Compositions and methods for enhancing amino acid levels in plants
An amino acid, plant technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as increased costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0237] Example 1: Isolation and cloning of the aspartokinase gene
[0238] The full-length coding sequence of the wild-type aspartokinase gene isolated from 30 ng of X. burgdorferi genomic DNA was amplified by PCR using oligonucleotide primers SEQ ID NO: 11 and SEQ ID NO: 12. Use Expand TM High-fidelity PCR kit (Boehringer Mannheim, Germany), PCR was performed in a total volume of reaction mixture of 50 μl. PCR conditions were as follows: 1 cycle of 4 minutes at 95°C; 26 cycles of 1 minute at 95°C, annealing at 56°C for 1 minute, and extension at 72°C for 2 minutes; 1 cycle. The resulting product was digested with appropriate restriction enzymes (NdeI and XhoI), gel-purified, and ligated into the corresponding sites in pET30a (Novagen), resulting in plasmid pMON81662 ( image 3 ; XbAK). The integrity of the gene sequence was confirmed by DNA sequence analysis.
Embodiment 2
[0239] Example 2: Identification of novel aspartokinase genes encoding variants with desirable enzymatic properties
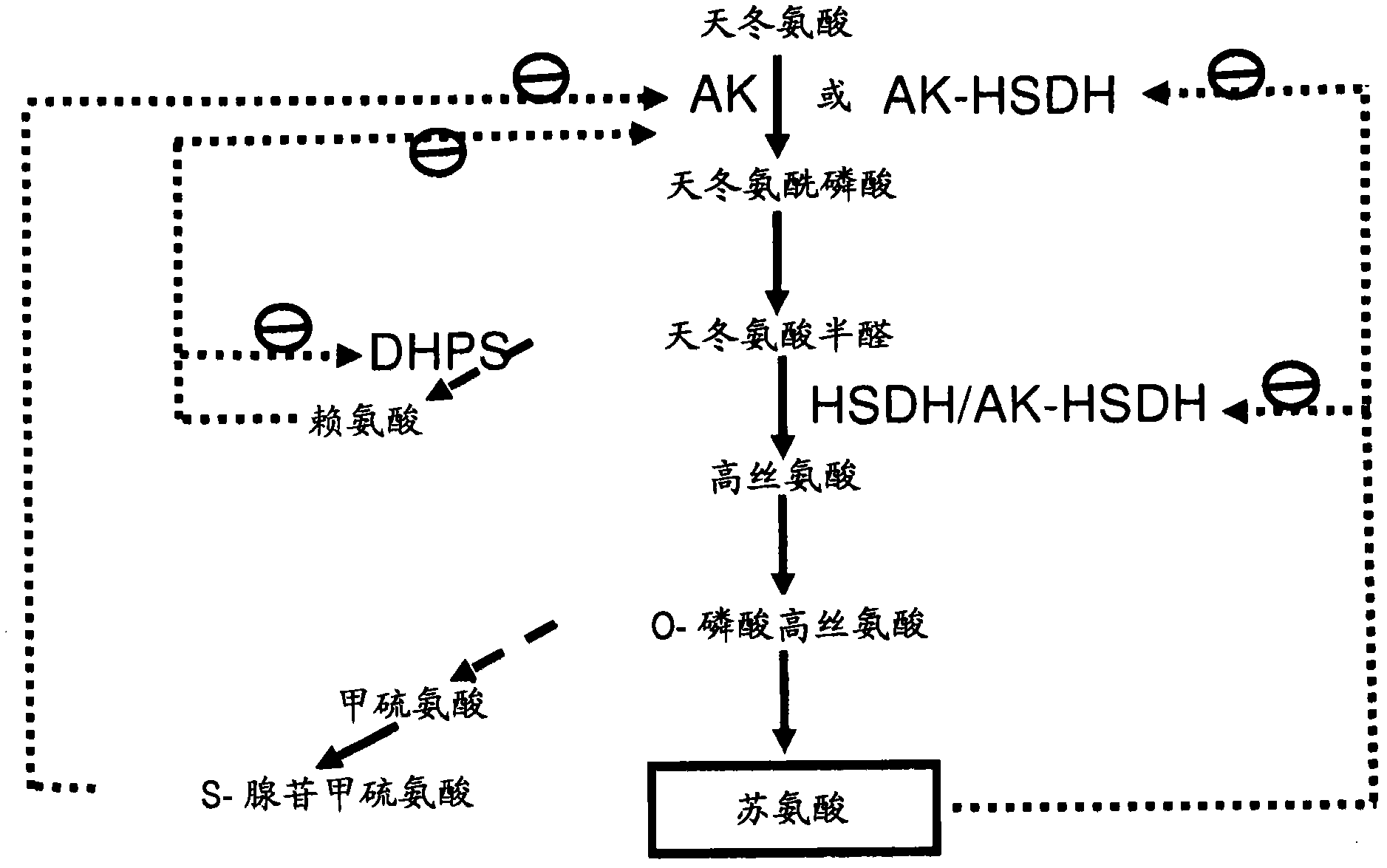
[0240] This example illustrates the identification of an AK gene encoding an enzyme with desirable enzymatic properties, ie, insensitivity to end-product inhibition by aspartic acid family amino acids and good kinetic properties. In order to characterize the AK variants, using recombinant E. coli lysC and E. coli T352I lysC (SEQ ID NO: 17) gene products as controls, a recombinant expression system and AK enzyme analysis were established. The E. coli lysC gene product is known to be sensitive to feedback inhibition by Lys, whereas the E. coli T352 IlysC gene product is known to be insensitive to lysine. Expression in plants of the E. coli T352I lysC gene product with aspartokinase activity resulted in a 6-7% increase in threonine content in seeds (Karchi, et al., THE PLANT J.3:721-727 (1993 ); Galili, et al., European Patent Application No. 0485970). The lysC ...
Embodiment 3
[0293] Example 3: Construction of Soybean Transformation Vectors Containing Feedback-Insensitive Aspartokinase Coding Sequences and Transformation into Soybean Plants
[0294] Six soybean transformation vectors (listed in Table 3) containing wild-type and mutant alleles of the X. burgdorferi AK gene were constructed and transformed into soybean.
[0295] Table 3. Soybean Transformation Vectors Containing Aspartokinase Coding Sequences
[0296] pMON number
pMON101817
CTP1-Pathogenus burgdorferi AK
pMON101818
CTP1-Pathogenus burgdorferi AK E257K
pMON101819
CTP1-Pathogenus burgdorferi AK T359I
pMON101820
CTP1-Pathogenus burgdorferi AK T359I
pMON101821
CTP1 - Pathogen burgdorferi AK T359I - non-native
pMON101822
CTP1 - Pathogen burgdorferi AK T359I - non-native
[0297] The coding sequence for CTP1 (SEQ ID NO: 13) was incorporated at the N-terminus of the bacterial protein to target...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com