Method for producing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid
A technology of hydroxybutyric acid and hydroxyacid dehydrogenase, which is applied in the field of producing D-α-hydroxybutyric acid and α-ketobutyric acid, can solve the problems of low enantiomeric excess rate and achieve simple separation and low cost Inexpensive, easy-to-get results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
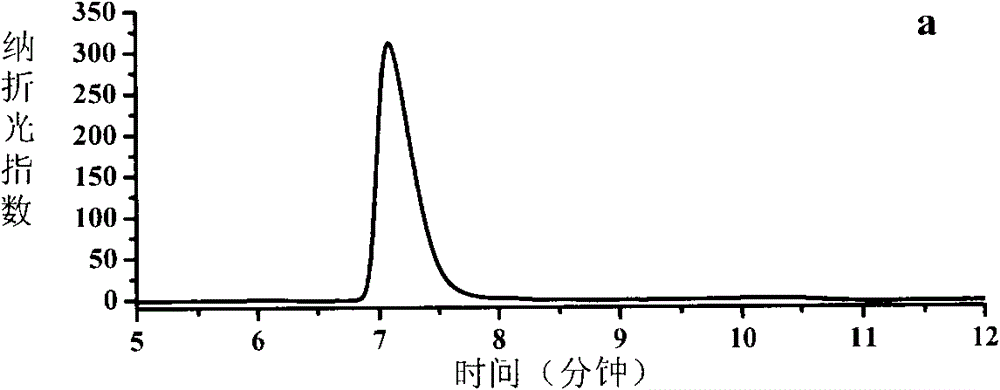
[0055] (1) Preparation of complete microbial cells containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: Pseudomonas putida ATCC12633 was selected for routine culture, and NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase was detected by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Hydrogenase activity, until its activity reaches 140 units / liter, stop the fermentation culture; separate and collect the thalline, wash the thalline twice with pH 7.4 potassium phosphate buffer, suspend the thalline resuspension in deionized water, make the thalline concentration reach 200 grams of wet cells / liter to obtain a complete cell suspension containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase, stored at 4°C for future use;
[0056] (2) Heat denaturation inactivates NAD-independent D-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: take the complete cell suspension containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase prepared in step (1) and place it in a 60°C water bath for treatment 10 minutes, store at 4°C for lat...
Embodiment 2
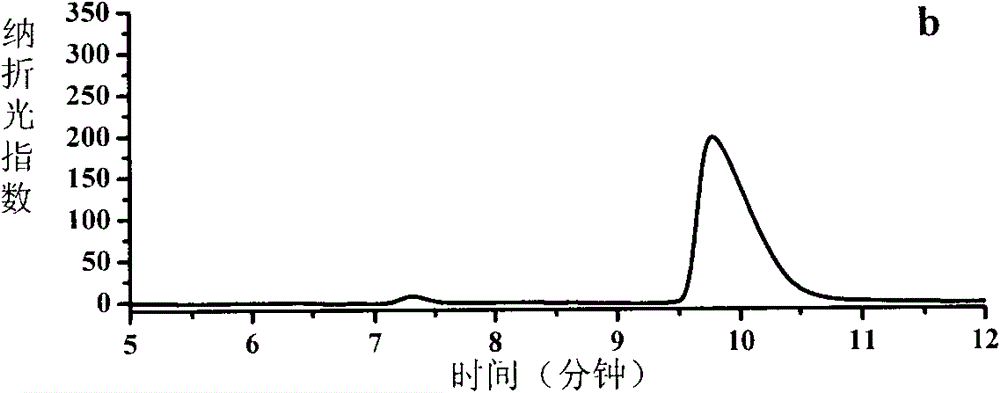
[0064] (1) Preparation of complete microbial cells containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) ATCC 10145 was selected and cultured routinely. Dependent on the activity of hydroxyacid dehydrogenase, when the activity reaches 160 units / liter, stop the fermentation culture; separate and collect the bacteria, wash the bacteria twice with pH 7.4 potassium phosphate buffer, and resuspend the bacteria in deionized water. Make the bacterial cell concentration reach 200 g wet cells / liter, obtain the complete cell suspension containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase, store at 4°C for later use;
[0065] (2) Heat denaturation to inactivate NAD-independent D-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: take the complete cell suspension containing NAD-independent hydroxyacid dehydrogenase prepared in step (1) and place it in a 55°C water bath for treatment 15 minutes, store at 4°C for later use;
[0066] (3) Resolution of racemic α-hydro...
Embodiment 3
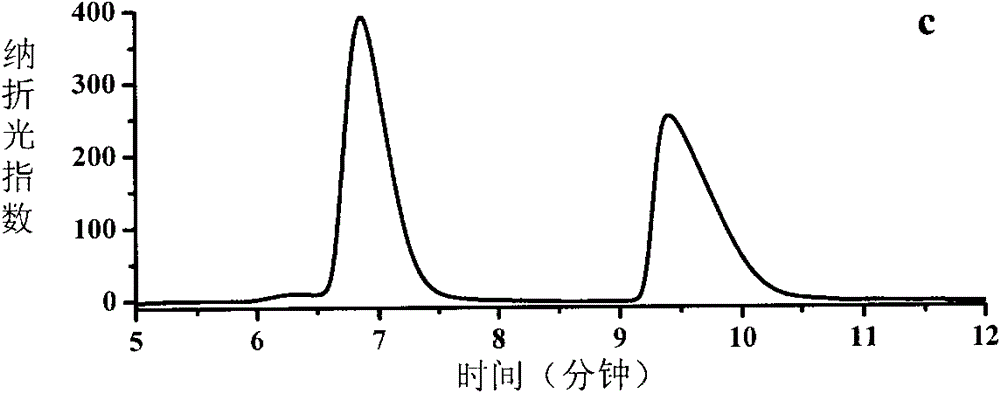
[0073] (1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution containing NAD-independent L-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: Pseudomonas stutzeri (Pseudomonas stutzeri) ATCC 17588 was selected and cultured routinely, during which the cells were detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) NAD-independent L-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase activity, when the activity reaches 170 units / liter, stop the fermentation culture; separate and collect the bacteria, wash the bacteria twice with pH 7.4 potassium phosphate buffer, and resuspend the bacteria in In deionized water, the concentration of bacteria reached 200 g wet cells / liter to obtain a complete cell suspension containing NAD-independent L-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase, and the complete cell suspension was ultrasonically crushed to obtain a crude enzyme solution, 4° C is stored for later use;
[0074] (2) Heat denaturation to inactivate NAD-independent D-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase: take the crude enzyme solution containing NAD-independent hydrox...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com