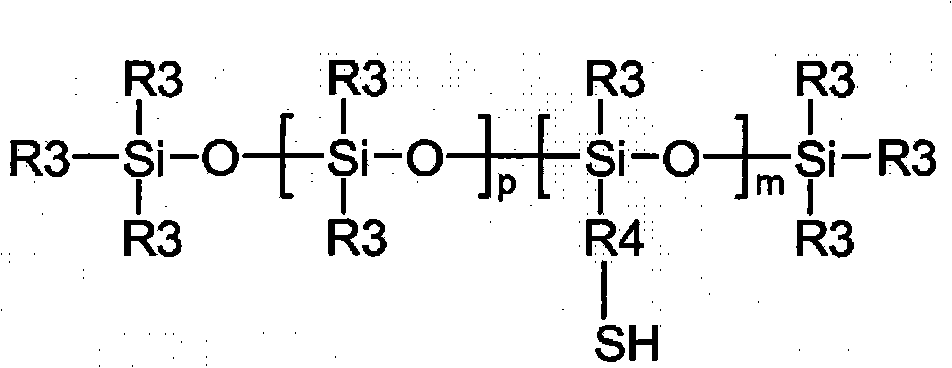
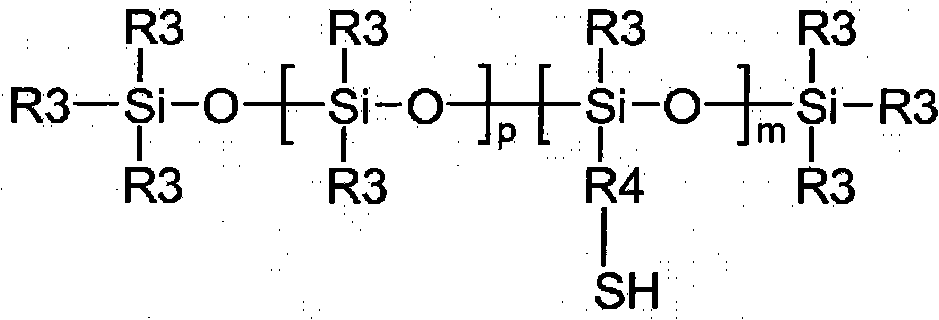
Copolymers of nanoparticles, vinyl monomers and silicone
A technology of vinyl monomers and nanoparticles, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, grafted polymer adhesives, etc., can solve the problems of accumulated peeling force and sheet removal force, and achieve the effect of stable peeling force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0098] Objects and advantages of this invention are further illustrated by the following examples, but the particular materials and amounts thereof recited in these examples, as well as other conditions and details, should not be construed to unduly limit this invention.
[0099] Material
[0100] demonstrative
[0101]
example 1
[0108] Example 1. Synthesis of KF-2001 / NVP / MA / AA / A-174 (33.7 / 35.5 / 24.8 / 4 / 2) modification 5nm silicon dioxide
[0109] 5nm modified with 40.44g KF-2001 (mercapto-functional silicone), 42.60g NVP (N-vinylpyrrolidone), 29.76g MA (methyl acrylate), 4.80g AA (acrylic acid), 6.86g A-174 Silica (35% solids in MEK), 175.54 g MEK, and 0.3602 g VAZO-64 (azobisisobutyronitrile) were added to a narrow mouth quart jar. In the resulting homogeneous mixture, N 2 5 minutes. The vial was sealed and placed in a hot water bath at 55°C with shaking for 24 hours. To convert to waterborne material, take 15 g of the above solventborne material (38.44% solids in MEK) into an 8 oz open bottle, then add 52 g of DI H 2 0 and 0.22 g ammonium hydroxide. The resulting homogeneous dispersion was vacuum stripped with a Rotovap at 50°C to remove MEK. After removing substantially all of the MEK, 10.3% aqueous material was obtained as a solid.
example 2
[0110] Example 2. Synthesis of KF-2001 / NVP / MA / AA / A-174 (33.7 / 32.5 / 24.8 / 4 / 5) modification 5nm silicon dioxide
[0111] The procedure of Example 1 was repeated except that the feeds were as follows: 40.44g KF-2001, 39g NVP, 29.76g MA, 4.8g AA, 17.14g A-1745nm modified silica (35% solids in MEK), 168.86g MEK and 0.3605g VAZO-64. To convert to a waterborne material, 15 g of the above solventborne material (38.25% solids in MEK) was added to an 8 oz open bottle followed by 51.6 g of DIH 2 O and 0.22 g ammonium hydroxide. The resulting homogeneous dispersion was vacuum stripped with a Rotovap at 50°C to remove MEK. After removing substantially all of the MEK, 10.4% aqueous material was obtained as a solid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com