Preparation method of composite anti-bacterium material
A compound antibacterial and ionic liquid technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, fungicides, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve the problems of toxicity, heat resistance, high price, and temperature resistance less than 200°C , to achieve the effect of increasing the thermal reaction temperature, excellent antibacterial performance and high heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
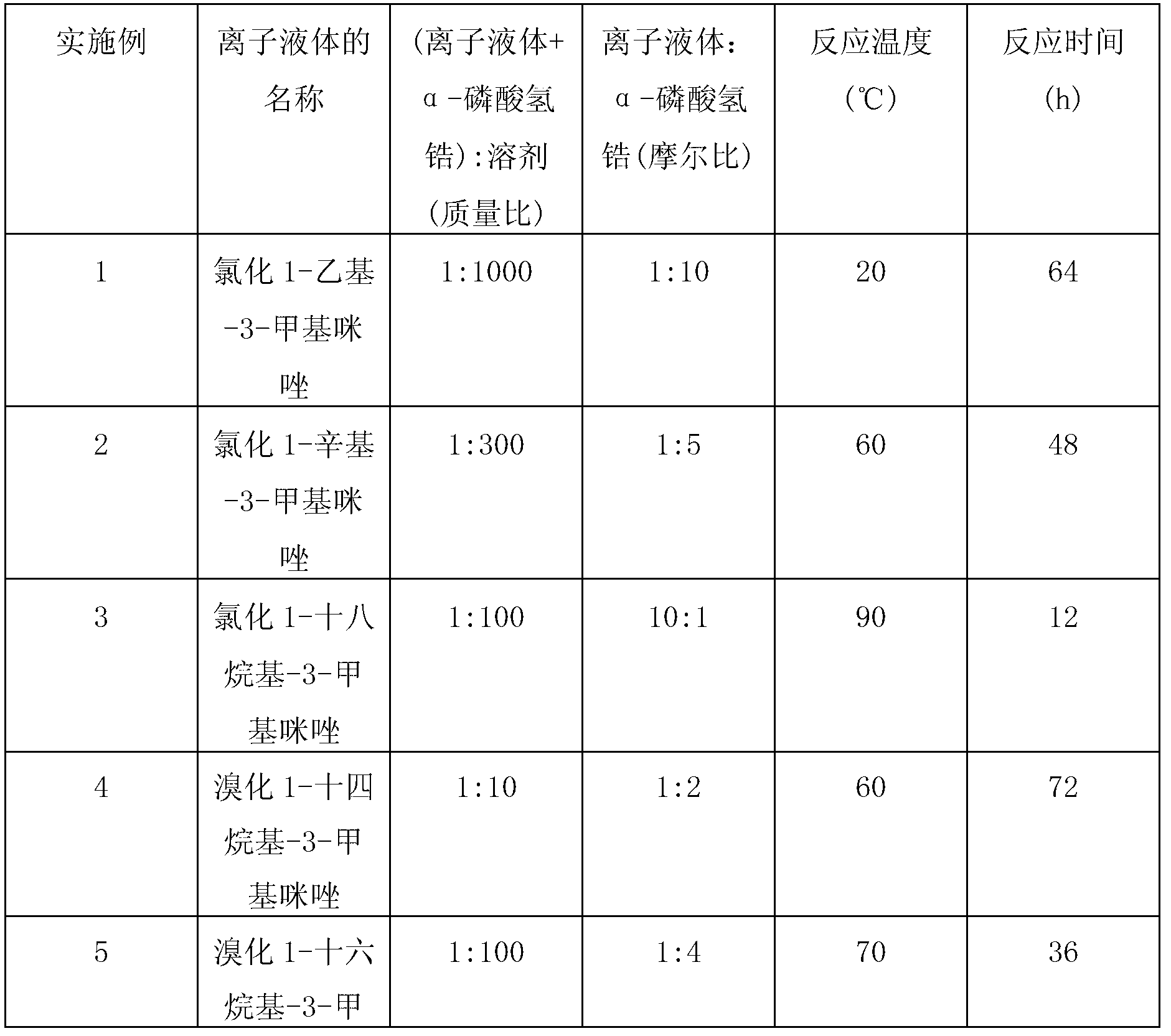
Embodiment 1
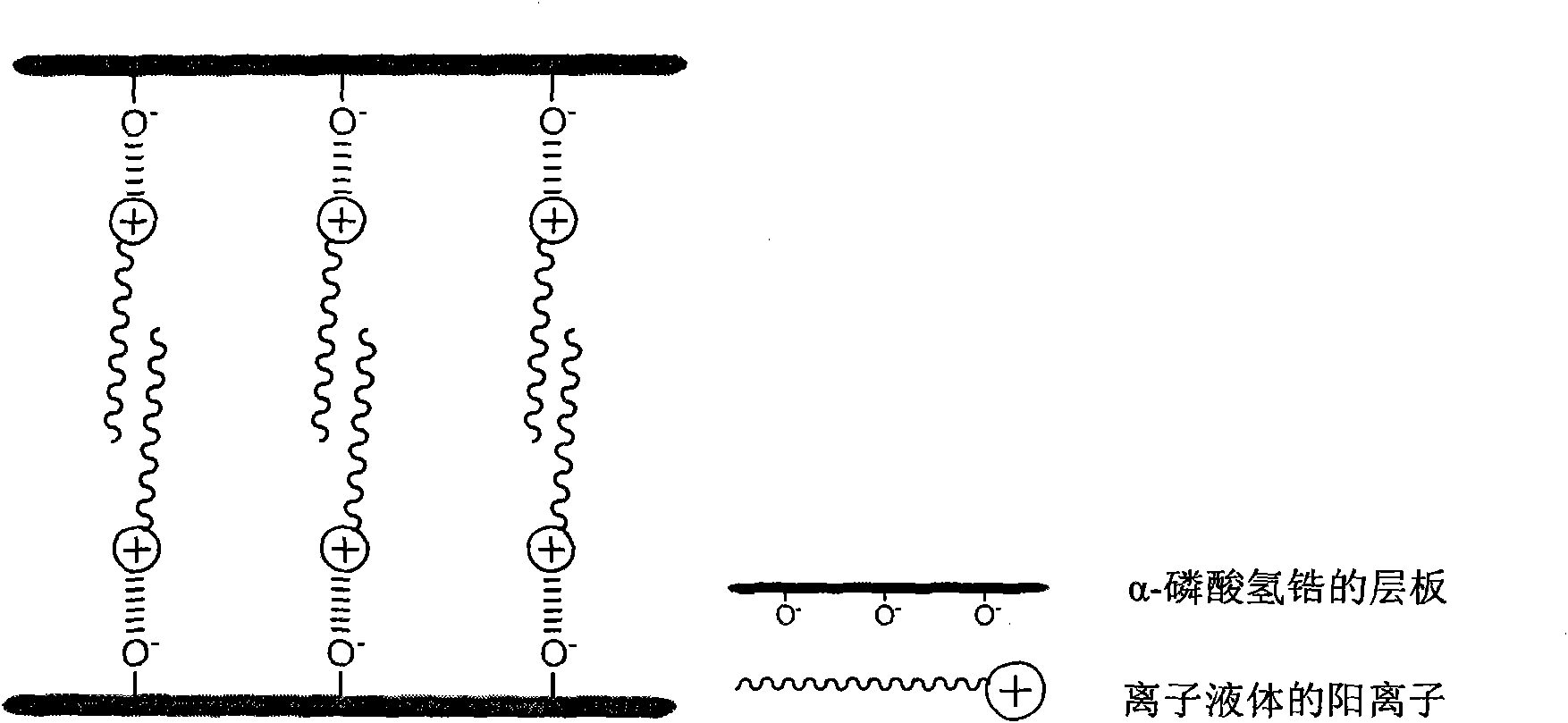
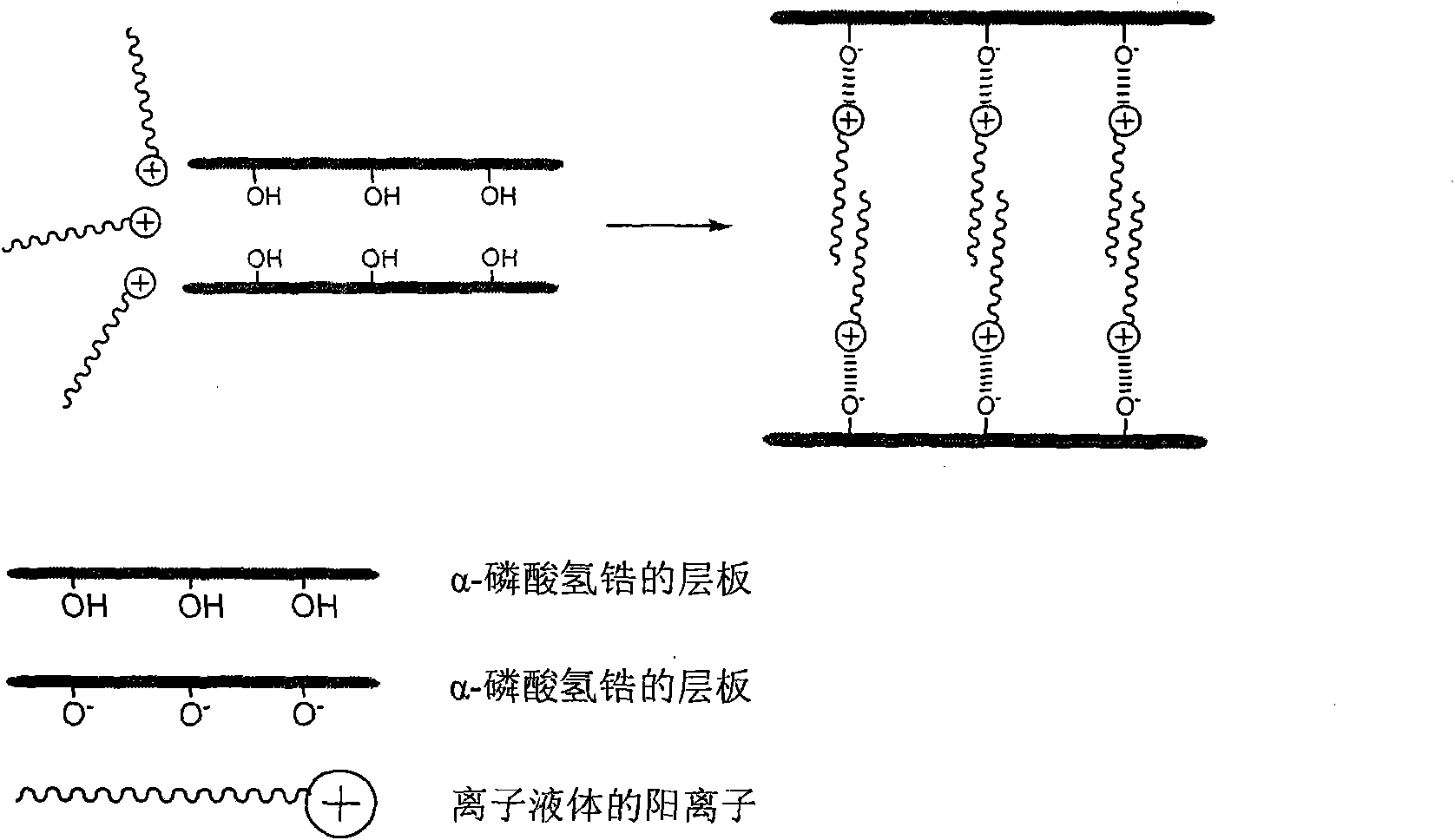
[0029] The present embodiment prepares chlorinated 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquid intercalation α-zirconium hydrogen phosphate composite antibacterial material (Zr(C) through the preparation method of the present invention n MIM) (PO 4 ) 2 ), (C n MIM) represents 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation (n is a natural number from 1 to 20), and the specific steps are as follows:
[0030] 1) According to the chlorinated 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquid (C 2 The molar ratio of MIMCl) and α-zirconium hydrogen phosphate is 1:10 to weigh.
[0031]The ionic liquid of this embodiment can also use pyridine ionic liquid, such as: 1-dodecylpyridinium chloride, or any of the following ionic liquids, such as imidazole ionic liquid, pyridinic ionic liquid, quaternary ammonium ionic liquid, quaternary Phosphorus ionic liquids, pyrrolidine ionic liquids, piperidine ionic liquids or morpholine ionic liquids are well known to those skilled in the art.
[0032] 2) The 1-ethyl-3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com