Ferrite heat resisting steel and manufacture method thereof
A manufacturing method and technology of heat-resistant steel, applied in the field of ferritic heat-resistant steel and its manufacturing, can solve the problems of reducing the impact toughness of materials, and achieve the effects of good thermal oxidation resistance, good durable strength, and good impact toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
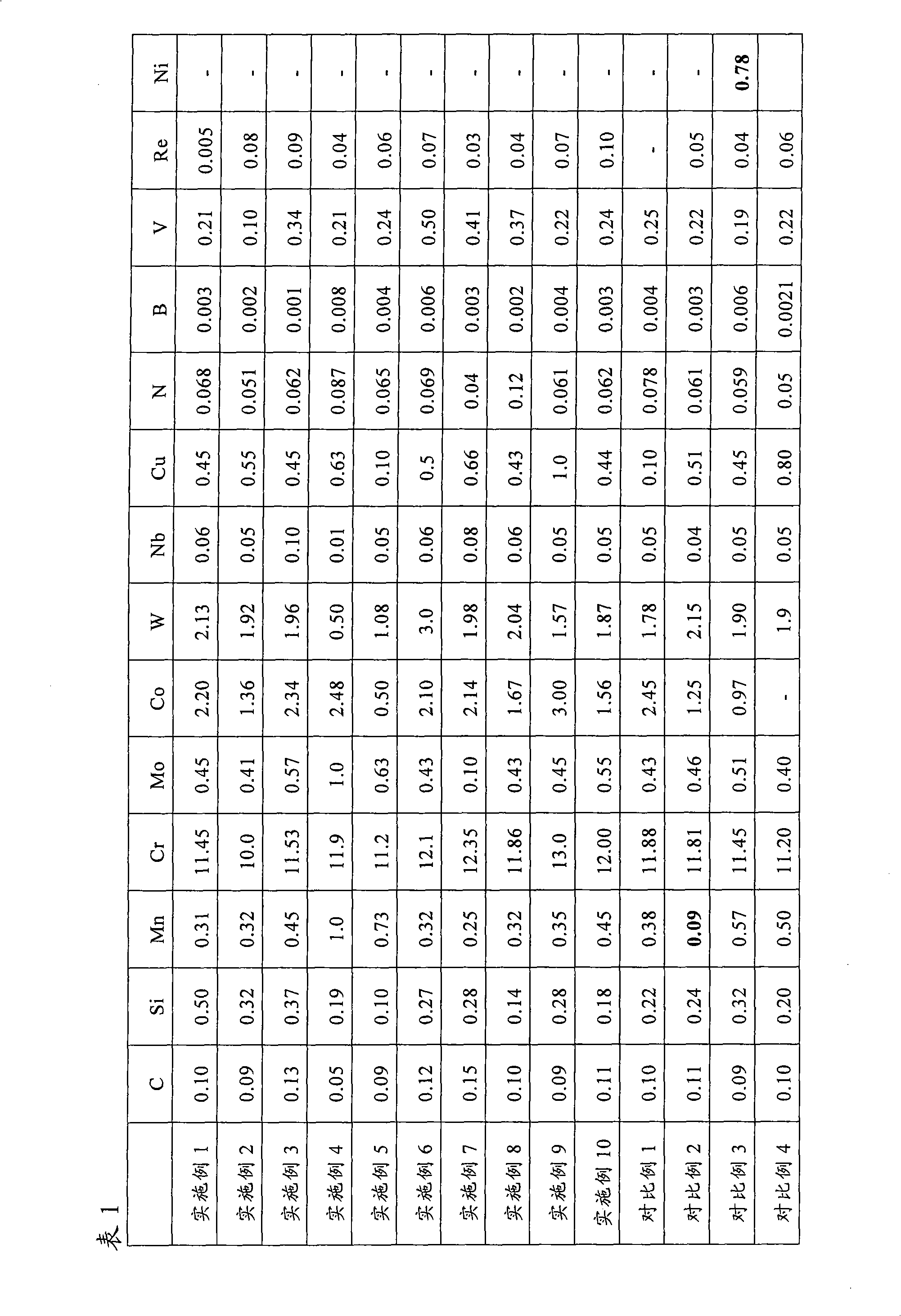
[0028] According to the composition of Example 1 in Table 1, the laboratory molten steel of 50Kg Example 1 was obtained in a vacuum smelting furnace and cast into an ingot.
[0029] The obtained steel ingot was heated to 1180 degrees, then forged into a steel plate with a thickness of 50 mm, air-cooled, then heated to 1180 degrees, and rolled into a steel plate with a thickness of 14 mm.
[0030]The steel plate is subjected to 1080-degree normalizing treatment and 780-degree tempering treatment.
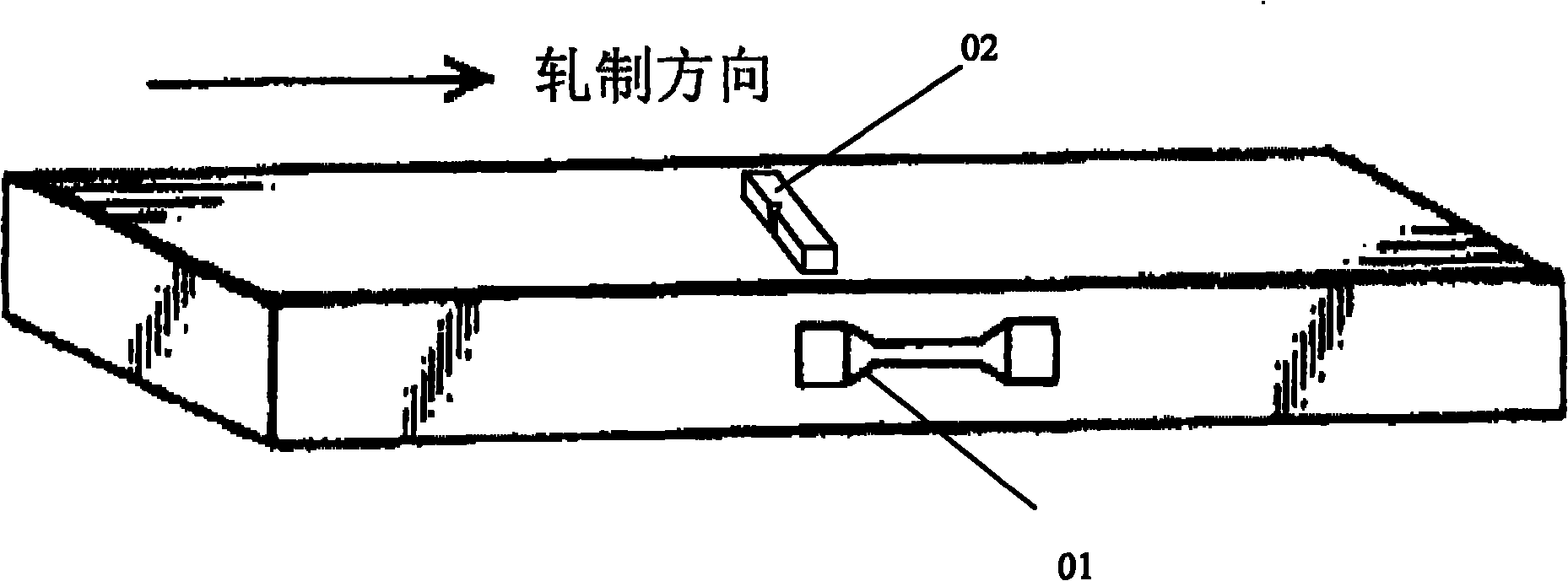
[0031] according to figure 1 As shown, samples were taken along longitudinal direction 01 for room temperature impact test, samples were taken along rolling direction 02 for durability tests at 650°C, 140Mpa and 650°C, 100Mpa, and impact tests were carried out at 0°C after aging treatment at 650°C for 5000 hours. The results are shown in Table 2.
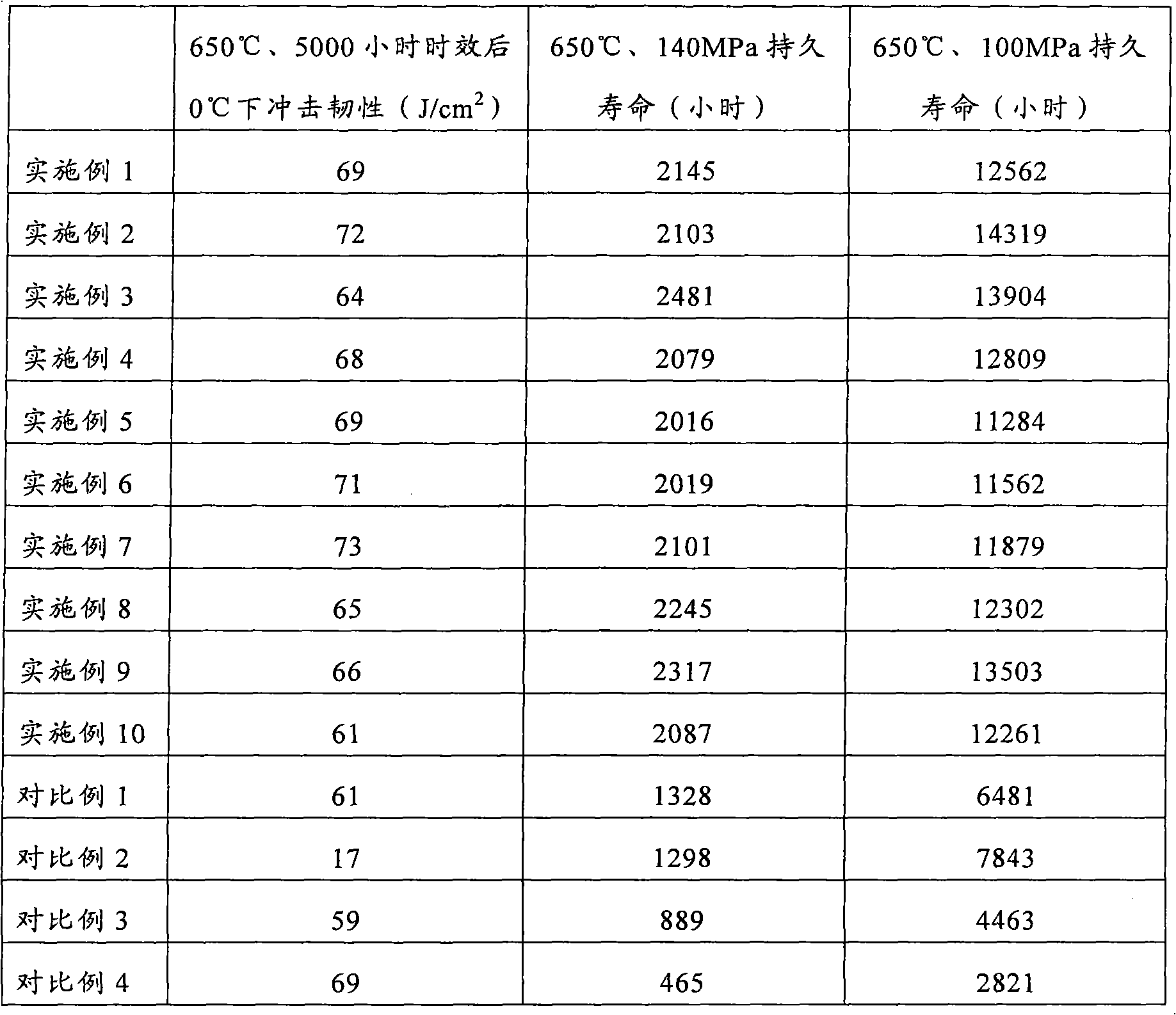
[0032] It can be seen from Table 2 that the durable life of the steel in this example reaches 2145 hours at 650°C and 140Mpa; the durab...
Embodiment 2
[0034] According to the composition of Example 2 in Table 1, the laboratory molten steel of 50Kg Example 2 was obtained in a vacuum smelting furnace and cast into an ingot.
[0035] The obtained steel ingot was heated to 1180 degrees, then forged into a steel plate with a thickness of 50 mm, air-cooled, then heated to 1180 degrees, and rolled into a steel plate with a thickness of 14 mm.
[0036] The steel plate is subjected to 1080-degree normalizing treatment and 780-degree tempering treatment.
[0037] according to figure 1 As shown, samples were taken along longitudinal direction 01 for room temperature impact test, samples were taken along rolling direction 02 for durability tests at 650°C, 140Mpa and 650°C, 100Mpa, and impact tests were carried out at 0°C after aging treatment at 650°C for 5000 hours. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0038] It can be seen from Table 2 that the durable life of the steel in this embodiment reaches 2103 hours at 650°C and 140Mpa; the d...
Embodiment 3
[0040] According to the composition of Example 3 in Table 1, the laboratory molten steel of 50Kg Example 3 was obtained in a vacuum smelting furnace and cast into an ingot.
[0041] The obtained steel ingot was heated to 1180 degrees, then forged into a steel plate with a thickness of 50 mm, air-cooled, then heated to 1180 degrees, and rolled into a steel plate with a thickness of 14 mm.
[0042] The steel plate is subjected to 1080-degree normalizing treatment and 780-degree tempering treatment.
[0043] according to figure 1 As shown, samples were taken along longitudinal direction 01 for room temperature impact test, samples were taken along rolling direction 02 for durability tests at 650°C, 140Mpa and 650°C, 100Mpa, and impact tests were carried out at 0°C after aging treatment at 650°C for 5000 hours. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0044] It can be seen from Table 2 that the durable life of the steel in this embodiment reaches 2481 hours at 650°C and 140Mpa; the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com