In-vitro inducing differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into tissue engineering skin seed cells
A technology for inducing differentiation and stem cells, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, bone/connective tissue cells, etc., can solve the problems of unstable curative effect, cell culture and single cell therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
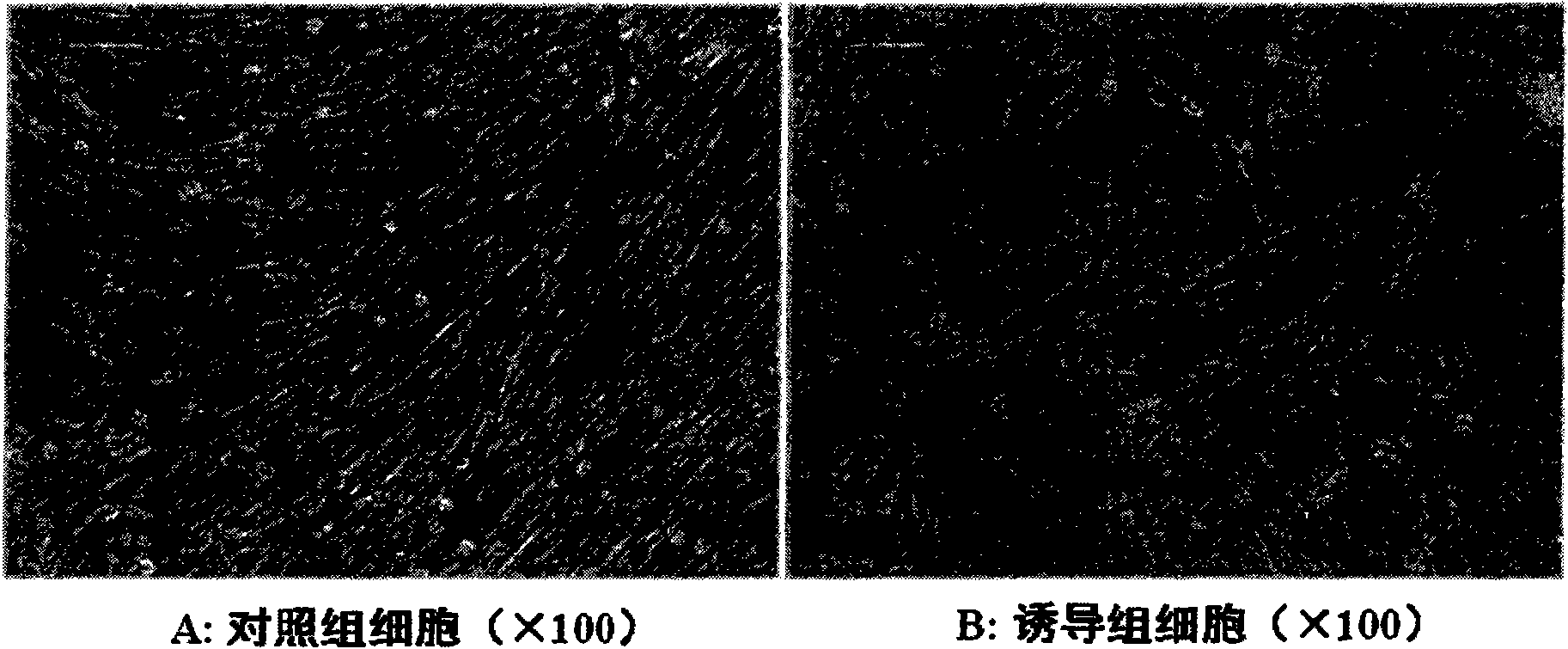
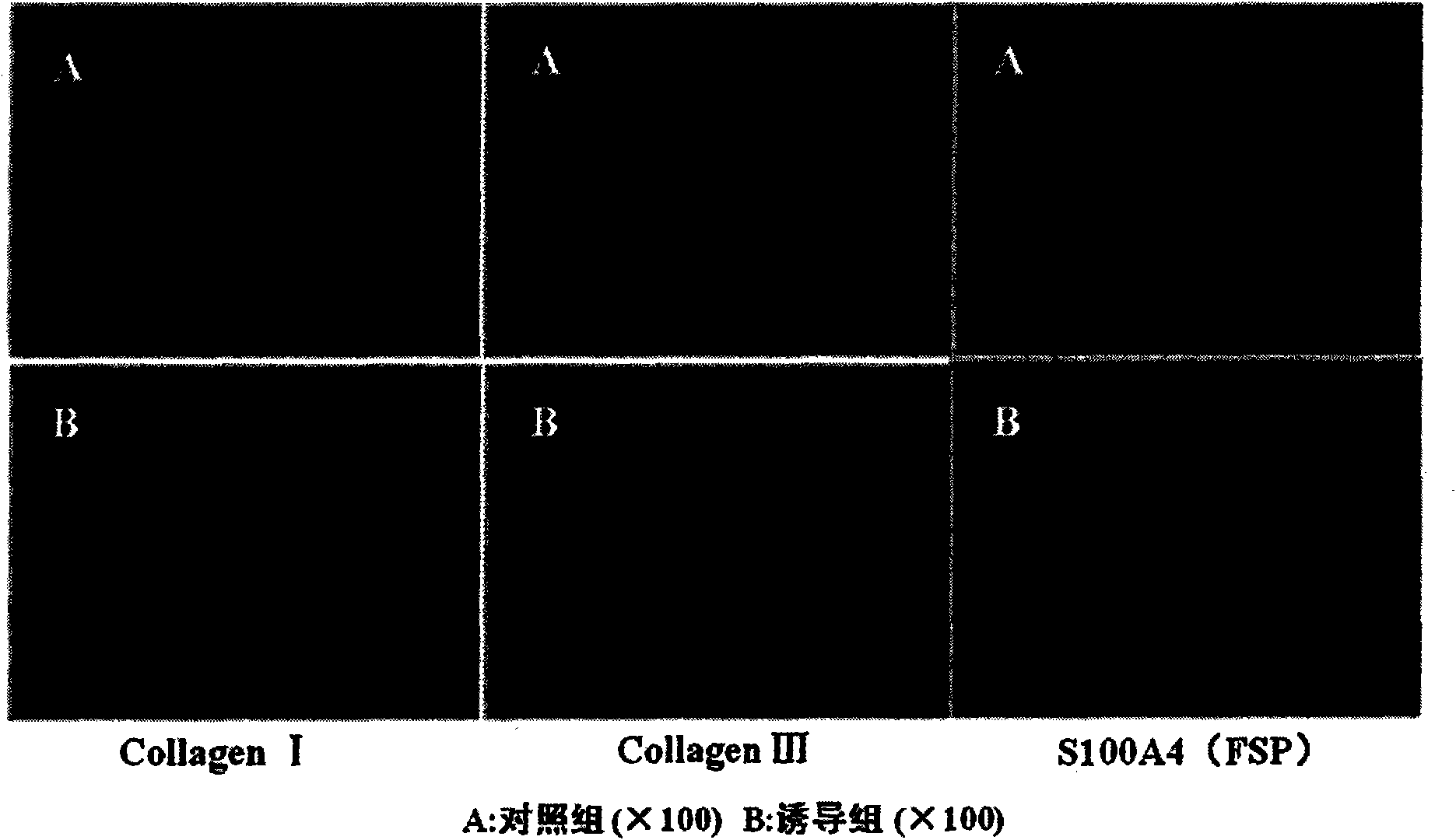
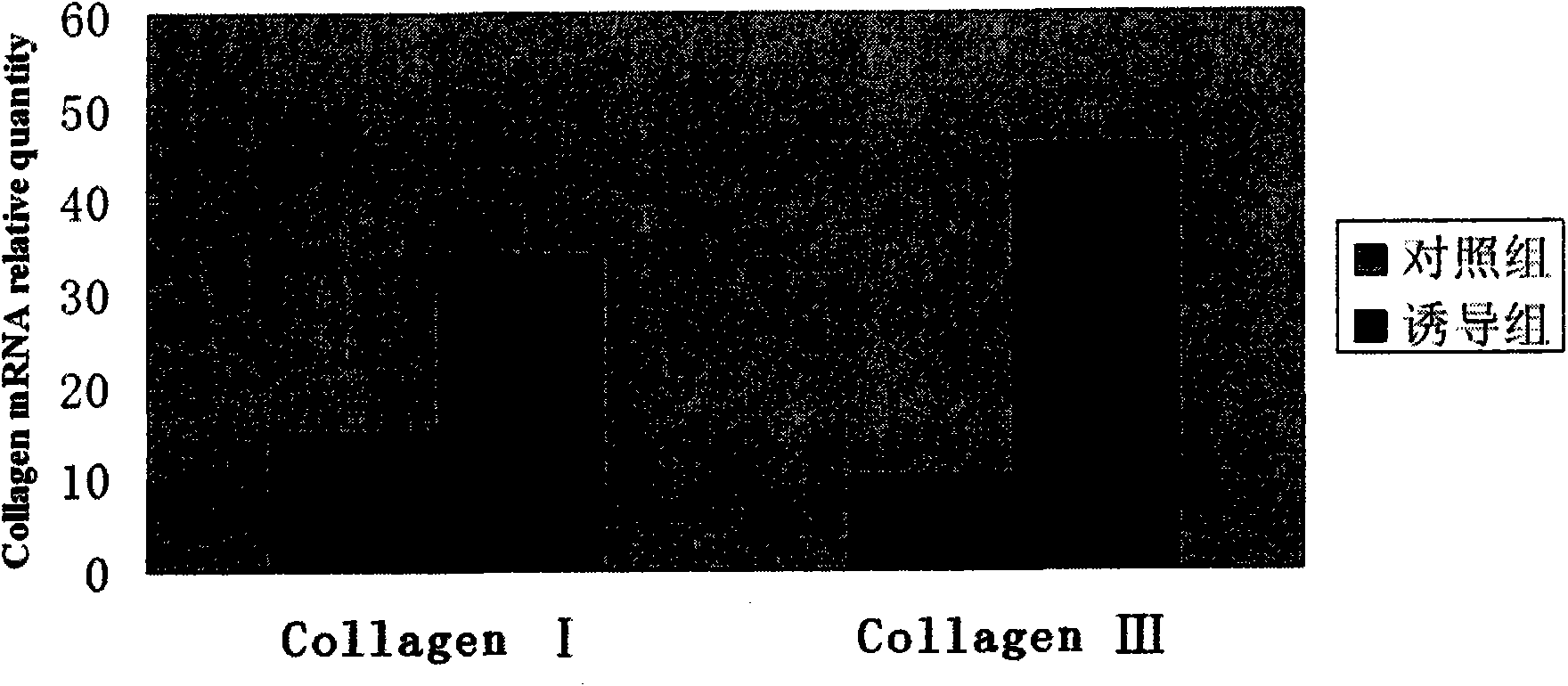
[0020] With the informed consent of pregnant women who underwent caesarean section, the umbilical cord was aseptically collected, and the primary umbilical cord MSCs were cultured by enzyme digestion or tissue block attachment method. Dermal induction conditions of 5% FBS, 15 ng / mL transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1, R&D), 20 ng / mL bFGF, 1% ITS, 0.1 μmol / L dexamethasone, 100 U / mL penicillin and 100 μg / mL streptomycin culture medium) to induce differentiation, observe the morphological changes of the cells under an inverted phase-contrast microscope, and use the Tagman probe method to perform Real-time PCR on the induced and control cells to detect the changes in the mRNA levels of collagen type Ⅰ and type Ⅲ in the induced differentiation cells. Under specific induction conditions, the umbilical cord MSCs were induced to differentiate into epidermal stem cells. The third generation umbilical cord MSCs were digested and collected, and divided into two groups, the induction gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com