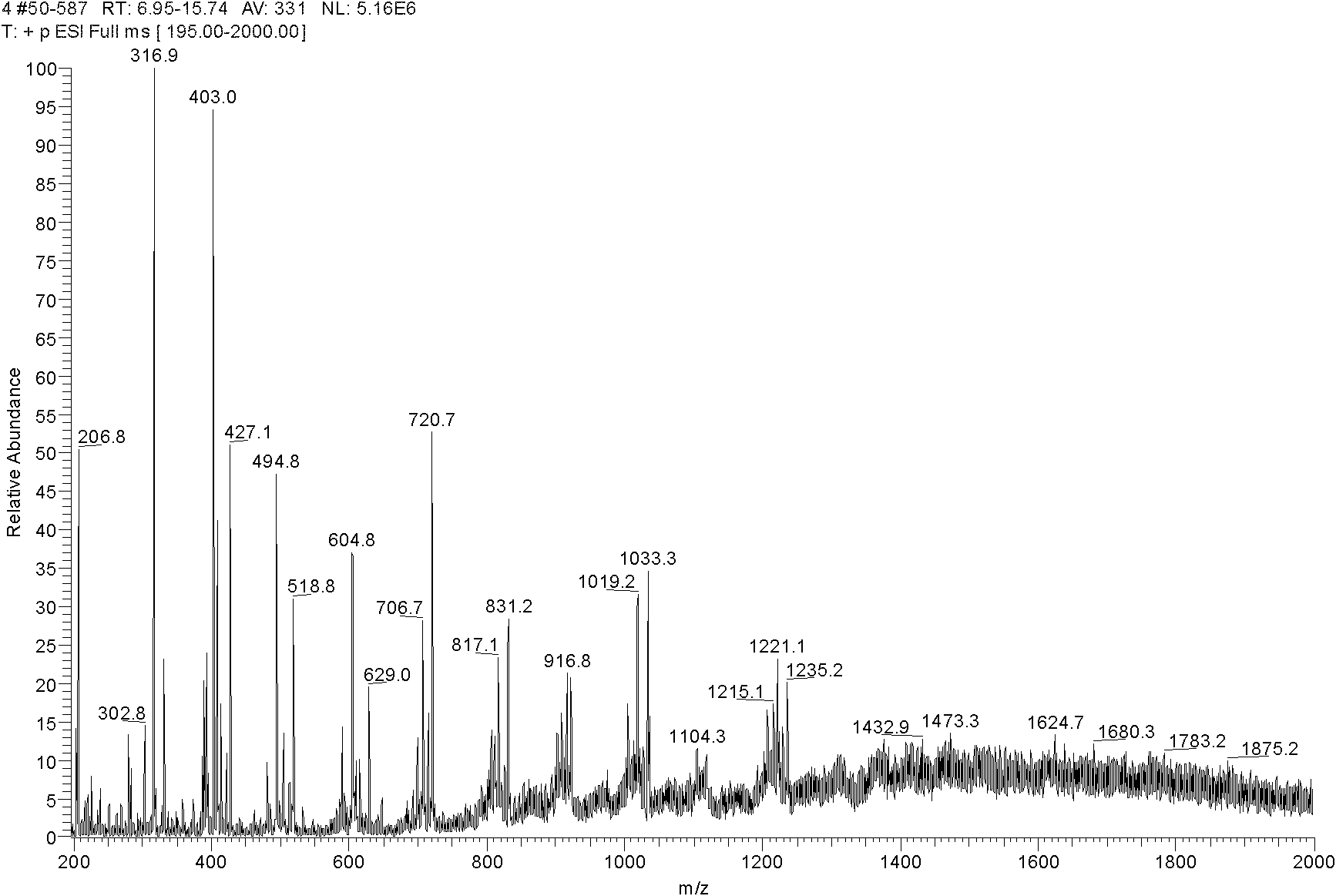
[0049] Embodiment 2, JD bacteria and genetically engineered bacteria extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharide hydrolyzate comparison
[0050] Inoculate the LB medium containing 1% (M / V) glucose with JD bacteria and genetically engineered bacteria GJ and cultivate until the end of producing extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharides, centrifuge the fermentation broth at a speed of 3000rpm for 20min, remove the supernatant, and take the centrifugal precipitate Add 2mL of 4% NaOH solution to the substance, pipette and suspend it, remove bacterial protein in a boiling water bath at 100°C for 30 minutes, then centrifuge to collect the precipitate, add an appropriate amount of neutral detergent and heat it in a water bath at 100°C for 1 hour to remove miscellaneous sugars and lipids in the precipitated substance Impurities such as species were washed repeatedly with deionized water, and after drying, cellulase was added to one third of the weight of extracellular water-insolub...
Embodiment 3
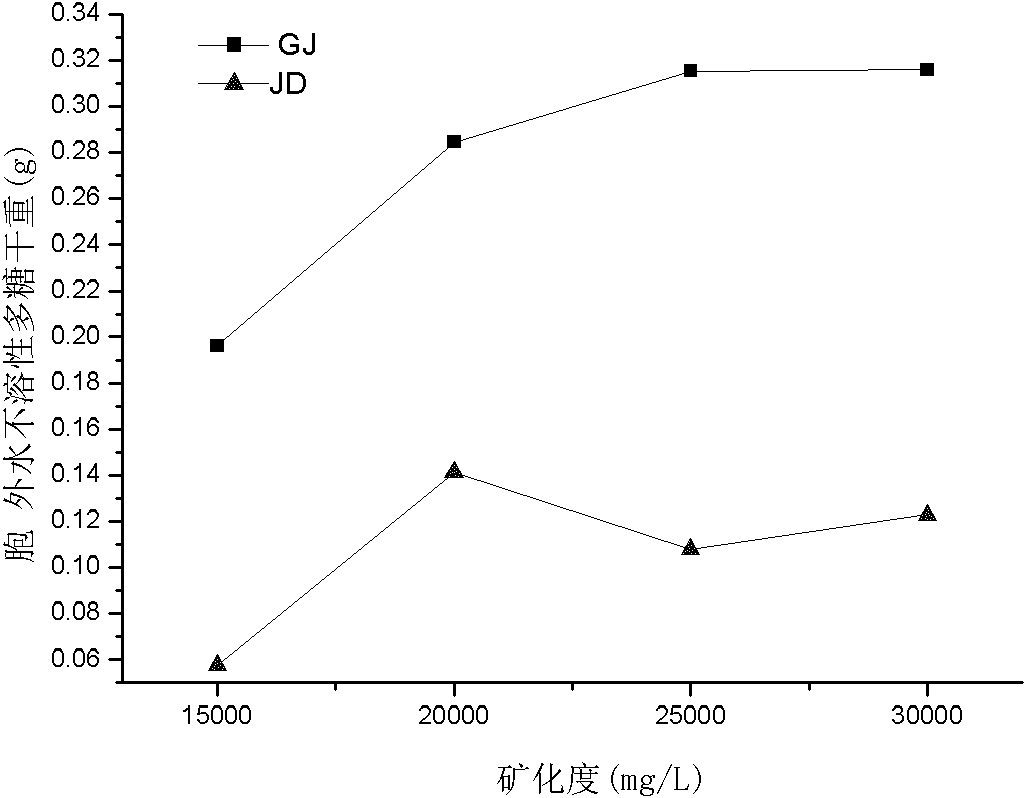
[0052] Embodiment 3, the impact of salt concentration on the extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharide produced by genetically engineered bacteria GJ
[0053] The medium is: molasses 4% (V / V), (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 0.1% (W / V), NaCl concentration gradients are 15000mg / L, 20000mg / L, 25000mg / L, 30000mg / L respectively, inoculated with activated JD and GJ, the inoculum size is 4%, the cultivation temperature of genetically engineered bacteria GJ The culture temperature of JD was 50°C, and the culture temperature of JD was 37°C, and cultured statically for 5 days.
[0054] After the cultivation, extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharides were obtained by filtering with filter paper, and weighed after drying. The effect of salt concentration on the extracellular water-insoluble polysaccharide produced by genetically engineered bacteria GJ is shown in image 3 , the genetically engineered strain GJ can still produce polysaccharides at a high salt concentration of 30,000mg / L, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com