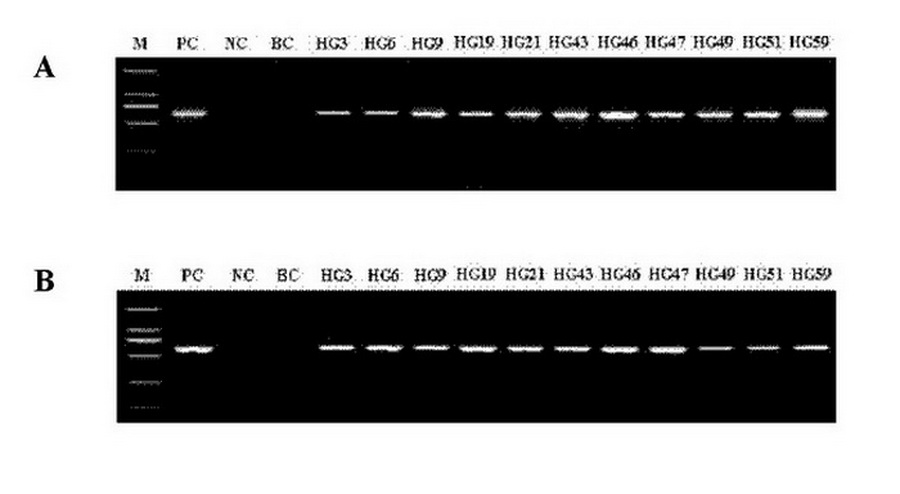
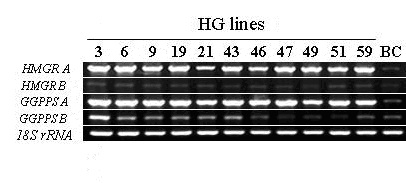
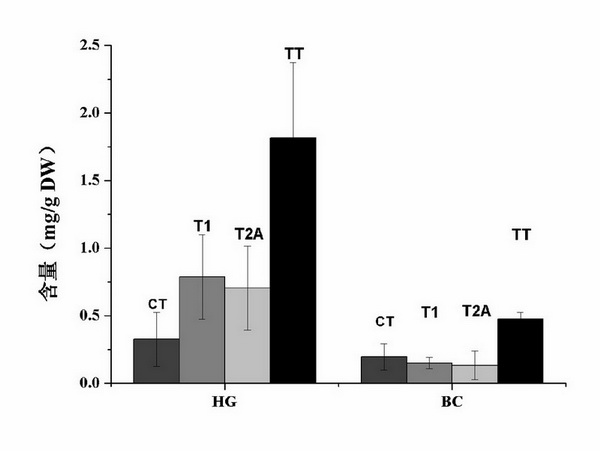
Method for increasing tanshinone content of salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by transferring SmGGPPS gene
A technology for tanshinone content and hairy roots, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of complex tanshinone structure, poor stability, and reduced active ingredient content, and achieve the effects of increasing total tanshinone content, reliable effect and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] (1) Extraction of total RNA from Salvia miltiorrhiza and synthesis of the first strand of cDNA:
[0073] Total RNA was extracted from the transgenic hairy roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza using the RNA prep pure plant kit provided by TIANGEN, following the steps specified in the kit instructions. The fresh weight of Salvia miltiorrhiza transgenic hairy root used to extract total RNA was 0.1 g, and the DNA in the sample was removed with DNase working solution during the extraction process. Measure the absorbance value of the extracted RNA on a spectrophotometer, and calculate the purity and concentration of the extracted RNA. After the concentration of different RNA samples was calculated, the first-strand cDNA was synthesized with reverse transcriptase XL (AMV) using 0.5 μg RNA as the initial amount, and the operation steps were in accordance with the instructions provided by Promega.
[0074] (2) SmGGPPS Design of coding sequence-specific primers and acquisition of targe...
Embodiment 2
[0077] contain SmGGPPS Construction of plant expression vectors for genes.
[0078] (1) Intermediate vector pCAMBIA1304 + The build:
[0079] Using pBI121 and pCAMBIA1304 as materials, construct the plant expression vector pCAMBIA1304 + . Specifically, pBI121 and pCAMBIA1304 were digested with HindIII / EcoRI; the pBI121-GUS expression cassette and the large pCAMBIA1304 fragment were recovered; ligation transformation was carried out, and single-clonal colonies were picked to extract plasmids for digestion verification. The results showed that the plant expression vector pCAMBIA1304 + The build was successful.
[0080] (2) Plant expression vector pCAMBIA1304 + - SmGGPPS The build:
[0081] The successful pCAMBIA1304 constructed above + Based on, using cloned from Salvia miltiorrhiza SmGGPPS gene replacement above GUS Gene. The specific method is BamHI / SacI double digestion of pMD18T- SmGGPPS and pCAMBIA1304 + ;Recycle SmGGPPS gene and pCAMBIA1304 + Large fragmen...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated SmGGPPS Genetic transformation of Salvia miltiorrhiza to obtain transgenic hairy roots.
[0085] (1) Containing plant expression vector pCAMBIA1304 + - SmGGPPS Obtaining Agrobacterium rhizogenes engineering bacteria:
[0086] Contain in embodiment 2 SmGGPPS Plant expression vector pCAMBIA1304 + - SmGGPPS Transformed into Agrobacterium rhizogenes C58C1, picked a single clone colony for PCR verification. The results showed that containing SmGGPPS The plant expression vector of the gene has been successfully constructed in Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain C58C1.
[0087] (2) Mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes SmGGPPS Genetic transformation of Salvia miltiorrhiza.
[0088] (3) Pre-cultivation of explants:
[0089] Cut 0.5 cm leaves of healthy aseptic seedlings of Salvia miltiorrhiza 2 , inoculated onto the pre-culture medium MS, and cultured in the dark at 25°C for 2 days.
[0090] (4) Co-cultivation of Agrobacterium and explan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com