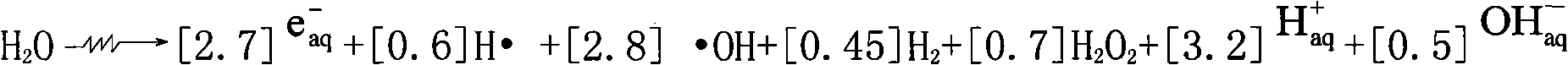Method for improving biodegradability of papermaking wastewater by using combined process of coagulation and irradiation
A technology of papermaking wastewater and combined process, which is applied in the field of nuclear technology application and environmental protection, can solve the problems of high energy consumption and large radiation dose, and achieve the effects of reducing radiation dose, improving biodegradability, and improving economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
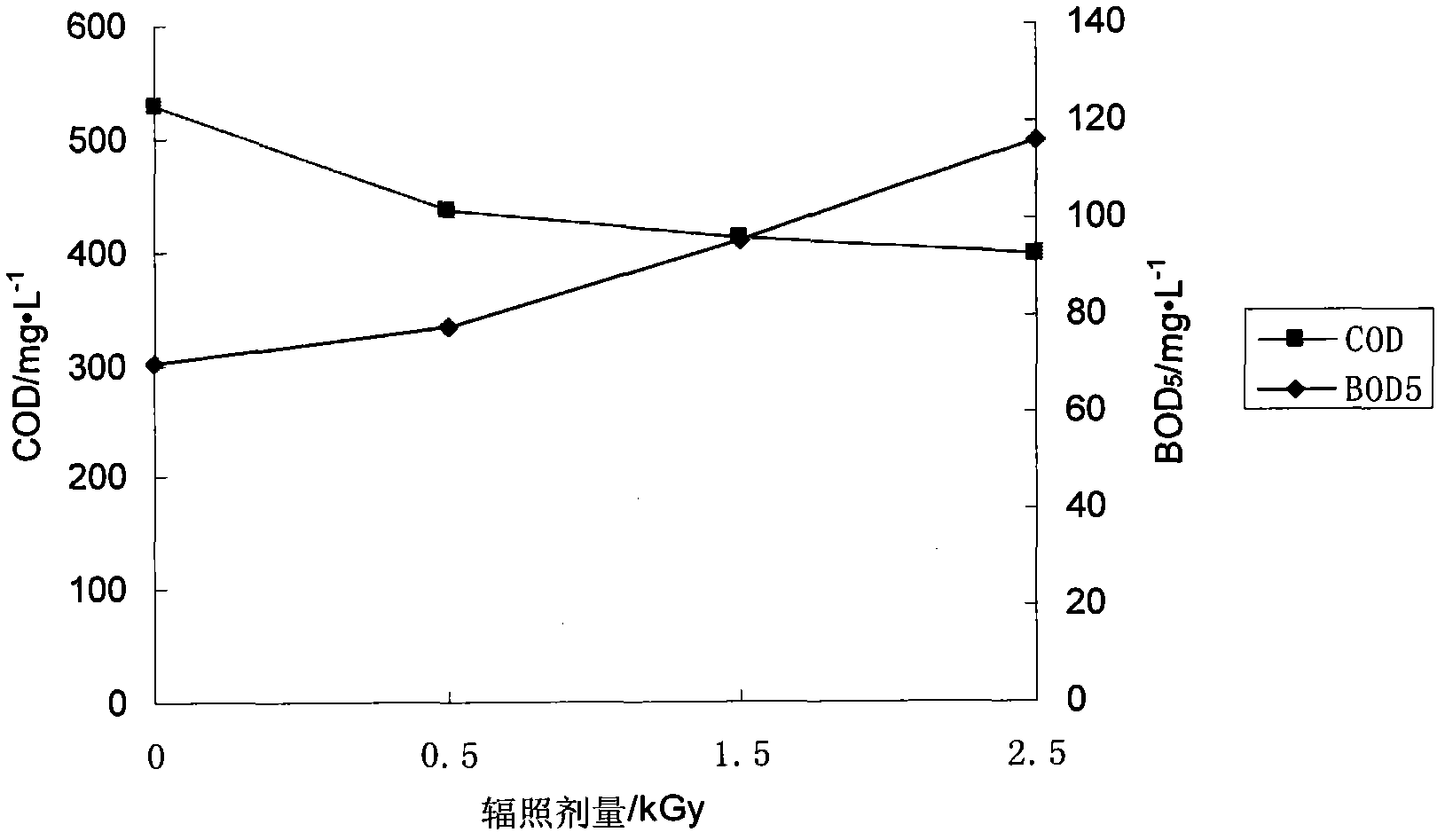
[0017] The papermaking wastewater comes from the wastewater before biochemical treatment in a sewage treatment plant of a papermaking company in Wuhan. The water quality of the wastewater is as follows: COD 722mg / L, BOD 5 427mg / L, DOC 173.6mg / L, pH 6.9. First, 300 mg of polyaluminium chloride was added to 1 liter of the waste water, and the supernatant was subjected to ionizing radiation treatment after coagulation and precipitation. 60 Co radiation device with a radioactivity of 481TBq. In the experiment, 20ml of papermaking wastewater was put into a 50ml radiation-resistant tube each time, and placed in a certain position in the irradiation field for irradiation. The irradiation time was 53-266min. Ferrous sulfate was used. The (Fricke) dosimeter measured the gamma dose rate at this position to be 9.4Gy / min. COD and BOD of papermaking wastewater by coagulation-irradiation combined process 5 see attached figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
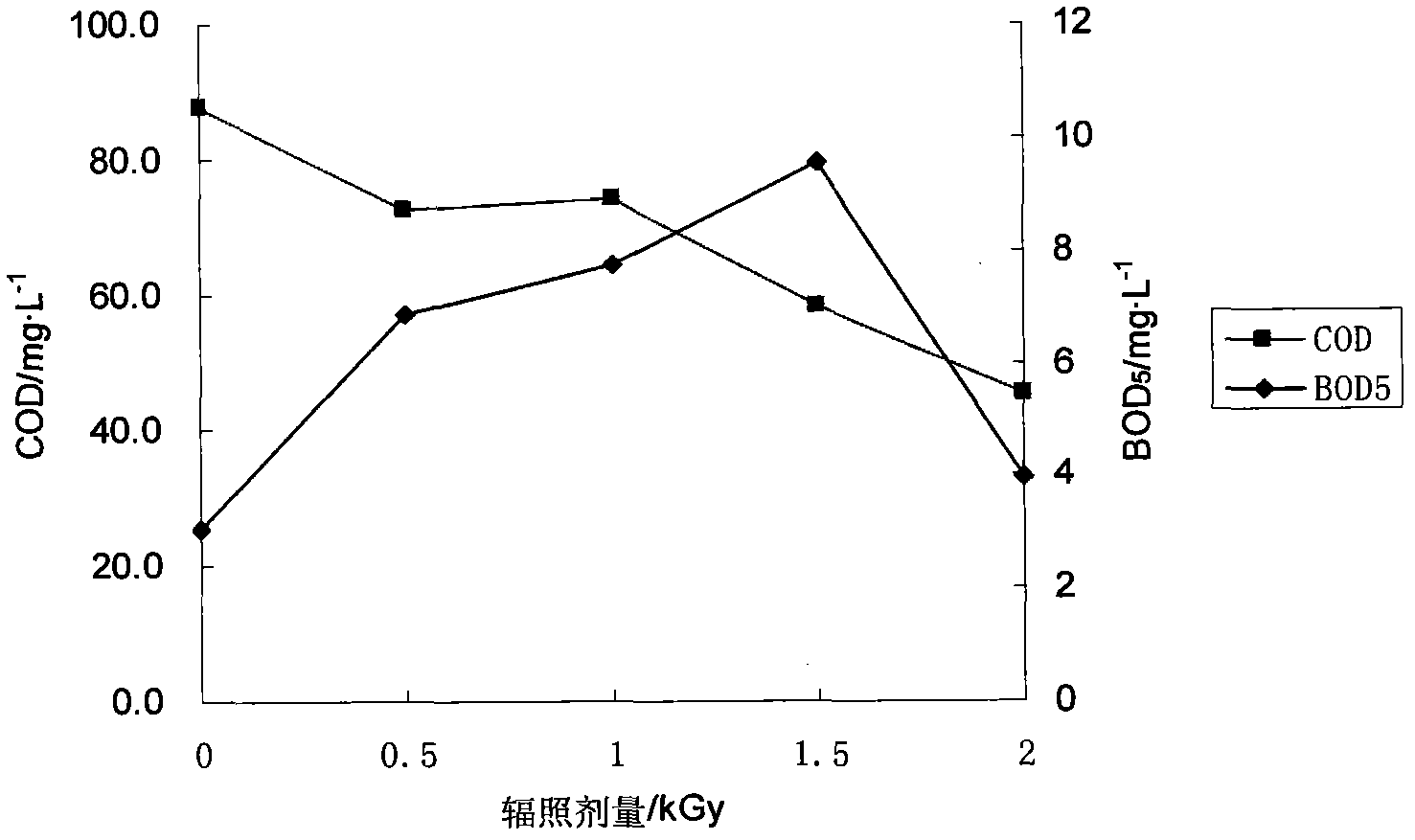
[0019] The papermaking wastewater comes from the secondary biochemical effluent of a sewage treatment plant of a papermaking company in Wuhan. The water quality of the wastewater is as follows: COD 105mg / L, BOD 5 3.05mg / L, DOC 33.4mg / L, pH 7.3. First, 300 mg of polyaluminium chloride was added to 1 liter of the waste water, and the supernatant was subjected to ionizing radiation treatment after coagulation and precipitation. 60 Co radiation device with a radioactivity of 481TBq. In the experiment, 20ml of papermaking wastewater was put into a 50ml radiation-resistant tube each time, and placed in a certain position in the irradiation field for irradiation. The irradiation time was 53-266min. Ferrous sulfate was used. The (Fricke) dosimeter measured the gamma dose rate at this position to be 9.4Gy / min. COD and BOD of secondary biochemical effluent of papermaking wastewater by combined coagulation-irradiation process 5 see attached figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0021] The papermaking wastewater comes from the wastewater before biochemical treatment in a sewage treatment plant of a papermaking company in Wuhan. The water quality of the wastewater is as follows: COD 722mg / L, BOD 5 427mg / L, DOC 173.6mg / L, pH 6.9. First, 300 mg of polyaluminium chloride was added to 1 liter of the waste water. After coagulation and precipitation, the supernatant was treated with ionizing radiation. The radiation source was a Dynamitron electron accelerator of 0.5 MeV and 40 mA, and the dose rate of the electron beam was 21.2 kGy / min. In the experiment, 20ml of papermaking wastewater was put into a 50ml radiation-resistant tube each time, and placed in a certain position in the irradiation field for irradiation. The irradiation time was 1.41-7S. COD and BOD of papermaking wastewater by combined coagulation-irradiation process 5 The impact and embodiment 1 change little.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com