Low carbon martensite aged stainless steel with high strength high toughness and high decay resistance performances
A low-carbon martensite, high-strength and high-toughness technology, which is applied in the field of iron-nickel-based martensitic precipitation hardening alloys, can solve the problems of low toughness and only reach the highest strength, and achieve the effect of high strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] According to the following nominal composition (weight percentage): C: 0.11%, Cr: 12.0%, Ni: 5.0%, Ti: 0.8%, Mo: 0.5%, Cu: 2.1%, Co: 2.0%, Nb: 0.5%, Mn: 0.6%, Si: 1.2%, N: 0.005%, V: 0.004%, Al: 0.008%, and Fe: the balance. After mixing, the materials are put into a vacuum induction furnace for smelting. The molten ingot is then subjected to thermal processing and heat treatment according to the following process conditions:
[0032] (1) Heating forging in austenite single-phase zone, forging pressure ratio of 7, air cooling after forging;
[0033] (2) Hot rolling after forging, the initial rolling temperature is 1150°C, the final rolling temperature is 800°C, air cooling after rolling, the cumulative reduction of hot rolling reaches 80%;
[0034] (3) Heat treatment system: 1150℃ solution treatment / 2h / oil quenching to room temperature +450-550℃ aging treatment / 6min-24h / air cooling to room temperature.
[0035] The materials were processed into specimens after heat treatment, a...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is that the content of some alloying elements is adjusted, and the type and quantity of precipitates are changed to obtain mechanical properties different from Example 1.
[0042] According to the following nominal composition (weight percentage): C: 0.1%, Cr: 11.9%, Ni: 4.1%, Ti: 0.3%, Mo: 0.5%, Cu: 2.0%, Co: 3.0%, Nb: 0.2%, Mn: 0.6%, Si: 1.0%, Al: 0.005%, N: 0.007%, V: 0.006%, and Fe: the balance. After mixing, the materials are put into a vacuum induction furnace for smelting. The smelted ingot was then subjected to thermal processing and heat treatment according to the process conditions described in Example 1.
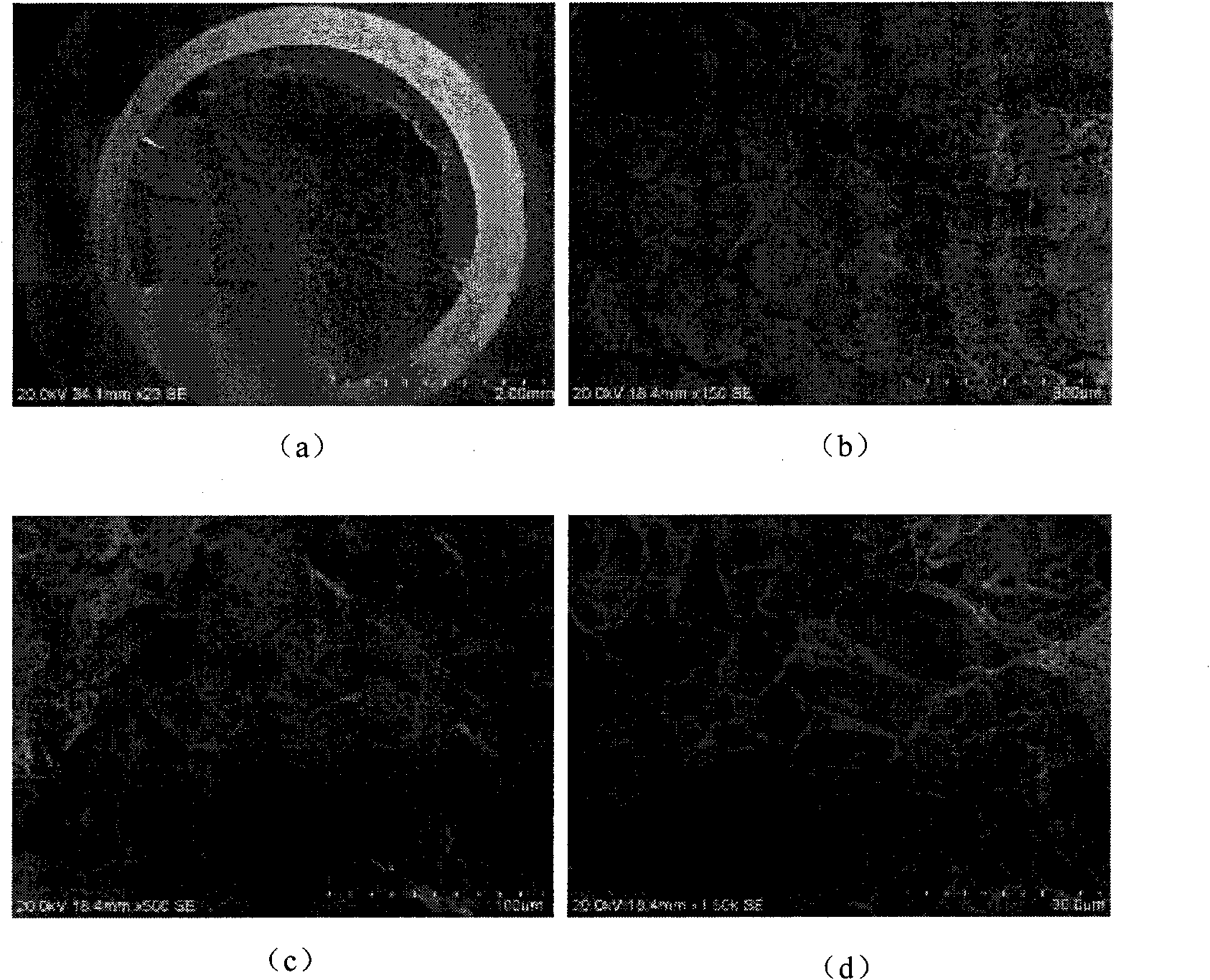
[0043] The materials were processed into samples after heat treatment, and their tensile properties at room temperature were tested respectively, and the tensile fracture was observed by scanning electron microscope. The tensile results are shown in Table 4, and the typical fracture morphology is as figure 2 Shown.
[0044] Table 4...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference from Example 1 lies in the fact that based on the experience of Example 2, the content of some alloying elements is adjusted, and the type and quantity of precipitated phases are changed to obtain mechanical properties superior to Example 1 and Example 2.
[0049] According to the following nominal composition (weight percentage): C: 0.1%, Cr: 11.5%, Ni: 4.1%, Ti: 0.5%, Mo: 0.5%, Cu: 2.0%, Co: 2.0%, Nb: 0.1%, Mn: 0.6%, Si: 0.5%, Al: 0.005%, N: 0.003%, V: 0.004% and Fe: the balance. After mixing, the materials are put into a vacuum induction furnace for vacuum melting. The smelted ingot was then subjected to thermal processing and heat treatment according to the process conditions described in Example 1.
[0050] The materials were processed into samples after heat treatment, and their tensile properties at room temperature were tested respectively, and the tensile fracture was observed by scanning electron microscope. The tensile results are shown in Table 5....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com