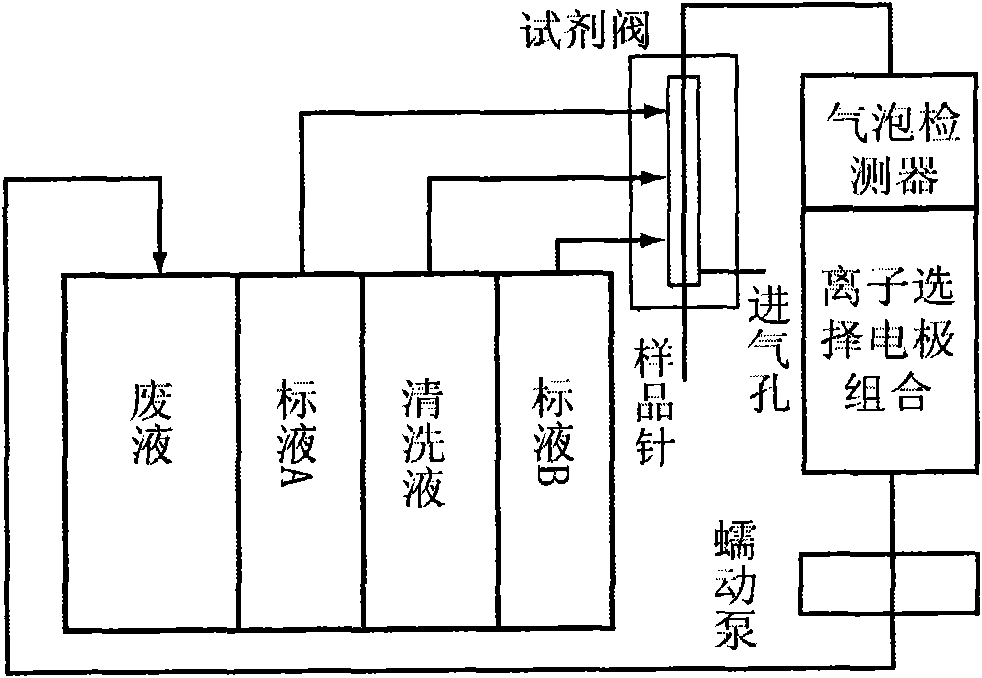
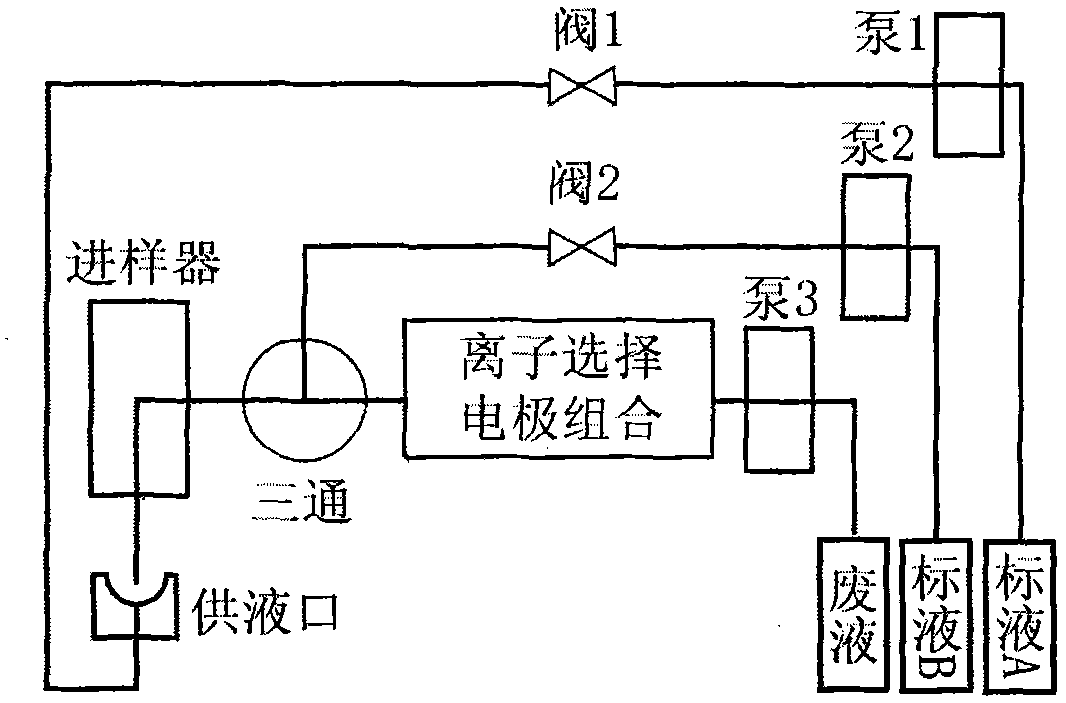
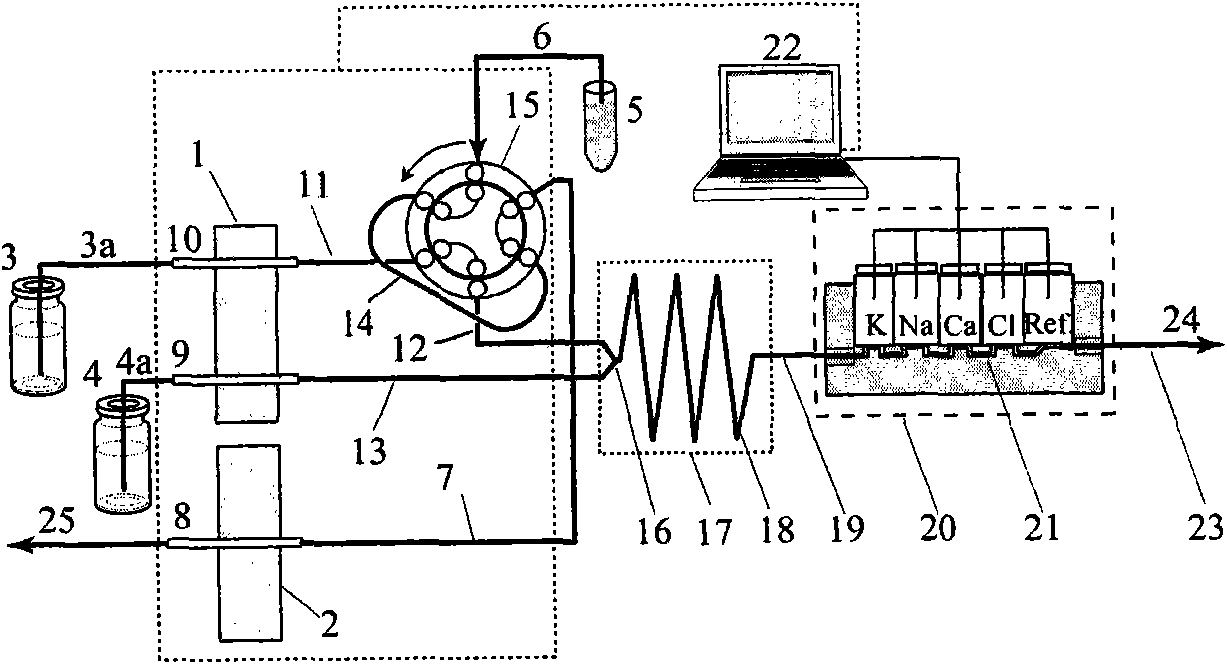
Flow injection serially connected microelectrode electrochemical automatic method and device for simultaneous measurement of various electrolytes in blood sample
A flow injection, electrochemical technology, applied in the field of clinical electrolyte analysis, can solve the problems of increased measurement result error, high instrument cost, increased components and control steps, etc., to reduce sampling and measurement errors, eliminate cross-contamination, and reduce operations. effect of steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Utilize the dual-pipeline "positive pressure" flow path system of the present invention (see image 3 ) For the three serum samples K + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Simultaneous measurement was performed. Experimental conditions: acidity regulator (4) is 100mmol L -1 Na 2 B 4 O 7 -H 3 BO 3 (pH7.4), carrier current (3) is 0.25mmol L -1 K + , 48.6mmolL -1 Na + , 2.5mmol L -1 Cl - And 0.25mmol L -1 Ca 2+ Electrolyte mixed standard solution; the mixing coil (8) uses a PTFE tube with a length of 30 cm and an inner diameter of 0.5 mm; the volume of the sampling ring (6) is 45 μL; the flow electrochemical detector (4) is K + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Miniature flow-through electrode series detector; computer automatic control and recording unit (5) is self-programmed.
[0043] K obtained + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Standard curve such as Figure 5 As shown, for the three serum samples K + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ The measurement data and the standard recovery experiment are shown in Table 1 and 2. It can b...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Using the dual-pipeline "negative pressure" flow path system to analyze the K in three serum samples + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Simultaneous measurement was performed. The experimental conditions are the same as the double-pipeline "positive pressure" flow path system. Na obtained + / K + / Cl - / Ca 2+ The standard curves are respectively: ΔE=0.08C Na +6.22, ΔE=3.68C K +21.91, ΔE=-0.22C Cl -28.013, ΔE=6.71C Ca +2.64, for K in three serum samples + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ The measurement data and the standard recovery experiment are shown in Tables 3 and 4. It can be seen that the recovery rate is between 96-105%; it can be seen that the dual-pipeline "negative pressure" flow path system can fully meet the requirements of clinical electrolyte determination.
[0051] Table 3. FI-ME-ECA system to determine K in blood samples + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Content result (dual pipeline "negative pressure" flow path system)
[0052]
[0053] *According to the result obtained by logarithmic equation...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Utilize the single pipeline "positive pressure" flow path system of the present invention (see Figure 4 ) For the three serum samples K + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Simultaneous measurement was performed. Experimental conditions: total ionic strength adjustment buffer (11) is 23mmol L -1 Na 2 B 4 O 7 -H 3 BO 3 (pH7.4), 0.25mmol L -1 K + , 48.6mmolL -1 Na + , 2.5mmol L -1 Cl - And 0.25mmol L -1 Ca 2+ The mixing coil (8) uses a PTFE tube with a length of 30cm and an inner diameter of 0.5mm; the volume of the sampling ring (6) is 45μL; the flow-through electrochemical detector (4) is K + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Miniature flow-through electrode series detector; computer automatic control and recording unit (5) is self-programmed.
[0058] Table 5. FI-ME-ECA system to determine K in blood samples + / Na + / Cl - / Ca 2+ Content result (single pipeline "positive pressure" flow path system)
[0059]
[0060] *According to the result of logarithmic equation (ΔE=27.89lgK + +5.69; ΔE=38.01lg Na ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com