Method for biosynthesizing astaxanthin by using exponential intermittent feed supplement mode
A biosynthesis and astaxanthin technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low natural astaxanthin output, competition, and high production costs, and achieve high promotion and application value, increase output, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
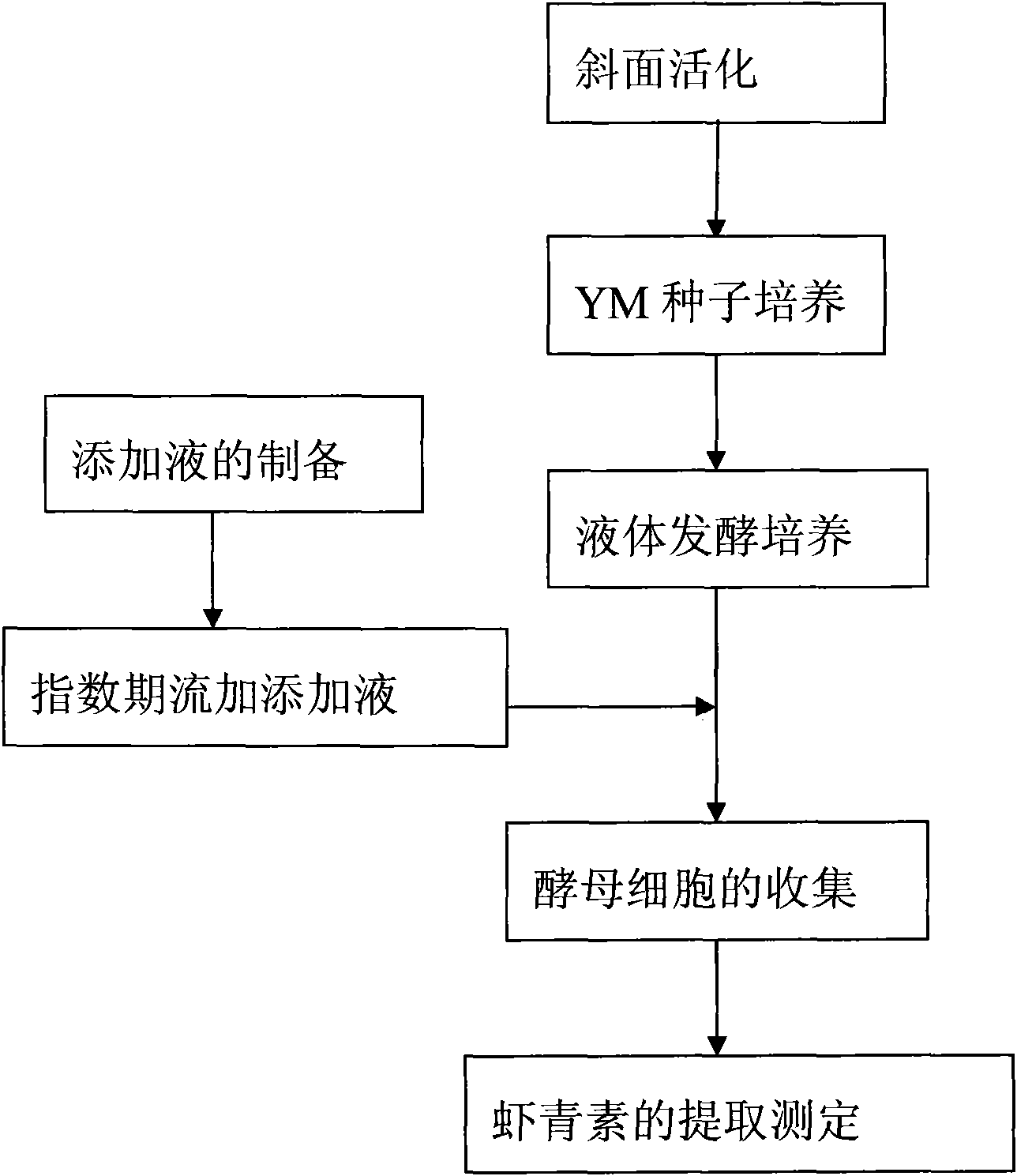
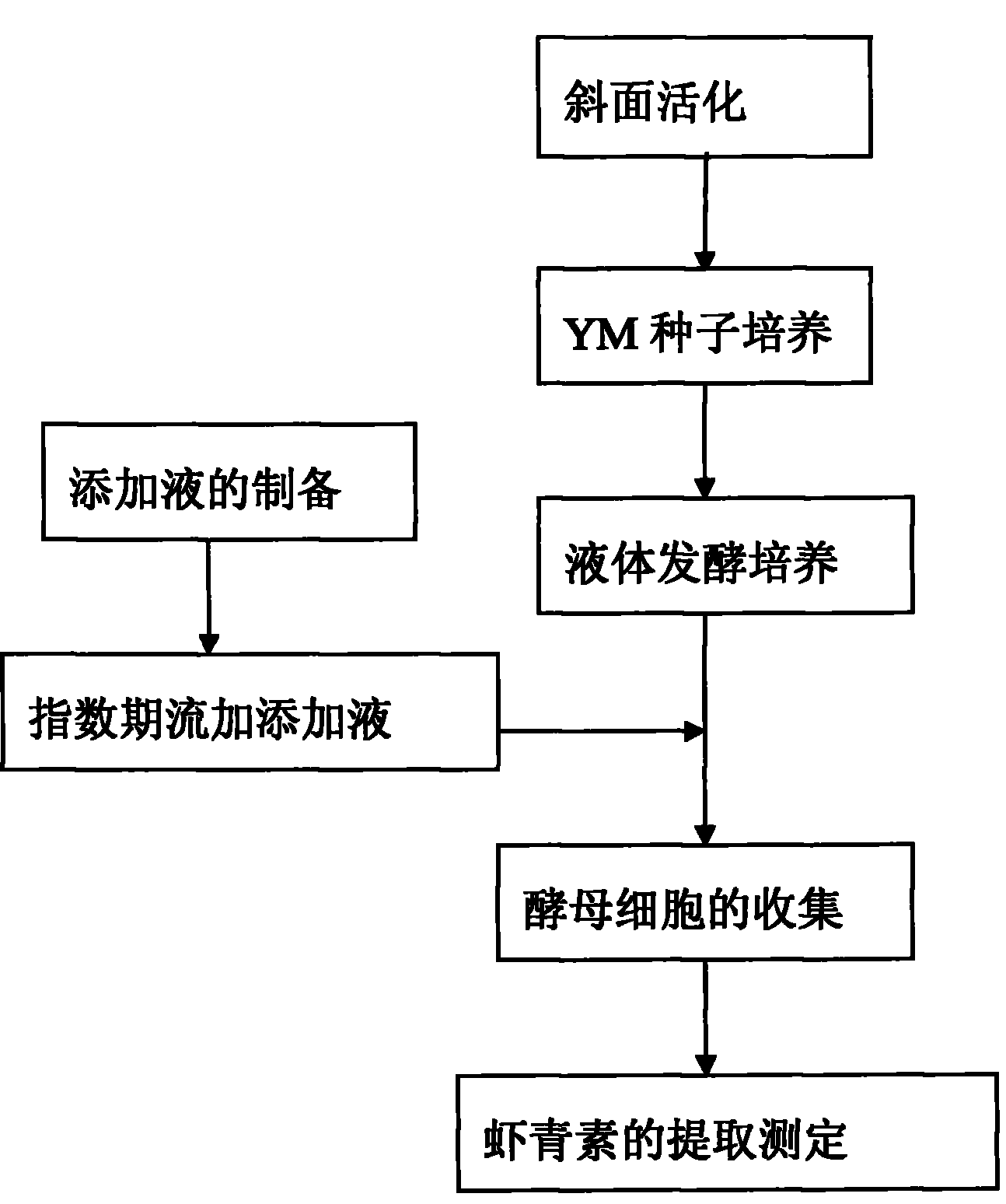
[0028] A. Selection of raw materials: select fresh and ripe tomatoes containing astaxanthin synthesis precursors, wash, cut into pieces, squeeze the juice, and filter. The filtrate was sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, and stored at 4°C for later use.
[0029] B. Activation of strains: The strains preserved on the slant were activated and cultivated on the YM slant medium at 23°C, and cultured in the YM medium at 23°C with liquid ventilation.
[0030] C. Liquid culture: the YM seed liquid was cultured at 23° C. for 36 hours in a liquid medium with an inoculum amount of 8%.
[0031] D. Fed-batch feeding of precursor-rich additive solution: After 36 hours of fermentation, 1% tomato juice was added every 12 hours. After two consecutive additions, feed feeding was stopped and culture continued for 36 hours.
[0032] E. Extraction of astaxanthin: determination of astaxanthin content in Phaffia rhodozyme.
[0033] The resulting cyanin content was increased by 91% compared with t...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Get carrot and implement by A, B steps in example 1.
[0036] C. Liquid culture: the YM seed liquid was cultured at 22° C. for 24 hours in a liquid medium with an inoculum amount of 10%.
[0037] D. Fed-batch feeding of precursor-rich additive solution: After 24 hours of fermentation, 0.5% carrot juice was added every 6 hours. After three consecutive additions, feed feeding was stopped and culture continued for 24 hours.
[0038] E. Extraction of astaxanthin: determination of astaxanthin content in Phaffia rhodozyme.
[0039] The resulting cyanin content was increased by 27% compared with the control group.
Embodiment 3
[0041] A. Take corn flour for gelatinization, then sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, and store it at 4°C for later use.
[0042] B. Activation of strains: the strains preserved on the slant were activated and cultivated on the YM slant medium at 24°C, and cultured in the YM medium at 24°C with liquid ventilation.
[0043] C. Liquid culture: the YM seed liquid was cultured at 24° C. for 48 hours in a liquid medium with an inoculum amount of 12%.
[0044] D. Feed-feeding of precursor-rich additive solution: After 48 hours of fermentation, 2% corn steep liquor was added every 3 hours. After 4 consecutive additions, feed-feeding was stopped and culture continued for 48 hours.
[0045] E. Extraction of astaxanthin: determination of astaxanthin content in Phaffia rhodozyme.
[0046] The resulting cyanin content was increased by 47% compared with the control group.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com