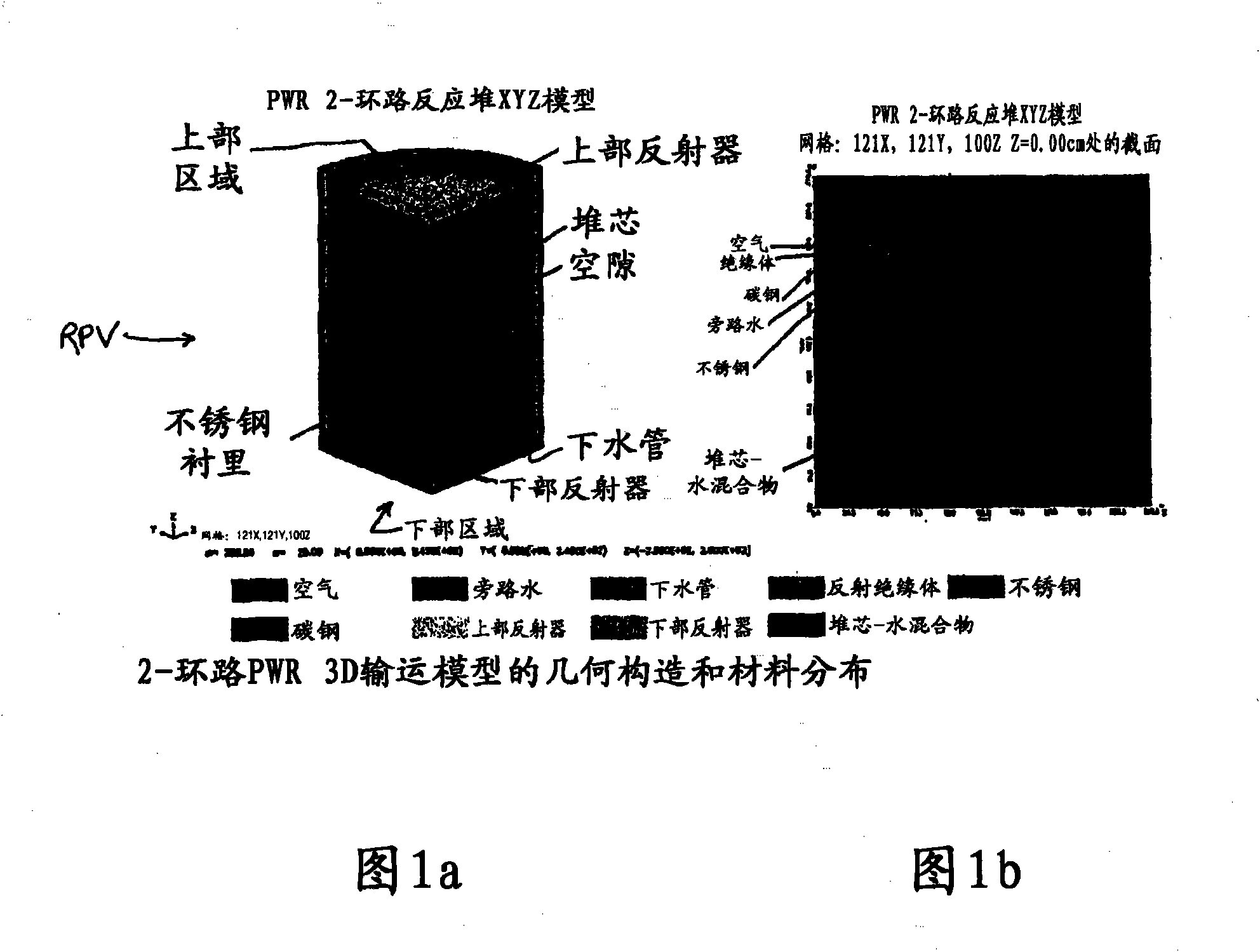
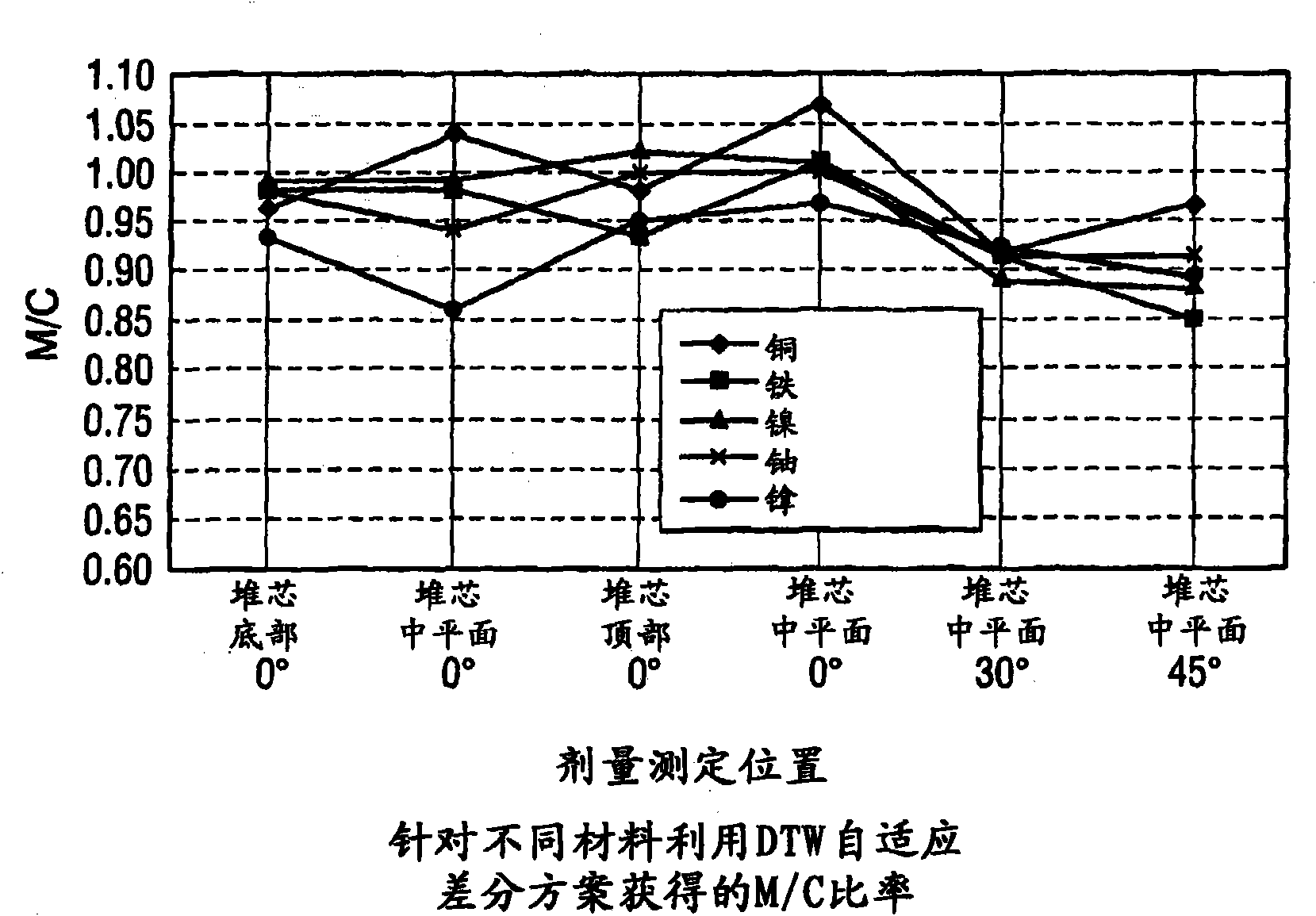
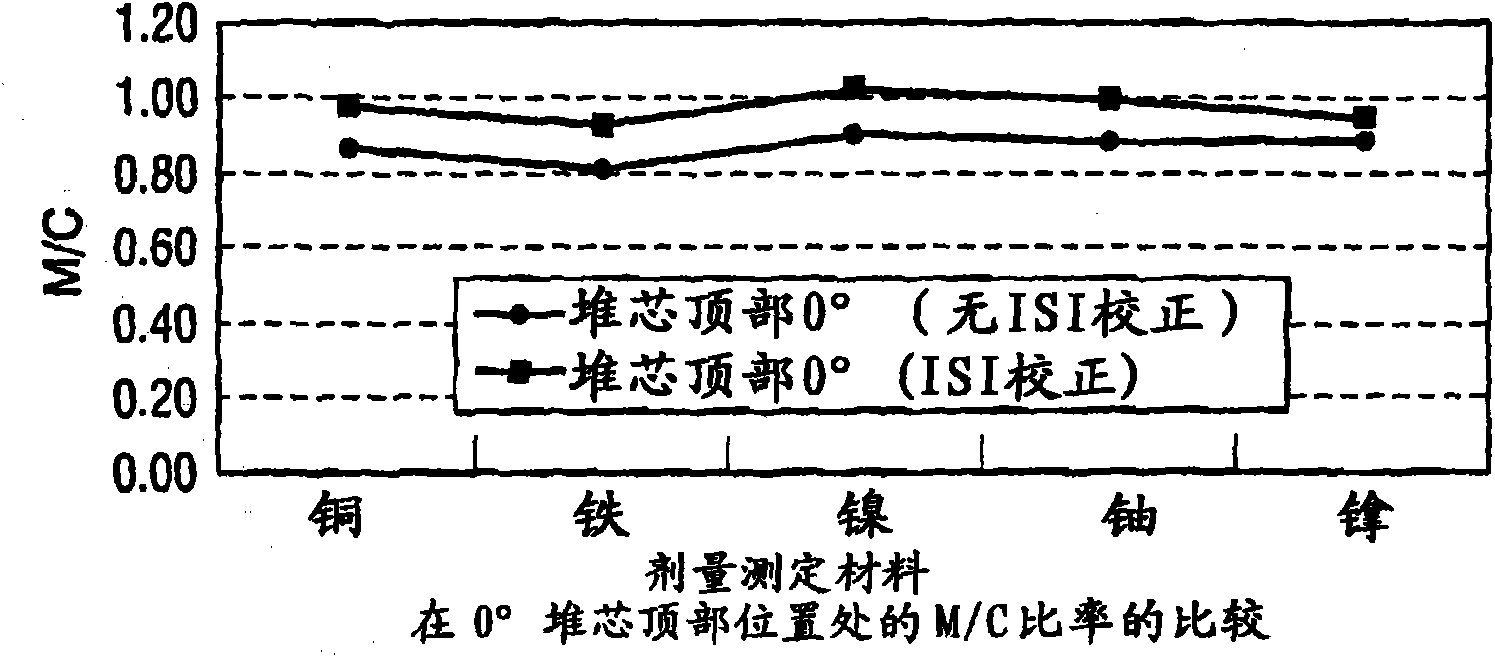
Reactor dosimetry applications using a parallel 3-D radiation transport code
A nuclear reactor and code technology, applied in the field of calculation of radiation field distribution, can solve problems that hinder single-processor workstations from solving problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0051] Example 1——RAPTOR-M3G Parallel Performance Analysis
[0052] The transport calculations discussed in "Examples" were performed with RAPTOR-M3G running on a 20-processor computer cluster (ie, EAGLE-1). The cluster consists of 5 nodes with 2 dual-core dual-processor AMD Opteron 64-bit architecture. The total cluster memory (ie, RAM) available is 40Gbytes; the network interconnection is characterized by 1GBit / s (bit / s) bandwidth. With this hardware configuration, RAPTOR-M3G completes the entire 3D transport calculation for 2-loop PWR in about 106 minutes on 20 processors. No significant performance difference was observed using DTW, TW or ZW differential schemes.
[0053] Also, set up simple test problems to analyze the parallel performance of your code. The test problem consisted of a 50x50x50 cm box discretized on a uniform grid of 1 cm with uniformly distributed stationary sources. Use S with an energy group section set 8 Quadrature group and P0 isotropic scatter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com